CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 22, No 3, May/June 2011
AFRICA
137
nadir CD
4
cell count group, the CD
4
cell counts were inversely
correlated with hsCRP (
r
=
–0.63,
p
=
0.01) and fibrinogen
values (
r
=
–0.78,
p
=
0.001).
Age correlated positively with cr-PWV values only in the
HIV-infected group (
r
=
0.14,
p
=
0.01) after adjusting for MAP
as well as tobacco and alcohol use. When the participants were
divided into age groups of 10-year intervals, and after adjusting
for gender, BMI, MAP, tobacco and alcohol use, a continuous
positive trend of increasing cr-PWV levels with age (
p
=
0.09)
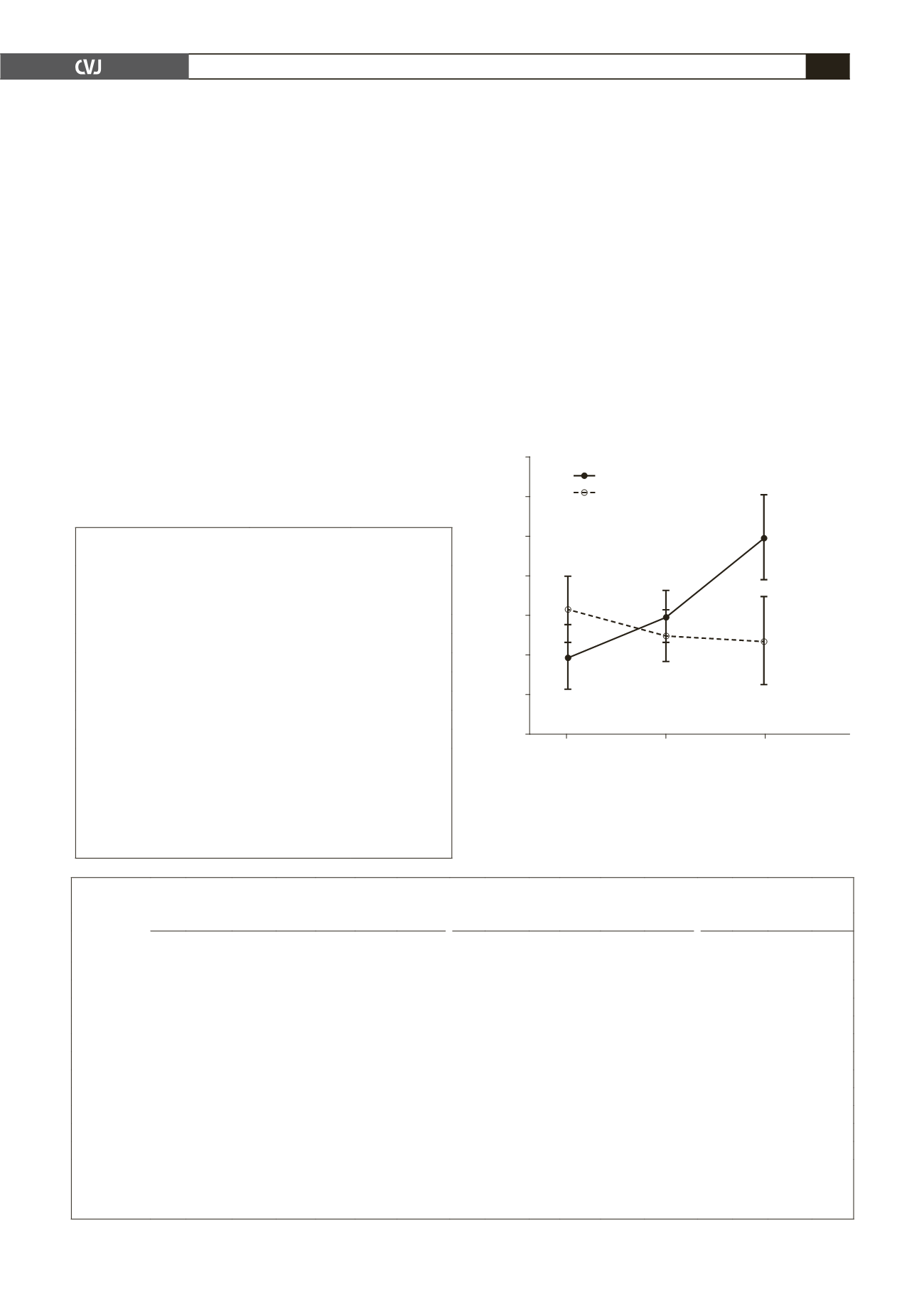
was detected only in the HIV-infected group (Fig. 1). In the age
group older than 50 years, the cr-PWV levels differed between
the infected and uninfected groups (
p
=
0.057).
