CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 27, No 4, July/August 2016
224
AFRICA
with pulmonary stenosis was significantly higher than that of the
control group (
p
=
0.019) (Table 5).
The VWF:Ag and VWF:RCo levels were not statistically
different among the patients with aortic stenosis according to
degree of stenosis (Table 6). PFA-100 collagen epinephrine
closure time was significantly higher in patients with severe
aortic stenosis than in those with mild or moderate aortic
stenosis (
p
=
0.003 and
p
=
0.01, respectively). PFA-100 collagen
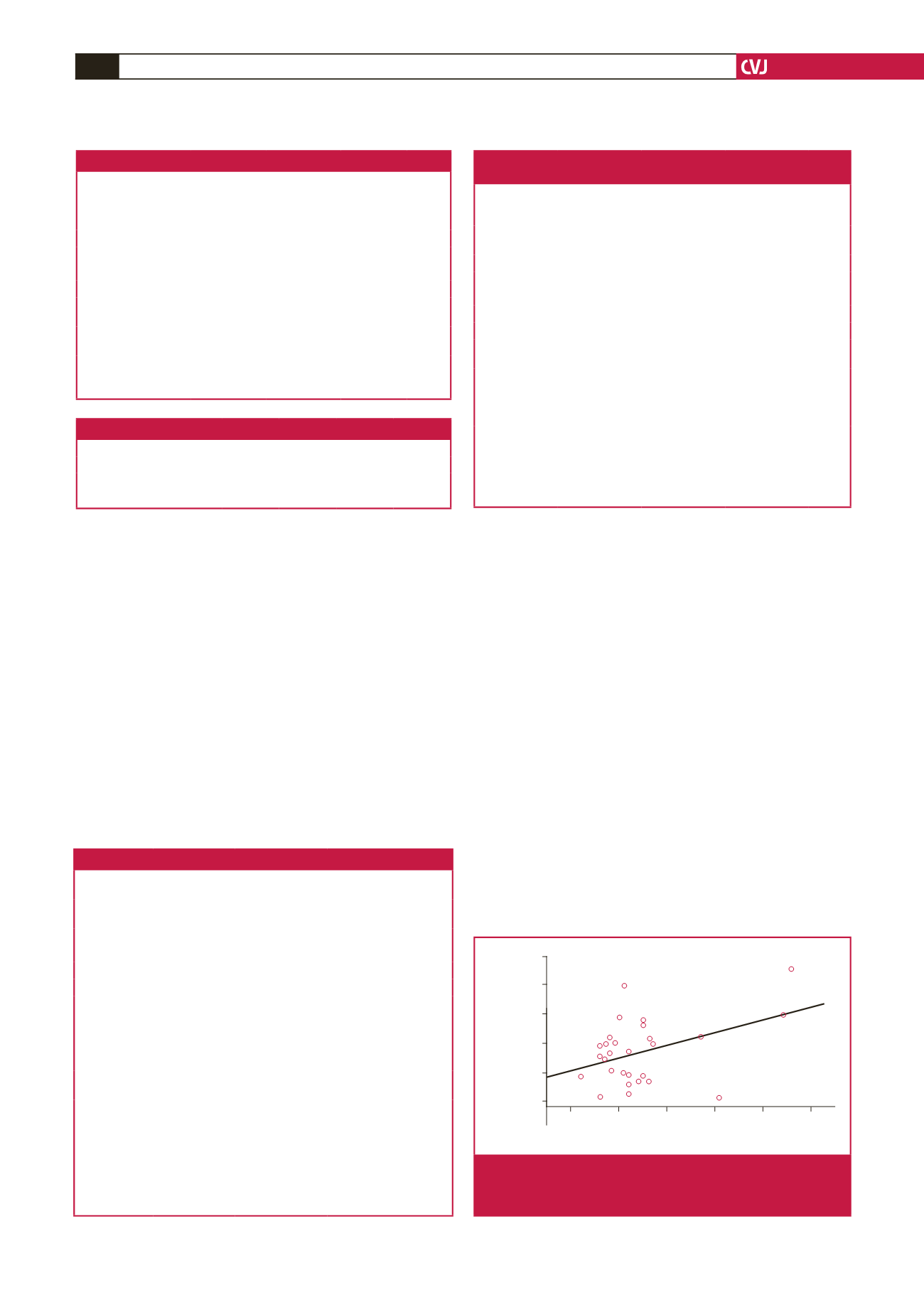
epinephrine closure times were positively correlated with degree
of aortic stenosis (
p
=
0.03) (Fig. 1).
