CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 27, No 1, January/February 2016
AFRICA
35
Bronchoscopy is useful for the airway evaluation of patients
with vascular rings, particularly in patients with complete
tracheal rings, tracheo- or bronchomalacia, or the identification
of an aberrant subclavian artery.
2
In patients with significant
proximal bronchus narrowing, CTA is superior to bronchoscopy
in evaluating the distal airways.
7
Vascular rings are corrected surgically.
8
Historically,
surgical exploration was undertaken based on CXR, CO and
echocardiography alone, occasionally leading to incorrect
thoracotomy placement (and associated morbidity) when the
intra-operative anatomy was inconsistent with the pre-operative
imaging. In the current era, pre-operative cross-sectional imaging
in the form of CTA or MRI allows accurate surgical planning,
and is considered mandatory.
2,8
We found excellent correlation
between CTA imaging and intra-operative findings.
The goal of surgery is to divide all vascular or ligamentous
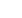
Fig. 5.
Right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery and left ligamentum arteriosum. (A) The plain chest radiograph demon-
strates an abnormal superior mediastinal silhouette, suggesting a right aortic arch. (B) Frontal contrast oesophagogram
(CO) demonstrates the fixed, extrinsic indentation (asterisk) of the mid-thoracic oesophagus from the right aortic arch. (C)
The oblique postero-anterior view on CO demonstrates a second indentation (asterisk) due to the aberrant left subclavian
artery. (D) The reconstructed oblique postero-anterior CTA image illustrates the aberrant left subclavian artery arising from
the proximal descending aorta and being tethered at the base (white asterisk) by the radiographically invisible ligamentum
arteriosum, which completes the vascular ring in this case. (E) Abnormal enlargement at the base of the aberrant left subcla-
vian artery (black asterisk) is termed a ‘Kommerell diverticulum’, which may become aneurysmal and require excision due to
compressive effects. RA: right arch; DA: descending aorta; ALSA: aberrant left subclavian artery.
A
D
B
C
E
*
*