CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 22, No 6, November/December 2011
AFRICA
317
SDF-1
α
were found after cardiac injury.
The interaction between SDF-1
α
and CXCR4 plays a crucial
role in immune defense and SDF-1
α
is up-regulated by numer-
ous stimuli including antigens, polyclonal stimulants, cell irri-
tants and cytokines.
14,15
In the present study, results show plasma
levels of SDF-1
α
were significantly increased after injury,
followed by a decrease to baseline four days after injury.
The number of CD34
+
CXCR4
+
cells was markedly increased
immediately after injury, followed by a gradual decline. The
administration with AMD3100 increased the number of
CD34
+
CXCR4
+
cells, but no statistical significance was observed
in the number of CD34
+
CXCR4
+
cells and plasma levels of
SDF-1
α
. Therefore, the increased plasma levels of SDF-1
α
and
the elevated numbers of CD34
+
CXCR4
+
cells after arterial injury
may have been related to neo-intimal repair.
Numerous studies have found that SDF-1
a
not only stimu-
lated haematopoietic stem cell engraftment but also recruited
progenitor cells to the ischaemic region by interacting with
CXCR4.
16
After heart surgery or acute myocardial infarction, the
expression of SDF-1
a
in the peri-injury zone was up-regulated,
with profoundly increased numbers of stem/progenitor cells in
the injured region.
17,18
Inhibition of the SDF-1
a
/CXCR4 axis could partially block
the recruiting of progenitor/stem cells to the injured tissues
or peri-infarct myocardium.
19
Likewise, inhibition of CXCR4
with the anti-CXCR4-antibody could also significantly reduce
SDF-1
a
-induced adhesion of EPC to mature endothelial cells,
the
in vitro
migration of EPC,
17
and the
in vivo
recruitment of
myeloid EPC to the ischaemic limb in a hind limb ischaemia
model.
20
Moreover, over-expression of SDF-1
a
enhanced the
homing and incorporation of stem cells into ischaemic tissues.
21,22
These findings support the notion that SDF-1
a
played a crucial
role in the recruitment of circulating or intravenously infused
cells.
In this study, our results showed the expression of SDF-1
a
mRNA was elevated immediately after injury and reached a
maximum four days later, followed by a decline to baseline seven
days after injury. However, the expression of CXCR4 mRNA was
increased four days after injury and reached a maximum seven
days after injury, followed by a gradual decrease to baseline.
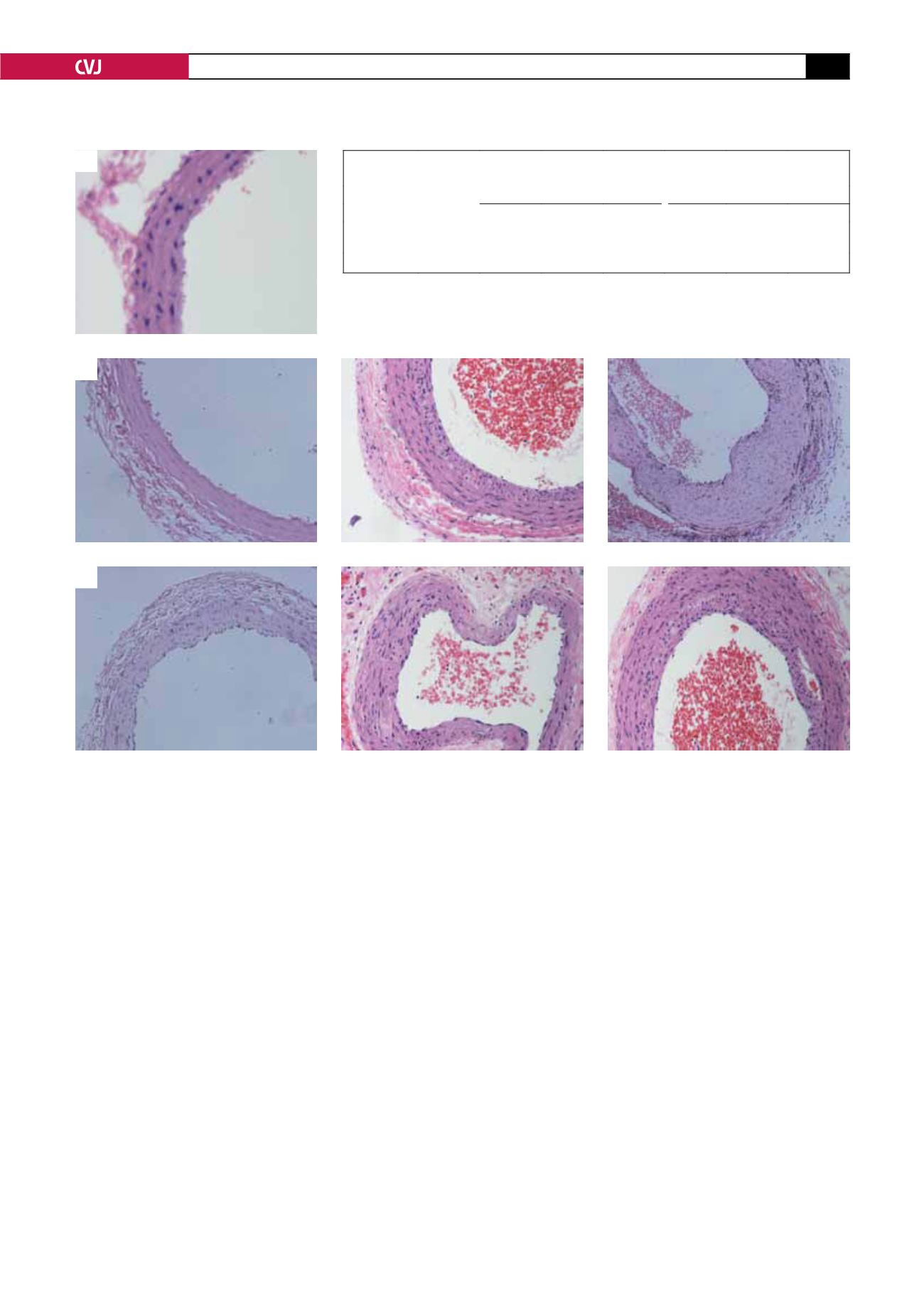
Immuno-histochemistry indicated CXCR4-positive staining
was found in the neo-intima (Fig. 4A, B) of the common carotid
Fig. 5. A: Normal rat carotid artery. B: The carotid artery intima of injured rats gradually underwent hyperplasia with
time in group S. C: The carotid artery intima of injured rats also gradually underwent hyperplasia with time in group
A, but the degree of proliferation was less than in group S.
C (100 ×)
S
1d
(100 ×)
S
1m
(100 ×)
S
3m
(100 ×)
A
1d
(100 ×)
A
1m
(100 ×)
A
3m
(100 ×)
A
B
C
TABLE 3. MEASUREMENT OF RAT CAROTIDARTERY STENOSIS
(
x
±
SD, mM,
n
=
12 PER GROUP)
Group C
Group S
Group A
S
1d
S
1m
S
3m
A
1d
A
1m
A
3m
Intima thick-
ness (
m
m)
45.367
±
17.486
47.018
±
5.967
106.195
±
15.342*
129.816
±
17.114**
45.918
±
12.584
78.368
±
16.511*
#
88.734
±
15.326*
#
*
p
<
0.05, **
p
<
0.01 vs group C;
#
p
<
0.05 vs group S.