The platelet count of patients with mild pulmonary stenosis
was significantly lower than that of patients with severe
pulmonary stenosis (
p
=
0.04). The PT of the patients with
severe pulmonary stenosis was significantly higher than that of
those with moderate pulmonary stenosis (
p
=
0.003). The aPTT
of the patients with mild pulmonary stenosis was significantly
higher than that of those with moderate and severe pulmonary
stenosis (
p
=
0.002 and
p
=
0.009, respectively) (Table 7). PFA-100
collagen epinephrine and PFA-100 ADP closure times were not
different among the patients with pulmonary stenosis (
p
=
0.93
and
p
=
0.18).
VWF:Ag levels were normal in all patients with aortic
stenosis and in the control group. However, it was low in three
patients with pulmonary stenosis (two female, one male) and all
were asymptomatic. The family histories of these three patients
were negative for bleeding. VWF:RCo was lower in one patient
who had a deficiency of VWF:Ag. Of the patients with low
VWF:Ag, PFA-100 ADP collagen closure time was prolonged
in two patients, and PFA-100 collagen epinephrine closure time
was prolonged in all of them. PFA-100 ADP collagen closure
time was prolonged in three patients with aortic stenosis and
PFA-100 collagen epinephrine closure time was prolonged in
four patients with aortic stenosis. Only two of four patients with
prolonged PFA-100 collagen epinephrine closure time had a
positive bleeding history (Table 8).
PFA-100 ADP collagen closure times and PFA-100 collagen
epinephrine closure times were performed only in patients
with aortic and pulmonary stenosis. PFA-100 ADP collagen
closure time was normal in 40 (66.7%) patients and prolonged
Table 4.The distribution of patients according to degree of stenosis
Group
Mild
Moderate
Severe
Total
Aortic stenosis,
n
(%)
19 (67.9)
6 (21.4)
3 (10.7)
28 (46.7)
Pulmonary stenosis,
n
(%)
3 (9.4)
25 (78.1)
4 (12.5)
32 (53.3)
Total,
n
(%)
22 (36.7) 31 (51.7)
7 (11.7)
60 (100)
Table 3. Demographic features of the study groups
Aortic stenosis
(
n
=
28)
Pulmonary
stenosis
(
n
=
32)
Control
(
n
=
24)
p-
value
Gender (M/F)
23/5
18/14
14/10
0.07
Age (year)
8.09
±
3.73 5.72
±
3.79 9.12
±
4.70 0.007
Follow-up period (year) 4.19
±
1.91 3.28
±
1.98
–
0.07
Aortic PPG (mmHg)
46.84
±
17.63
*
13.24
±
2.78 10.71
±
2.34
<
0.001
Aortic MPG (mmHg) 24.43
±
10.59
–
–
0.004
Pulmonary PPG
(mmHg)
12.7
±
1.49 47.15
±
11.70
**
11.26
±
2.18
<
0.001
Pulmonary MPG
(mmHg)
–
24.95
±
7.65
–
0.003
M: male, F: female, MPG: mean pressure gradient, PPG: peak pressure gradient.
*
p
<
0.001 aortic stenosis versus pulmonary stenosis and control.
**
p
<
0.001 pulmonary stenosis versus aortic stenosis and control.
