CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 30, No 4, July/August 2019
e2
AFRICA
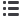
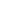
described as biphasic T waves in V2–V3, which was the finding
in our patient (Fig. 1B). The more common type 2 Wellens’
accounts for the remaining 76% of cases and is identified by
deep, symmetrically inverted T waves in V1–V4. This T-wave
pattern is well recognised by junior doctors. It is important to
emphasise that the T-wave changes of Wellens’ syndrome occur
during pain-free periods, while during an episode of chest pain,
the T waves normalise.
The criteria for Wellens’ syndrome are as follows: previous
history of chest pain, no Q waves or loss of R waves, no
significant ST-segment elevation, normal or minimally elevated
cardiac markers, and biphasic/inverted T-wave changes in the
precordial leads. Without prompt diagnosis and aggressive
intervention, patients with Wellens’ syndrome may rapidly go
on to develop extensive anterior wall myocardial infarction,
with a mean time of 8.5 days. As a result, patients with Wellens’
syndrome should undergo immediate or rapid invasive coronary
strategy.
7
Conclusion
We highlight three learning points about this case: (1) immediate
repetitive ECG evaluation after the chest pain subsides, even
in young patients without significant risk factors; (2) timely
recognition of the diagnostic ECG pattern of Wellens’ syndrome;
(3) emergency coronary angiography should be conducted if
diagnosed.
References
1.
Coutinho Cruz M, Luiz I, Ferreira L, Cruz Ferreira R. Wellens’
syndrome: A bad omen.
Cardiology
2017;
137
(2): 100–103.
Fig. 1.
A. ECG obtained during onset of pain, showing no obvious T-wave changes. B. Pain-free ECG was then performed, which
showed biphasic T waves in leads V2–V4.
A
B
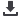
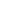
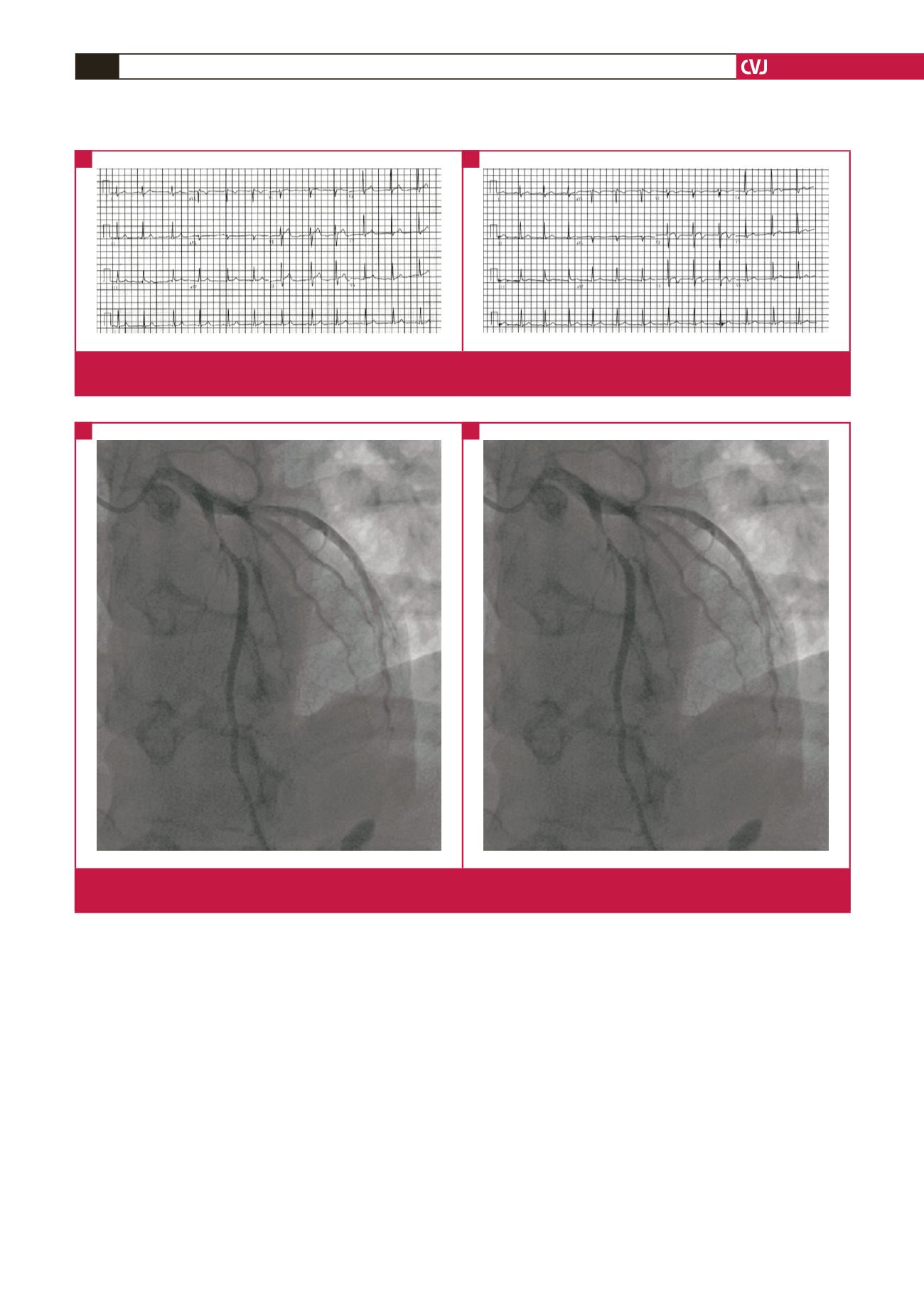
Fig. 2.
A. After coronary angiography, 95% stenosis of the proximal left anterior descending coronary artery was seen. B. After the
stenosis was treated with a drug-eluting stent.
A
B