CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 23, No 9, October 2012
AFRICA
497
STEMI patients had less-extensive coronary atherosclerosis
than STDMI patients. There were more patients with three- or
two-vessel disease in the STDMI group than in the STEMI
group (73.0 vs 58.2%,
p
<
0.001).
Severe left main stenosis was
also more often present in STDMI patients compared to STEMI
patients (6.0 vs 1.1%,
p
<
0.001).
The left circumflex artery was
more likely to be the infarct-related artery in STDMI compared
to STEMI patients (37.5 vs 14%,
p
<
0.001).
Moreover, nearly
one-third of all STDMI patients had a TIMI 0 flow before PCI.
The infarct-related artery was more often totally occluded in
STEMI patients compared to STDMI patients (57.2 vs 27.3%,
p
<
0.001).
Emergency PCI was performed in 88.1% of STEMI patients
versus 61.8% of STDMI patients. The success rates were higher
in STDMI patients (94.5 vs 90.8%,
p
<
0.012) (
Table 2). Rates of
acute coronary bypass grafts were significantly higher in patients
with STDMI (Fig. 1).
Despite the higher mean ejection fraction, in-hospital
mortality was slightly but insignificantly higher in STDMI
patients compared to STEMI patients (6.3 vs 5.4%,
p
=
0.330).
There was no significant difference regarding in-hospital
mortality between STEMI and STDMI patients who were treated
using emergency PCI (5.3 vs 6.78%,
p
=
0.274).
However, there
was a large difference regarding in-hospital mortality between
STDMI patients treated using PCI (6.78%) and STDMI patients
without revascularisation (13.19%) (
p
=
0.032).
Using logistic regression analysis, the independent risk factor
for mortality was patient age (OR 1.03, 95% CI: 1.015–1.049,
p
<
0.001);
there was a 1.03-fold increased risk for every
additional year of age. Killip class
>
I on admission was also a
strong predictor of mortality (OR 2.54, 95% CI: 1.754–3.685,
p
<
0.001).
A lower risk of death was associated with higher
ejection fractions (OR 0.982, 95% CI: 0.967–0.997,
p
<
0.024).
Patients presenting with MI and any bundle branch block
(
left or right bundle branch block
±
left anterior/posterior
hemiblock) represented the highest risk group, with in-hospital
TABLE 1. BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS IN
STEMI AND STDMI PATIENTS
STEMI
STDMI
p
-
value
Age in years
±
SD
64.5
±
12.4 69.5
±
10.7
<
0.001
Age
<
75
years (%)
74.5
63.6
<
0.001
Females (%)
31.3
34.6
0.055
Previous myocardial infarction (%)
13.8
29.3
<
0.001
Diabetes mellitus (%)
24.1
36.8
<
0.001
Killip class
>
I (%)
27.4
29.5
<
0.001
Killip class IV (%)
6.7
4.4
<
0.001
STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction; STDMI: ST-depression
myocardial infarction.
TABLE 2. ANGIOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICSAND
PROCEDURAL OUTCOMES IN STEMI AND STDMI PATIENTS
STEMI
STDMI
p
-
value
Number of involved vessels (%)
One-vessel disease
37.3
17.2
<
0.001
Two-vessel disease
28.2
19.9
Three-vessel disease
30.0
53.1
Infarct-related artery (%)
Left main
1.1
6.0
<
0.001
Left anterior descending
45.0
31.5
Left circumflex
14.0
37.5
Right coronary
39.1
21.2
CABG
0.8
3.8
Pre-PCI TIMI flow (%)
TIMI flow 0
57.2
27.3
<
0.001
TIMI flow 1
8.8
7.7
TIMI flow 2
18.5
24.5
TIMI flow 3
15.5
40.6
Post-PCI TIMI flow (%)
TIMI flow 3
90.8
94.5
<
0.012
LVEF (%), mean
±
SD
46.3
±
12.0 50.1
±
13.5
<
0.001
STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction; STDMI: ST-depression
myocardial infarction; TIMI: thrombolysis in myocardial infarction flow;
CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; PCI: percutaneous coronary inter-
vention; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction.
