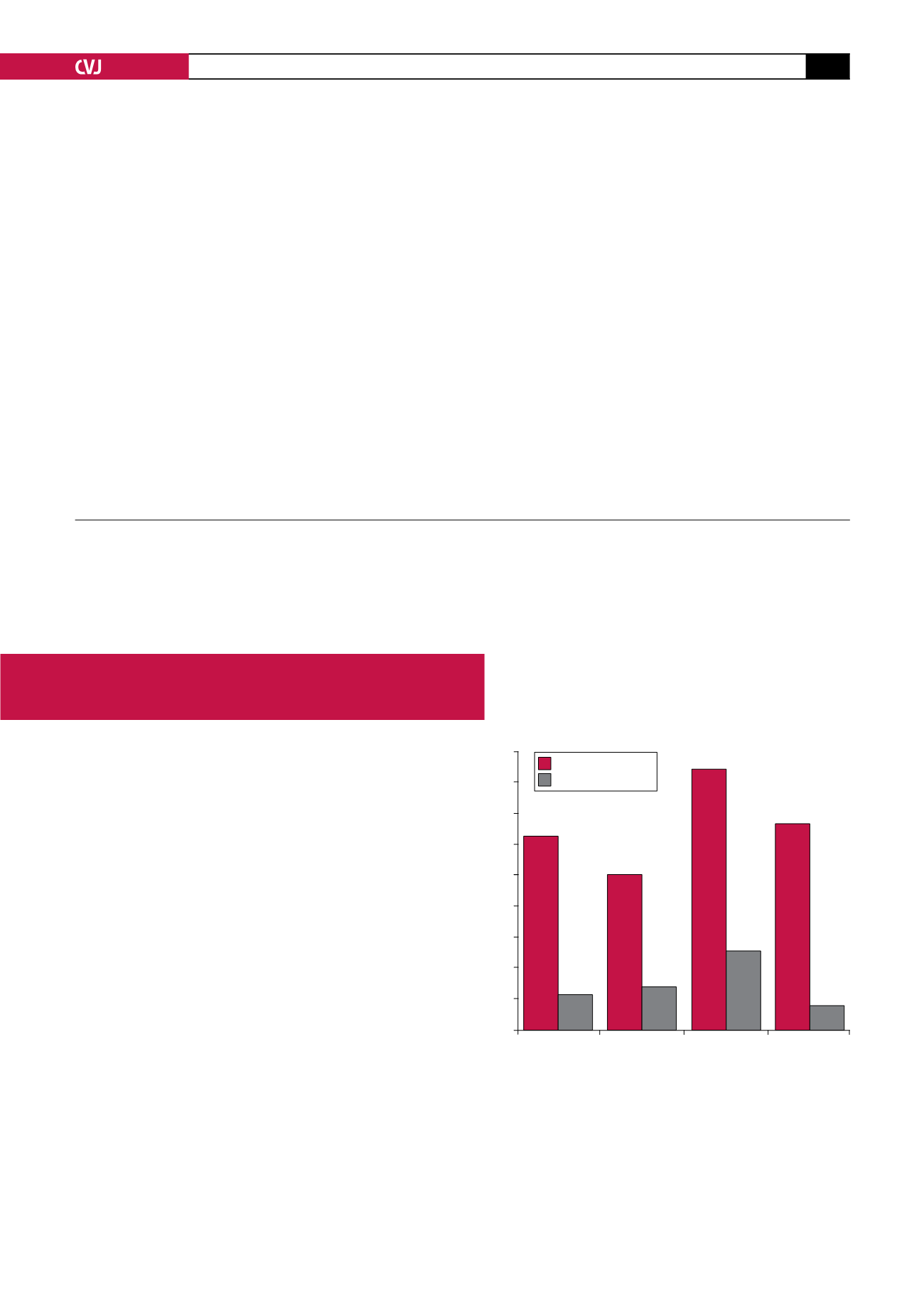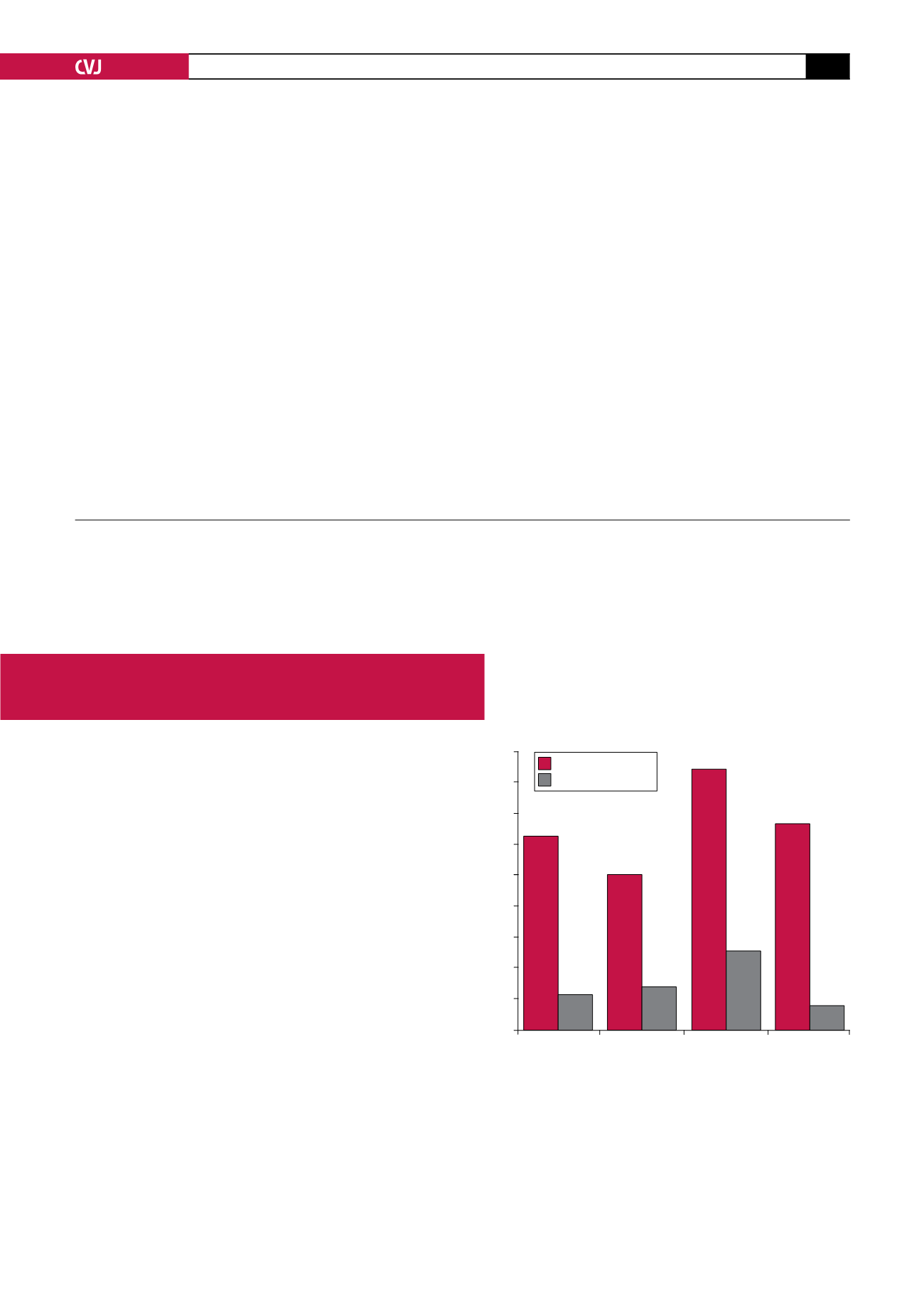
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 21, No 4, July/August 2010
AFRICA
185
References
1. Opie L, Seedat YK. Hypertension in Sub-Saharan African populations.
Circulation
2005;
112
: 3562–3568.
2. Hamer M, Malan L. Psychophysiological risk markers of cardiovascular
disease. In: Psychophysiological Biomarkers of Health. Special Edition:
Neurosc Biobehav Rev
2010 (in press).
3. Lazarus RS. Coping theory and research: past, present, and future.
Psychosom Med
1993;
55
: 234–247.
4. McEwen BS. Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation:
central role of the brain.
Physiol Rev
2007;
87
: 873–904.
5. Korner PI.
Essential Hypertension and its Causes: Neural and
Non-Neural Mechanisms
. New York: Oxford University Press, 2007:
347–358.
6. Hamer M, Malan L, Schutte AE, Huisman HW, van Rooyen JM, Schutte
R,
et al
. Plasma renin responses to mental stress and carotid intima
media thickness in black Africans: The SABPA Study.
J Hum Hypertens
2010 (in press).
7. Malan L, Schutte AE, Malan NT,
et al
. Specific coping styles of Africans
during urbanization: comparing cardiovascular responses and perception
of health data.
Biol Psych
2006;
72
: 305–310.
8. Grassi G, Arenare F, Quarti-Trevano F, Seravelle G, Mancia G.
Heart rate, Sympathetic Cardiovascular Influences, and The Metabolic
Syndrome.
Prog Cardiovasc Dis
2009;
52
: 31–37.
9. Malan L, Malan NT, Wissing MP, Seedat YK. Coping with urbaniza-
tion: a cardiometabolic risk? The THUSA study.
Biol Psychol
2008;
79
: 323–328.
10. Selye H.
