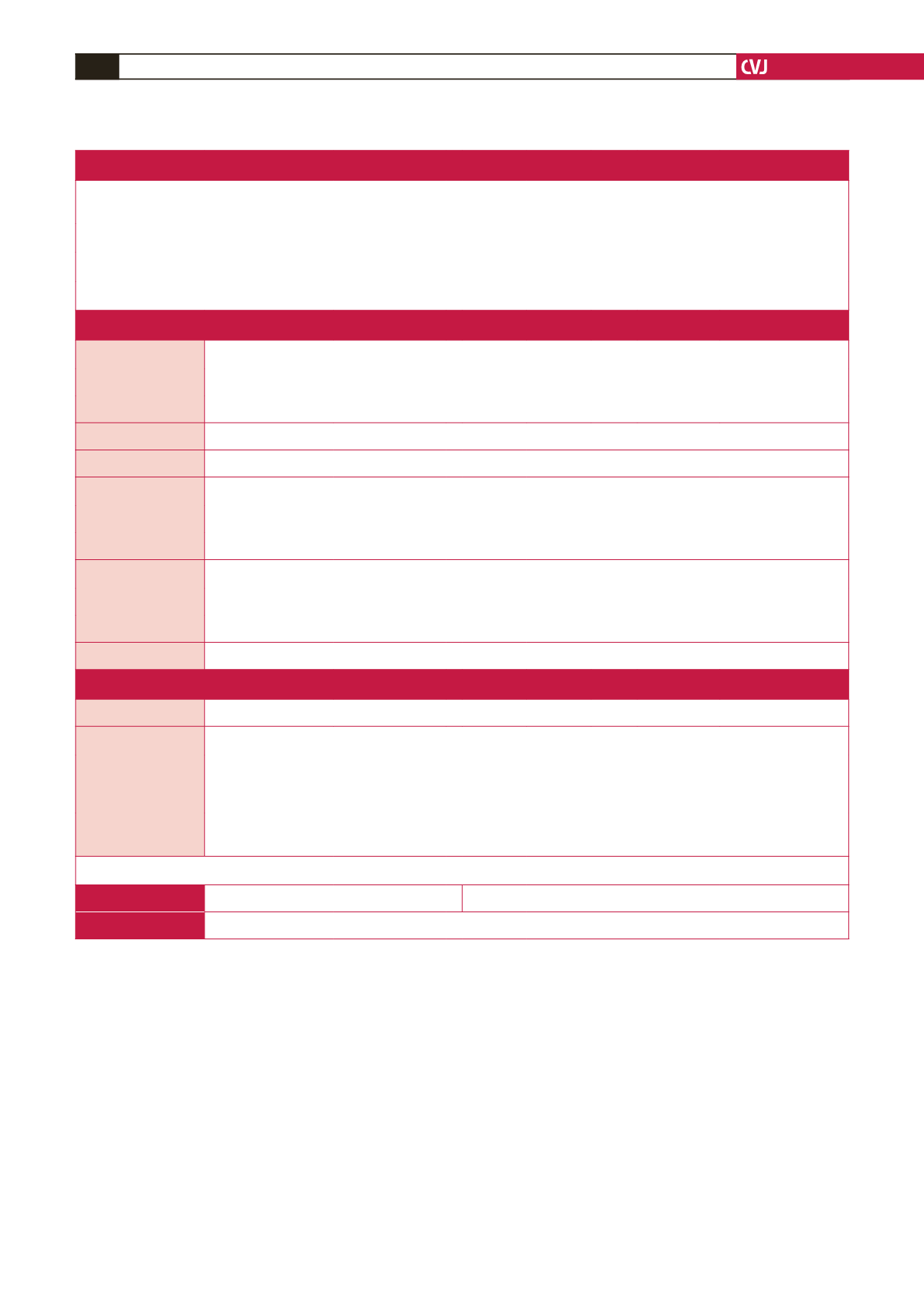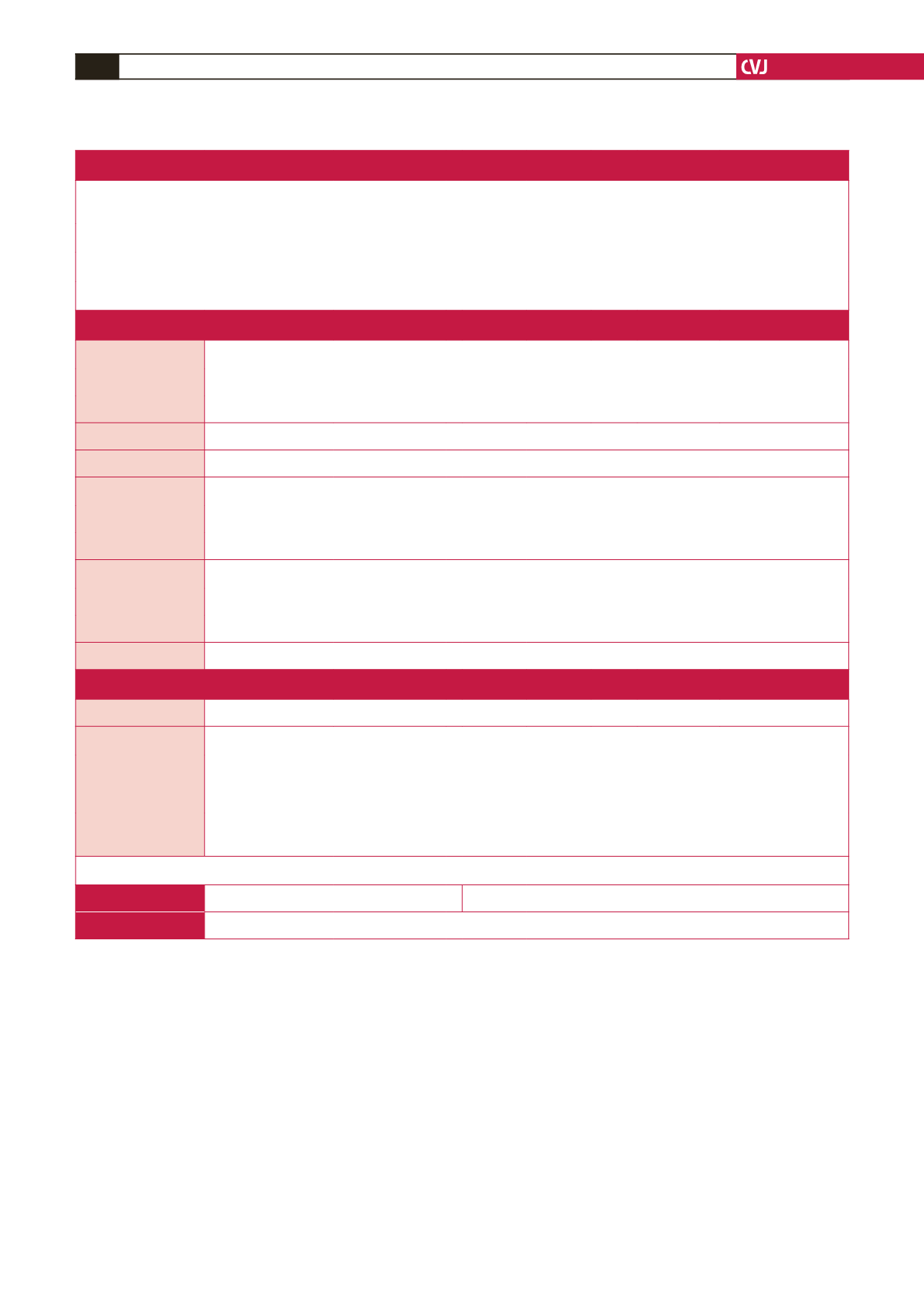
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 25, No 4, July/August 2014
184
AFRICA
MEDICAL HISTORY
❏
Beta-blockers
❏
ACE inhibitors/
ARB-II
❏
Diuretics
❏
Antialdosterone
❏
Digoxine
Current treatment
❏
Anti-arrhythmic drugs
__________________________________
❏
Antihistaminic drugs/Antibiotics (erythromycin,pentamidine..)
❍
Antiepileptic drugs
❍
Psychotropic drugs
❏
Traditional
❏
Prolonged-QT
❏
Other, precise ___________________________________________
CLINICAL EVALUATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Physical examination
❍
Not available
❍
Normal
❍
Abnormal, precise
❏
BMI
Value of BMI
❍
Measured
❍
Visual
ECG
❍
Available
❍
Not Available
❍
Normal
❍
Abnormal, precise
Blood biochemistry
❍
Normal
❍
Abnormal, precise
Non-invasive
screening test
❏
TTE
❏
Holter ECG
❏
Stress test
❏
SA-ECG
❏
Cardiac MRI
❍
Normal
❍
Normal
❍
Normal
❍
Normal
❍
Normal
❍
Abnormal, precise
❍
Abnormal, precise
❍
Abnormal, precise
❍
Abnormal, precise
❍
Abnormal, precise
Invasive screening
test
❏
Coronarograpy
❏
Electrophysio-logical study
❏
Autopsy
❍
Normal
❍
Normal
❍
Normal
❍
Abnormal, precise
❍
Abnormal, precise
❍
Abnormal, precise
Genetic screening test
❍
Normal
❍
Abnormal, precise
DIAGNOSTIC HYPOTHESIS: CLINICAL/ECG/BIOLOGY/NON- AND/OR INVASIVE SCREENING TESTS
Diagnostic
❍
Certain
❍
Probable (clinical suggestive but not sure)
❍
Unknown
Heart disease
❏
Acute MI
❏
Dilated CM
❏
Hypertrophic CM
❏
Other inherited CM ___________________
❏
Congenital
coronary
Anomalies
❏
CAD
❏
AV block