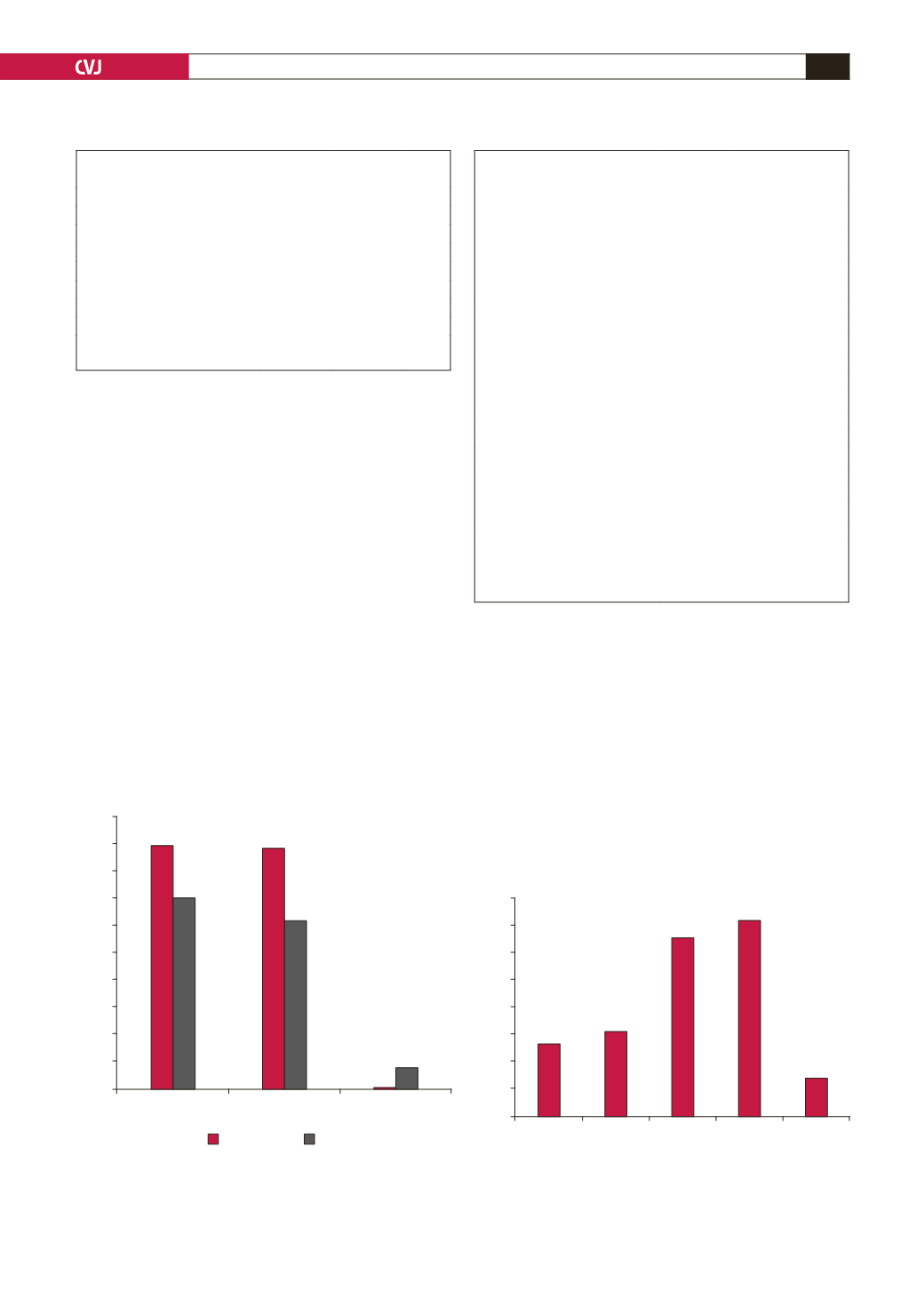
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Any
revascularisation
Acute PCI
Acute CABG
STEMI
STDMI
Fig. 1. Bar graphs show the type of revascularisa-
tion therapy used in ST-segment elevation (STEMI) and
ST-segment depression (STDMI) myocardial infarctions.
All values are percentages (
p
<
0.001).
CABG: coronary
artery bypass graft.
89.1
69.8
88.1
61.8
0.6
8.0
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
STEMI
STDMI
LBBB RBBB Other ECG
5.4
6.3
13.1
14.3
2.9
Fig. 2. Bar graph demonstrates the in-hospital mortal-
ity rates in different ECG groups of acute myocardial
infarction patients. All values are percentages (
p
<
0.001).
STEMI/STDMI: ST-segment elevation/depression myocar-
dial infarction. LBBB/RBBB: left/right bundle branch block.