Discussion
In this case–control study, the HIV-infected participants, who
had never received antiretroviral therapy, showed lower HDL-C
and higher hsIL-6, hsCRP, sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 levels than
their age-, gender-, BMI- and locality- (urban, rural) matched
controls. The higher levels of inflammatory markers and low
HDL-C levels could point to endothelial dysfunction, which is
seen as the link between infection, inflammation and athero-
sclerosis.
10
Furthermore, in the older HIV-infected participants,
a positive trend of increasing peripheral cr-PWV was detected,
which was not observed in the uninfected participants. This
could indicate accelerated vascular aging in these participants.
No differences in coagulation factors were detected between the
infected and uninfected groups.
The contribution of HIV to endothelial dysfunction is diffi-
cult to distinguish from traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
Therefore we carefully matched the control participants’ gender,
age, BMI and locality to minimise the confounding effect of
these conditions on the study findings.
In epidemiological studies, high plasma levels of HDL-C
protect against the development of atherosclerosis.
25
Besides
HDL-C’s known ability to promote the efflux of cholesterol
Fig. 1. cr-PWV in the HIV-infected and uninfected group
with increasing age. Adjusted for gender, BMI, MAP, self-
reported alcohol and tobacco use. Values are means
±
SEM. *cr-PWV of HIV-infected and uninfected participants
differ (
p
=
0.057).
12.00
11.75
11.50
11.25
11.00
10.75
10.50
10.25
<
40
40–50
>
50
cr-PW (m/s)
Age group (years)
HIV infected
HIV uninfected
p
trend = 0.09
p
trend = 0.78
*
TABLE 2. ODDS RATIOS OF HIV-INFECTED PARTICIPANTS
VS UNINFECTED PARTICIPANTS
Odds ratios
HIV infected vs
HIV uninfected
95% CI
HDL-C
<
1.36 mmol/l
3.69
2.6–5.2*
TG
≥
1.0 mmol/l
1.70
1.2–2.3*
TG:HDL ratio
≥
0.75
3.33
2.4–4.7*
hsCRP
≥
2.7 mg/l
1.78
1.3–2.5*
hsIL-6
≥
4.2 pg/ml
1.67
1.2–2.3*
sICAM-1
≥
516 ng/ml
2.04
1.5–2.8*
sVCAM-1
≥
693ng/ml
3.92
2.8–5.5*
HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: triglycerides;
TG:HDL: triglycerides–high-density lipoprotein ratio; hsCRP: high-
sensitivity C-reactive protein; hsIL-6: high-sensitivity interleukin
6; sICAM-1: serum intercellular adhesion molecule-1; sVCAM-1:
serum vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. For all variables, the median
of total group was used as cut-off value.
*Significant.
TABLE 3. PARTIAL CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS BETWEEN THE DIFFERENTVARIABLES OF THE HIV-UNINFECTED, -INFECTEDAND
NADIR (
<
200 CELLS/MM
3
) CD
4
CELL COUNT GROUPS
HIV uninfected (
n
=
300)
HIV infected (
n
=
300)
Nadir CD
4
cell count (
n
=
18)
Variables
Age cr-PWV HDL-C TG
Log
hsIL-6
Log
hsCRP
Log
sICAM-1 Age HDL-C TG
Log
hsIL-6
Log
hsCRP
Log
sICAM-1 CD
4
Age HDL-C
Log
hsCRP
Age
cr-PWV
0.14
HDL-C
TG
–0.23
0.14 –0.16
–0.55
Log hsIL-6
–0.21
Log hsCRP
0.45
0.52
–0.63
Log sICAM-1
–0.14
0.14
–0.15 0.12 0.17 0.14
Log sVCAM-1
0.27
0.30
Fibrinogen
–0.12
–0.17 0.29 0.45
0.24 0.33
–0.78
0.58
Log PAI-1
0.17
0.18
–0.67
Log eCrCl
–0.14
–0.25
n
: number of participants; cr-PWV: carotid radialis pulse wave velocity; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; hsIL-6: high-sensitivity inter-
leukin 6; hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; sICAM-1: serum intercellular adhesion molecule-1; sVCAM-1: serum vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; PAI-1:
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; eCrCl: estimated creatinine clearance. Adjustments were made for mean arterial pressure, tobacco and alcohol use.
Only significant (
p
<
0.05) correlation coefficients given.