Table 5. Comparison of haematological parameters of the groups
Haematological
parameters
Aortic stenosis
(
n
=
28)
Pulmonary stenosis
(
n
=
32)
Control
(
n
=
24)
p-
value
Platelet count
(cells/mm³)
336.570
±
58.053 356.440
±
103.244 346.920
±
58.670 0.62
PT (s)
13.46
±
0.64
13.34
±
0.68
13.87
±
0.75
a
0.017
aPTT (s)
29.55
±
2.06
30.49
±
3.48
b
28.82
±
1.50 0.059
Factor VIII (%) 123.57
±
42.92 118.69
±
47.71 130.79
±
37.35 0.58
VWF:Ag (%)
100.86
±
31.97 98.44
±
31.34
97.42
±
21.49 0.90
VWF:RCo (%)
94.75
±
29.36 97.28
±
34.28
89.00
±
19.04 0.56
PFA-100
CADP (s)
116.86
±
45.14 117.34
±
46.75
–
0.96
PFA-100
CEPI (s)
178.64
±
56.19 168.22
±
55.44
–
0.47
VWF:RCo/
VWF:Ag
0.95
±
0.21
1.01
±
0.35
0.91
±
0.12 0.36
PT: prothrombin time; aPTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; PFA-100
CADP: platelet-function analyser-100 adenosine diphosphate collagen closure
time; PFA-100 CEPI: platelet-function analyser-100 collagen epinephrine closure
time; VWF:Ag: von Willebrand factor antigen; VWF:RCo: ristocetin co-factor.
PFA-100 ADP closure time was carried out in only patients with aortic and
pulmonary stenosis (
n
=
60), but the other tests were done in all children (
n
=
84).
a
p
=
0.03, aortic stenosis versus control group and
p
=
0.006, pulmonary stenosis
versus control group.
b
p
=
0.019, pulmonary stenosis versus control group.
Table 6.The comparison of haematological parameters of patients with
aortic stenosis according to degree of stenosis
Mild aortic
stenosis (
n
=
19)
(mean
±
SD)
Moderate aortic
stenosis (
n
=
6)
(mean
±
SD)
Severe aortic
stenosis (
n
=
3)
(mean
±
SD)
p-
value
Platelets
(cells/mm³)
329.680
±
57.915 352.000
±
60.332 349.330
±
69.292 0.67
PT (s)
13.579
±
0.642 13.183
±
0.752 13.267
±
0.208 0.37
aPTT (s)
30.005
±
1.658 28.300
±
3.039 29.167
±
1.656 0.20
Factor VIII (%) 120.21
±
39.76 132.67
±
63.96 126.67
±
6.02 0.82
VWF:Ag (%)
101.32
±
35.17 95.17
±
27.27 109.33
±
24.50 0.82
VWF:RCo (%)
95.11
±
29.37 98.00
±
29.67 86.00
±
39.05 0.85
PFA-100
CADP (s)
110.74
±
39.79 119.00
±
32.33 151.33
±
92.13 0.36
PFA-100
CEPI (s)
166.37
±
52.05 173.50
±
34.51 266.67
±
46.14
c
0.01
VWF:RCo/
vVWF:Ag
0.95
±
0.19
1.03
±
0.27
0.76
±
0.20 0.21
PT: prothrombin time; aPTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; PFA-100
CADP: platelet-function analyser-100 adenosine diphosphate collagen closure
time; PFA-100 CEPI: platelet-function analyser-100 collagen epinephrine closure
time; VWF:Ag: von Willebrand factor antigen; VWF:RCo: ristocetin co-factor.
c
p
=
0.003, severe versus mild aortic stenosis,
p
=
0.01, severe versus moderate
aortic stenosis.
10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00 60.00
Mean pressure gradient (mmHg)
PFA-100 CEPI (sec)
300
250
200
150
100
50
Fig. 1.
Correlation between PFA-100 collagen epinephrine
closure time and mean pressure gradient in patients
with aortic stenosis.