CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 4, July/August 2017
AFRICA
239
<
0.001); SBP and WC (
r
= 0.30,
p
= 0.004); SBP and BMI (
r
=
0.24,
p
= 0.03) and DBP and WC (
r
= 0.26,
p
= 0.01). There was
a negative correlation between HDL-C and TG levels (
r
= –0.45,
p
= 0.02) (Table 5). In the south there was a positive correlation
between TC and TG levels (
r
= 0.48,
p
= 0.02); TC and SBP or
DBP (
r
= 0.44,
p
= 0.03;
r
= 0.54,
p
= 0.006, respectively); LDL-C
and BG (
r
= 0.43,
p
= 0.03); LDL-C and DBP (
r
= 0.49,
p
= 0.01)
and TG and SBP (
r
= 0.54,
p
= 0.006) (Table 6).
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, CVD risk factors in northern and
southern Cameroonians have not been studied before. Average
WC and BMI from the studied population were significantly
higher in the south than the north. However, the prevalence
of obesity, determined by either BMI (
±
21%) or WC (
±
65%),
was comparable between northern and southern Cameroonians,
but based on BMI, higher than that in the entire Cameroonian
population (
±
10%).
14
In addition, our data are in agreement
with a study performed on the urban labour force from Douala
(south) showing an obesity prevalence of 23%, based on BMI.
17
The range limits used to establish each category (normal,
overweight and obese) could explain the lack of difference in
obesity prevalence between southerners and northerners, despite
differences in average BMI and WC values. Based on BMI
measurements, southern women displayed higher prevalence
of obesity compared to northern women (34 vs 20%). Obesity
prevalence determined in southern women (34%) was close to
Table 4. Anthropometric and biochemical parameters
among subjects of two age groups
Parameters
35–50 years
51–65 years
p-
value
WC (cm) (
n
= 192)
Mean
±
SEM
91.48
±
1.77
91.01
±
1.92
0.86
Normal,
n
(%)
37 (19)
69 (36)
0.50
Obese,
n
(%)
37 (19)
49 (26)
BMI (kg/m
2
) (
n
= 192)
Mean
±
SEM
29.42
±
0.86
26.00
±
0.93
0.01
Normal,
n
(%)
37 (19)
33 (17)
0.08
Overweight,
n
(%)
38 (20)
39 (20)
Obese,
n
(%)
31 (16)
14 (8)
BG (mg/dl) (
n
= 192)
Mean
±
SEM
92.46
±
11.63 117.48
±
12.60
0.15
[mmol/l]
[5.13
±
0.65]
[6.52
±
0.70]
Normal,
n
(%)
78 (41)
65 (34)
0.42
Limit,
n
(%)
22 (11)
12 (6)
Diabetes,
n
(%)
6 (3)
9 (5)
SBP (mmHg) (
n
= 192)
Mean
±
SEM
115.61
±
8.80
135.17
±
9.53
0.14
Normal,
n
(%)
71 (37)
47 (25)
0.05
Hypertensive,
n
(%)
35 (18)
39 (20)
DBP (mmHg) (
n
= 192)
Mean
±
SEM
88.65
±
2.44
94.14
±
2.65
0.13
Normal,
n
(%)
53 (28)
41 (21)
0.43
Hypertensive,
n
(%)
53 (28)
45 (23)
p