❏
Toxic/latrogenic/Proarrhythmic (precise)
__________________________________
❏
Tropical disease (precise)
__________________________________
❏
Others, precise
________________________________________________________
❏
Absence of structural heart disease-idiopathic VF (in this case, expert ECG reviewing)
Date of death:
❍
Cardiac
❍
Non-cardiac
❍
Unknown
Aetiology*:
All information of interest for establishing causes of death will be recorded in the e-CRF. These data include socio-demographic (identity, age, gender,
nationality, employment status, monthly incomes), past medical history focusing on cardiovascular conditions, the aetiology of death and associated
medical conditions. In-hospital/out-of-hospital, unwitnessed/witnessed deaths, activity of the time of SCD, time of occurrence (day/night) and post-
resuscitation outcome will be noted. Medical history reports heart diseases (as HF, MI, CM, CAD, RHD), neurological, tropical, infectious and other.
Clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests refer to physical examination, 12-lead ECG, blood biochemistry, non-invasive cardiac tests (TTE, Holter ECG,
stress imaging, signal-averaged ECG, cardiac MRI), invasive tests (coronarography, electrophysiological study, autopsy) and genetic screening.
e-CRF: electronic case report form; SCD: sudden cardiac death; HF: heart failure; MI: myocardial infarction; CM: cardiomyopathy; CAD: congenital
heart disease; RHD: rheumatic heart disease; ECG: electrocardiogram; TTE: transthoracic echocardiography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.