The Stress of Life
. London: Longmans Green, 1956.
11. Du Plessis A, Malan L, Malan NT. Coping and metabolic syndrome indi-
cators in urban black South African men: the SABPA study.
Cardiovasc
J Afr
2010;
21
(4): 206–211.
From the Editor’s Desk
Advance publications
The office of the
Cardiovascular Journal of Africa
has recently
experienced a dramatic increase in the number of articles submit-
ted to this journal. The articles emanate from authors in many
diverse countries. As a consequence of the volume of articles,
we are experiencing delays in the length of time to publish them.
To obviate this, we have now made available an additional
option for authors to advance publish their articles online. We
must charge for this option as it involves additional expense.
Local authors in Africa will pay R1 000 and those overseas
R2 500. This amount could be budgeted for in the research grant
if one knows beforehand that the article needs to be advance
published.
Authors will now have the immediate benefit of having their
article appear online on PubMed, but will have to wait as usual
for the article to appear in the printed journal. We trust that this
will be of help in getting your important research to the immedi-
ate attention of other interested researchers and readers.
Please contact Elsabé Burmeister at
for
more information.
Fig. 1. The ratio of articles received and rejected for the
Cardiovascular Journal of Africa
from January 2007 to
July 2010.
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
2007
2008
2009
2010
6 months
Articles received
Articles rejected
Year
Number of articles