CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 22, No 3, May/June 2011
AFRICA
131
baseline (
p
<
0.01 and
p
<
0.05, respectively). Pre-treatment of
isoflurane did not affect AaDO
2
significantly over the experi-
ment, compared to the control group (
p
>
0.05).
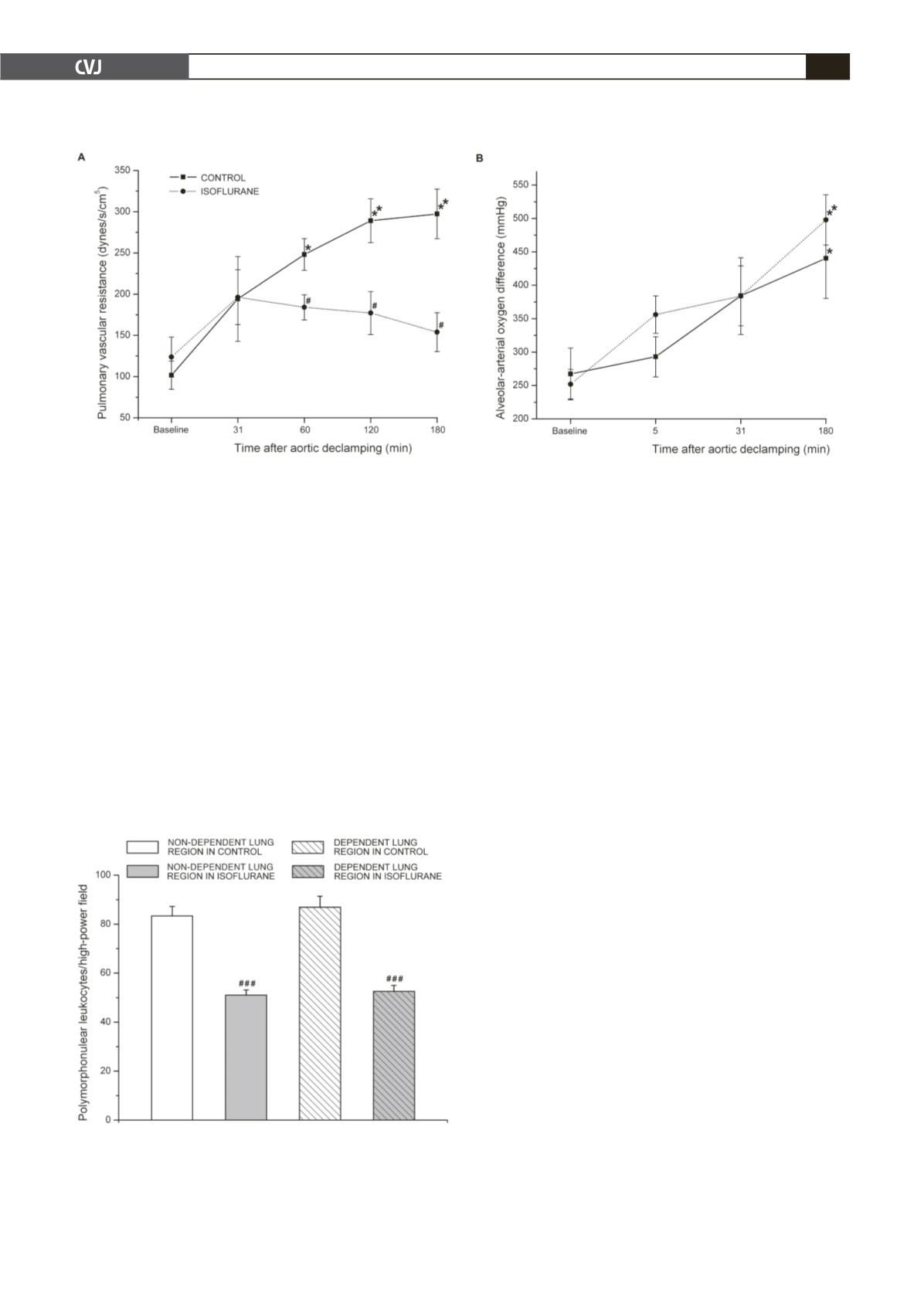
PMNs infiltrations in both the non-dependent and dependent
lung regions were significantly lower in the isoflurane group
compared to those in the controls (both
p
<
0.001). No differ-
ences in PMN counts were detected between the non-dependent
and dependent lung regions or between left and right lungs in
each group (
p
>
0.05) (Figs 2 and 3).
Discussion
Mechanisms of lung injury and respiratory complications
following CPB are multi-factorial, including aspects due to
CPB.
22
During CPB, blood contact with the artificial surface
of the bypass circuit, coupled with IR injury contribute to the
initiation of SIRS which is partially attributed to activation of
PMNs with up-regulation of adhesion molecules. This process
may ultimately result in adhesion of PMNs to the endothelium of
the lung vessels, and endothelial damage due to protease release.
1
Researchers in multi-disciplinary fields have been attempting
to find better lung protective and therapeutic strategies against
CPB-associated lung injury. Few currently developed strategies,
however, have been demonstrated to be clinically beneficial.
22
Recently, some literature reports that volatile anaesthetics
showed protective effects against lung injury.
9-13
In a male mouse
model of endotoxin-induced lung injury, isoflurane pre-treat-
ment significantly attenuated PMN recruitment into the injured
lung.
12
The clinical dilemma of lung injury during CPB and this
encouraging
in vitro
and
in vivo
evidence gave us insight into
conducting the experiment. The primary findings of the current
experiment were that isoflurane pre-treatment before CPB allevi-
ated PMN accumulation in the lungs, reduced PVR, and did not
affect AaDO
2
during the early post-CPB stage, compared to the
controls.
Reduced static and dynamic compliance is one of the char-
acteristics of pulmonary function in patients after exposure to
CPB.
23,24
Postulated causes include atelectasis, pulmonary oede-
ma, inflammation, increased capillary permeability, and pleural
Fig. 1A reflects the pattern of PVR changes in each group
during the study. At baseline, PVR in the isoflurane group
was comparable to that in the control. Following CPB, in the
control group, PVR was significantly increased at 60 (
p
<
0.05
vs baseline), 120 (
p
<
0.01 vs baseline) and 180 min (
p
<
0.01
vs baseline) after declamping. No differences in PVR were
found within the isoflurane group (
p
>
0.05 vs baseline). There
were significant differences in PVR between the isoflurane and
control groups (
p
<
0.05). At 60, 120 and 180 min after declamp-
ing, PVR values were lower in the isoflurane group compared to
those in the control group (
p
<
0.05).
Fig. 1B shows the changes in AaDO
2
in the isoflurane and
control groups over the experimental time. At baseline, AaDO
2
did not differ between the isoflurane and control groups (
p
=
0.429). Within both the isoflurane and the control group, AaDO
2
at 180 min after declamping was markedly higher than that at
Fig. 1. Changes in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) at baseline and 31, 60, 120 and 180 min after aortic declamp-
ing (A), and alveolar arterial oxygen difference (AaDO
2
) at baseline and 5, 31 and 180 min after aortic declamping (B),
of the control and isoflurane groups. Data shown are mean
±
SEM. *
p
<
0.05 vs baseline and **
p
<
0.01 vs baseline;
#
p
<
0.05 compared with control at a given time point.
Fig. 2. Lung tissue polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN)
counts (expressed as PMNs/field) in 10 different fields,
excluding airways and pulmonary vessels under 400
×
magnification in non-dependent and dependent lung
regions of the control and isoflurane groups. Data shown
are mean
±
SEM.
###
p
<
0.001 vs control.