-value for the comparison of means by Student’s
t
-test for independent samples
or Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test and chi-squared test for the comparison of
percentages between the two age groups.
WC, waist circumference; BMI, body mass index; BG, blood glucose; SBP,
systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
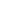
Table 5. Correlations between parameters in the northerners
BG TC HDL-C TG LDL-C SBP DBP WC BMI
BG CC 1
Sig
n
89
TC CC 0.13 1
Sig 0.54
n
25
25
HDL-C CC 0.17 –0.03 1
Sig 0.41 0.87
n
25
25
25
TG CC 0.23 0.61 –0.45 1
Sig 0.27 0.001 0.02
n
25
25
25
25
LDL-C CC 0.004 0.95 –0.21 0.49 1
Sig 0.98
<
0.001 0.32 0.01
n
25
25
25
25 25
SBP CC 0.09 –0.20 0.07 –0.18 –0.19 1
Sig 0.39 0.32 0.75 0.39 0.36
n
89
25
25
25 25
89
DBP CC 0.14 –0.16 0.10 0.03 –0.24 0.82 1
Sig 0.21 0.44 0.64 0.88 0.26
<
0.001
n
89
25
25
25 25
89
89
WC CC 0.02 –0.06 0.36 –0.38 –0.05 0.30 0.26 1
Sig 0.87 0.77 0.08 0.06 0.81 0.004 0.01
n
89
25
25
25 25
89
89 89
BMI CC 0.01 0.02 0.29 –0.11 –0.04 0.24 0.19 0.72 1
Sig 0.93 0.92 0.15 0.61 0.86 0.03 0.07
<
0.001
n
89
25
25
25 25
89
89 89
89
CC, correlation coefficient;
n
, sample size; Sig,
p
-value; WC, waist circumference; BMI,
body mass index; BG, blood glucose; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipo-
protein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; SBP,
systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
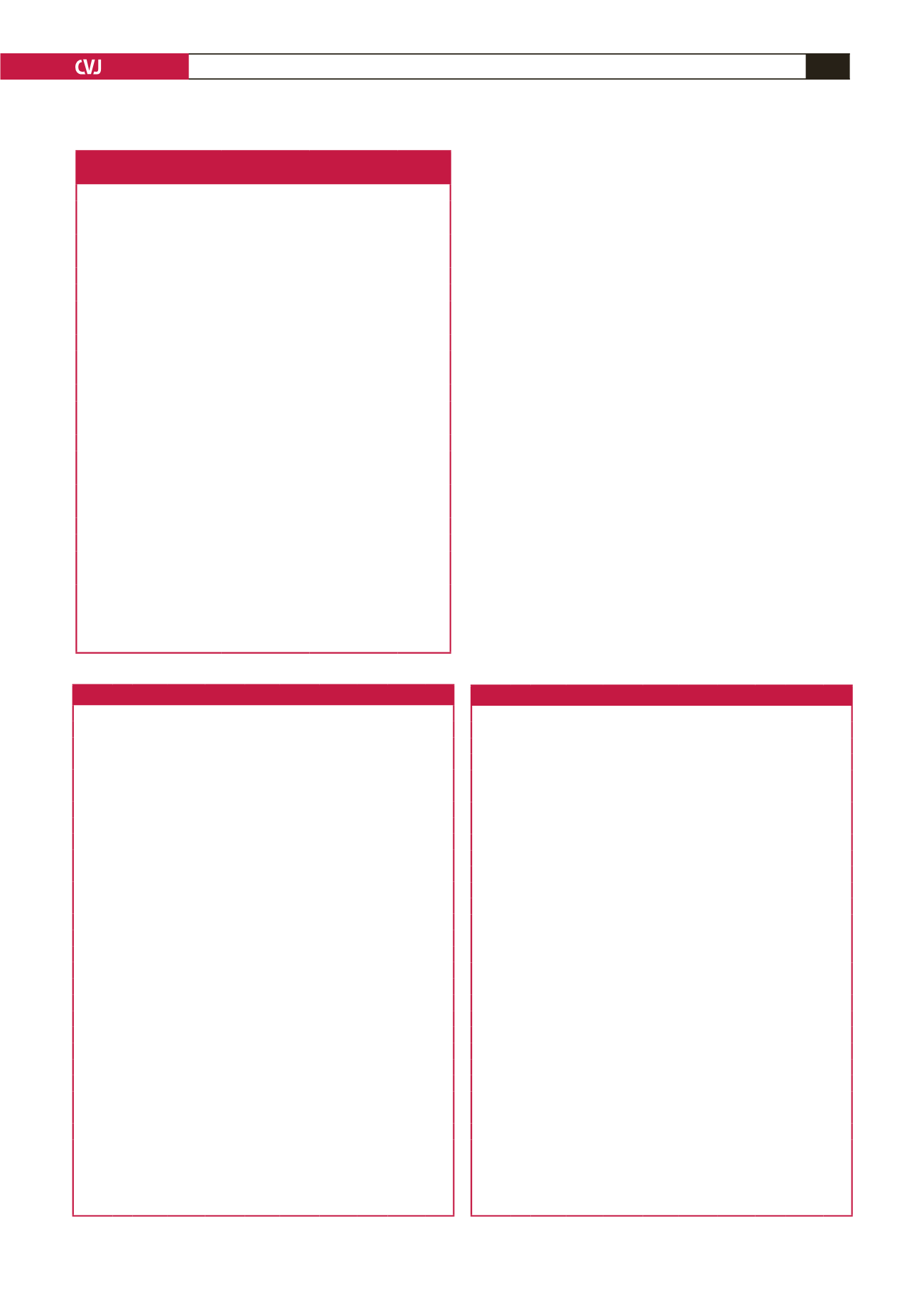
Table 6. Correlations between parameters in the southerners
BG TC HDL-C TG LDL-C SBP DBP WC BMI
BG CC 1
Sig
n
103
TC CC 0.36 1
Sig 0.07
n
25 25
HDL-C CC –0.03 0.25 1
Sig 0.88 0.23
n
25 25
25
TG CC –0.01 0.48 0.013 1
Sig 0.95 0.02 0.951
n
25 25
25
25
LDL-C CC 0.43 0.89 –0.14 0.25 1
Sig 0.03
<
0.001 0.51 0.23
n
25 25
25
25 25
SBP CC –0.18 0.44 0.29 0.54 0.22 1
Sig 0.08 0.03 0.16 0.006 0.28
n
103 25
25
25 25
103
DBP CC –0.02 0.54 0.02 0.39 0.49 0.71 1
Sig 0.85 0.006 0.92 0.06 0.01
<
0.001
n
103 25
25
25 25
103 103
WC Cc 0.19 0.03 0.03 –0.37 0.13 0.12 0.13 1
Sig 0.07 0.88 0.90 0.07 0.54 0.25 0.21
n
103 25
25
25 25
103 103 103
BMI CC 0.13 –0.09 0.03 –0.21 0.04 0.15 0.16 0.80 1
Sig 0.22 0.68 0.90 0.10 0.86 0.16 0.12
<
0.001
n
103 25
25
25 25
103 103 103 103
CC, correlation coefficient;
n
, sample size; Sig,
p
-value; WC, waist circumference; BMI,
body mass index; BG, blood glucose; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipo-
protein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; SBP,
systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.