
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 26, No 3, May/June 2015
AFRICA
121
after surgery and the ECG and echocardiographic examinations
performed at that visit were also recorded.
After the exclusion of patients with any missing information,
the remaining 36 out of 44 patients with LA myxoma who
were surgically treated in our institution were included in the
study. Postoperative AF was defined as any episode of atrial
tachyarrhythmia, including AF or atrial flutter that lasted more
than 30 seconds, diagnosed with a rhythm monitor/telemetry
and/or ECG, and/or initiation of treatment for atrial fibrillation
such as amiodarone or cardioversion during hospitalisation.
14,15
Surgery was performed via a median sternotomy under
cardiopulmonary bypass with cardioplegic arrest. The LA
myxoma was excised through a left atriotomy with trans-septal
approach or via a biatrial approach in suitable cases. After
removing the mass, the resulting atrial septal defect was repaired
by direct suture or insertion of a Dacron patch.
Evaluation of pre- and postoperative ECGs
All patients had standard pre-operative (one day before surgery)
and postoperative (one week after surgery) 12-lead ECGs, which
were recorded at a paper speed of 25 mm/s, a sensitivity of 1 mV/
cm and filter settings of 0.05–40 Hz. The ECGs were scanned
and magnified five times.
P-wave duration and dispersion were measured as previously
described.
16
Briefly, P-wave duration was measured in three
consecutive complexes of each lead, from the junction between
the iso-electric line and the beginning of the P-wave deflection
to the junction between the end of the P wave and isoelectric
line, by a single observer who was blinded to the patients. To
improve accuracy, measurements were made using calipers and
a magnifying lens. P-wave dispersion was defined as the time
measured from the onset to the offset of the P wave.
The P
max
and the P
min
were measured in all 12-lead surface
ECGs. The Pd was defined as the difference between the P
max
and
the P
min
. Intra-observer variability was found to be 4.5% for P
max
and 4.1% for Pd. A Pd
>
40 ms was defined as increased Pd.
17
The
P–R interval, QRS duration, QT and rate-corrected QT interval
were measured similar to previous studies.
18,19
Evaluation of echocardiography
All patients underwent transthoracic echocardiography, performed
according to American Society of Echocardiography recommenda-
tions before surgery and three months after surgery.
20
LA diameter
and LV dimensions of the patients obtained by M-mode echo-
cardiography in the parasternal long-axis view were recorded. Mitral
regurgitation (MR) was graded by standard Doppler criteria.
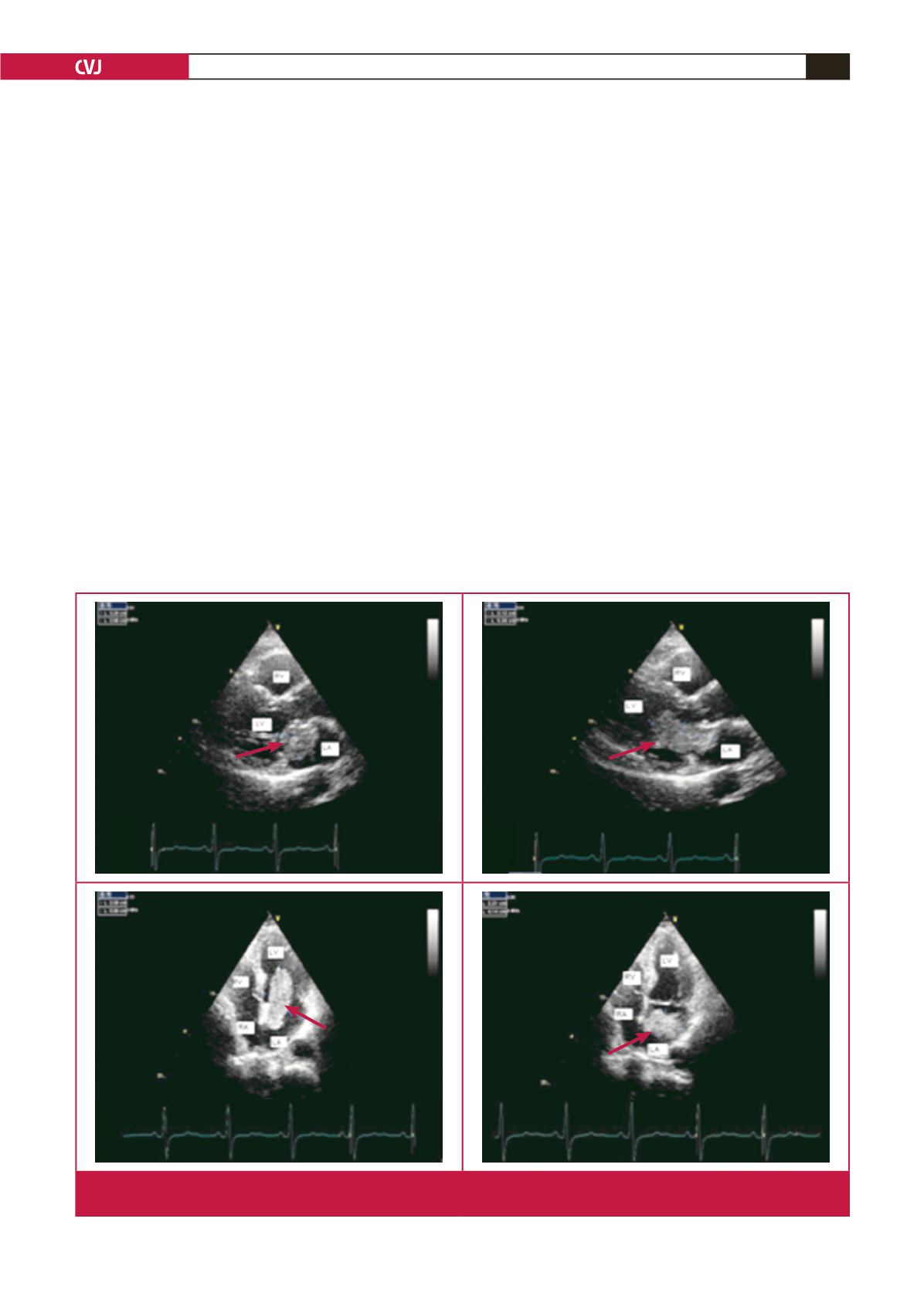
Fig. 1.
Measuring the tumour dimensions in different planes. LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle;
arrow: myxoma.

















