CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 25, No 4, July/August 2014
154
AFRICA
Methods
A longitudinal, prospective cohort study was conducted. It was
approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty
of Health Sciences of the University of Cape Town. Before
participating in the study, procedures and risks were explained
to the patients, who gave written informed consent to take part
in the study.
This study formed part of an as yet unpublished larger
longitudinal study, investigating the metabolic complications
of ART in an HIV-positive population, at an HIV clinic in
a community health centre in Cape Town, South Africa. All
patients recruited for the parent study over a six-month period
were enrolled into this study (Fig. 1).
The following measurements were done at baseline and
repeated at six months: urine dipstick (AccuBioTech Co. Ltd,
Beijing, China), office BP, serum creatinine (umol/l), spot
urine microalbumin–creatinine ratio (mg/mmol), and estimated
glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (ml/min/1.73 m
2
). Three office
BP readings were performed on the right arm with the patient in
a seated position using a mercury barometer in accordance with
the South African hypertension guidelines.
15
A urinary albumin–creatinine ratio between 3 and 30 mg/
mmol was identified as microalbuminuria and a level greater
than this as macroalbuminuria.
16
eGFR was estimated using the
four-variable Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD)
equation, which accounts for the gender, age, creatinine level and
race of a patient.
17
Clinical guidelines from the Kidney Disease:
Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) work group were used
to categorise CKD.
18
After the baseline measurements, all patients were started
on ART (Table 1). The treatment regimen used depended on
the date of enrolment into the study. Initially patients were
prescribed stavudine (D4T), lamivudine (3TC) and efavirenz
(EFV) according to the previous national guidelines, but later
tenofovir (TDF) replaced D4T.
19,20
All enrolled patients were invited to participate in the ABP
substudy. Consenting individuals underwent ABP monitoring
prior to and after the initiation of ART. A control group
of confirmed serologically HIV-negative patients formed the
control group of another study from our institution investigating
HIV-associated dementia.
21
They were originally recruited by
trained fieldworkers from a community primary healthcare clinic
in Cape Town.
Seventeen individuals froma list of 32 contacted telephonically
were available to participate. They were equally matched for
age, body mass index (BMI) and socio-economic background.
Patients were excluded if they had underlying hypertension,
diabetes mellitus, ischaemic heart disease, concurrent illness or
any condition affecting BP (i.e. pregnancy or renal disease).
ABP monitoring was set up by a trained nurse on a weekday,
with an oscillometric device (SpaceLabs Medical Inc, WA,
USA). BP and heart rate were recorded every 20 minutes during
the day (06:00 to 22:00) and every 30 minutes at night (22:00
to 06:00). Hypertension was defined as a SBP
≥
140 mmHg or
diastolic BP (DBP)
≥
90 mmHg, in accordance with the South
African hypertension guidelines 2011.
15
Non-dipping was defined
as a nocturnal reduction of SBP ≤ 10%.
22
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using STATA statistical
software, version 11.0 (STATA Corporation, College Station,
Texas, USA). Mean
±
standard deviation was used for normally
distributed data and median plus interquartile ranges for skewed
data. Continuous and categorical variables were compared using
chi-square, Student’s
t
-test or Pearson’s
χ
2
as appropriate. All
p
-values were considered significant at
p
≤ 0.05.
Table 1. Patient characteristics and demographics
Baseline
(
n
=
64)
Six months
(
n
=
53)
ABPM group at
baseline
(
n
=
30)
ABPM group at six
months
(
n
=
28)
Controls
(
n
=
17)
Age (years) mean
±
SD
33
±
7
33
±
7
32
±
8
32
±
8
31
±
9
Men (%)
23
23
37
36
40
Women (%)
77
77
63
64
60
BMI (kg/m
2
) mean
±
SD
24.8
±
5.4
25.7
±
5.2
24.6
±
5.2
24.8
±
5.4
24.0
±
4.8
Men
22.5
±
4.6
23.1
±
4.8
22.9
±
5.0
22.7
±
5.3
22.8
±
5.1
Women
25.5
±
5.4
26.9
±
5.6
25.4
±
4.9
25.8
±
5.4
25.2
±
4.8
CD
4
(cells/mm
3
) median
239
359
242
361
N/A
(IQR)
(169–322)
(231–411)
(165–330)
(240–406)
ART regimen (%)
–
Current
–
67
–
72
–
Earlier
–
29
–
26
–
Other
–
4
–
2
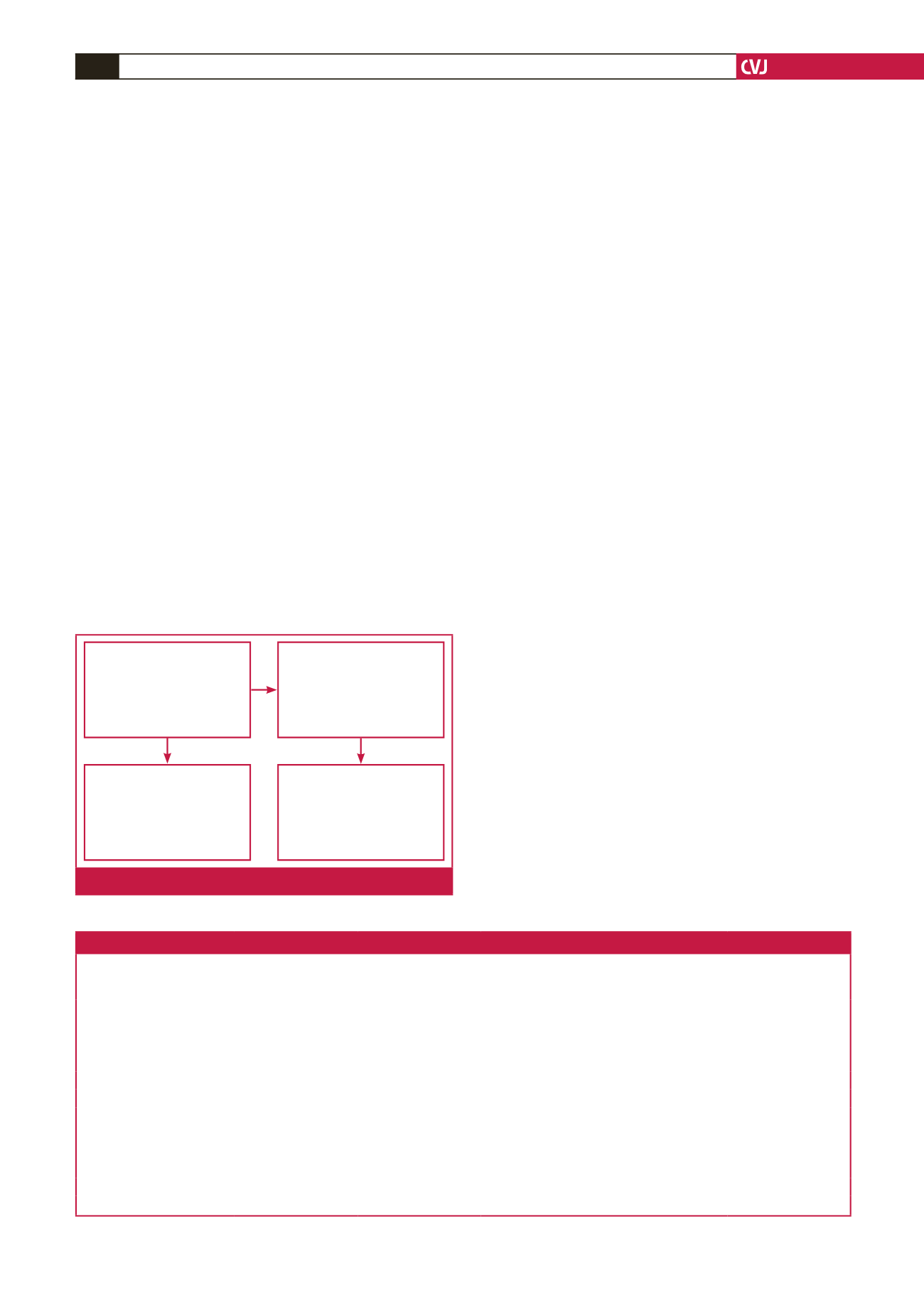
Initially included (n
=
64)
A cross-section of
asymptomatic HIV-positive
patients
Six months (n
=
53)
Excluded
=
11
Reasons for exclusion:
• Defaulted on ART (n
=
8)
• Pregnancy (n
=
3)
ABP substudy (n
=
30)
Enrolled patients willing to
participate
Six months (n
=
28)
Excluded
=
2
Reasons for exclusion:
• Pregnancy (n
=
2)
Fig. 1.
Flow of study.


