CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 6, November/December 2017
AFRICA
399
countries and articles involving women post delivery of their
babies (Fig. 1).
The results of the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool are displayed in
Table 2, highlighting the criteria for assessing quality and risk of
bias. Two of the included six articles displayed adequate sequence
generation, allocation concealment, and addressed incomplete
outcome data.
14,15
However, only one of these reported a low
risk of bias for ‘blinding’ of participants.
14
The final outcome of
the quality assessment showed that five out of the seven articles
(71%) were of poor quality.
Table 2. Reporting quality and risk-of-bias assessment
Author
Cochrane tool for assessing bias
Sequence
generation
Allocation
concealment
Blinding
Incomplete
outcome data
Selective outcome
reporting
Other threats to
validity
Final
outcome
Santos
et al
., 2005
14
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Unclear
Yes
Good
Sedaghati
et al
., 2007
16
No
No
No
Yes
Unclear
No
Poor
Garshasbi
et al
., 2005
19
Unclear
Unclear
No
Yes
Unclear
Yes
Poor
Prevedel
et al
., 2003
17
Unclear
Unclear
No
No
Yes
Yes
Poor
Cavalcante
et al
., 2009
18
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Good
Malpeli
et al
., 2013
11
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
Poor
Ghodsi & Asltoghiri, 2012
15
No
No
No
Yes
Unclear
Yes
Poor
Titles excluded
(
n
=
1635)
• systematic reviews, literature reviews,
summaries
• management guidelines, policies
• domestic violence
• TB, HIV, influenza, cancer
• adolescents healthy eating
• developed countries
• schizophrenia, depression
• undernutrition, micronutrient deficiency,
diabetes
• unable to find full text
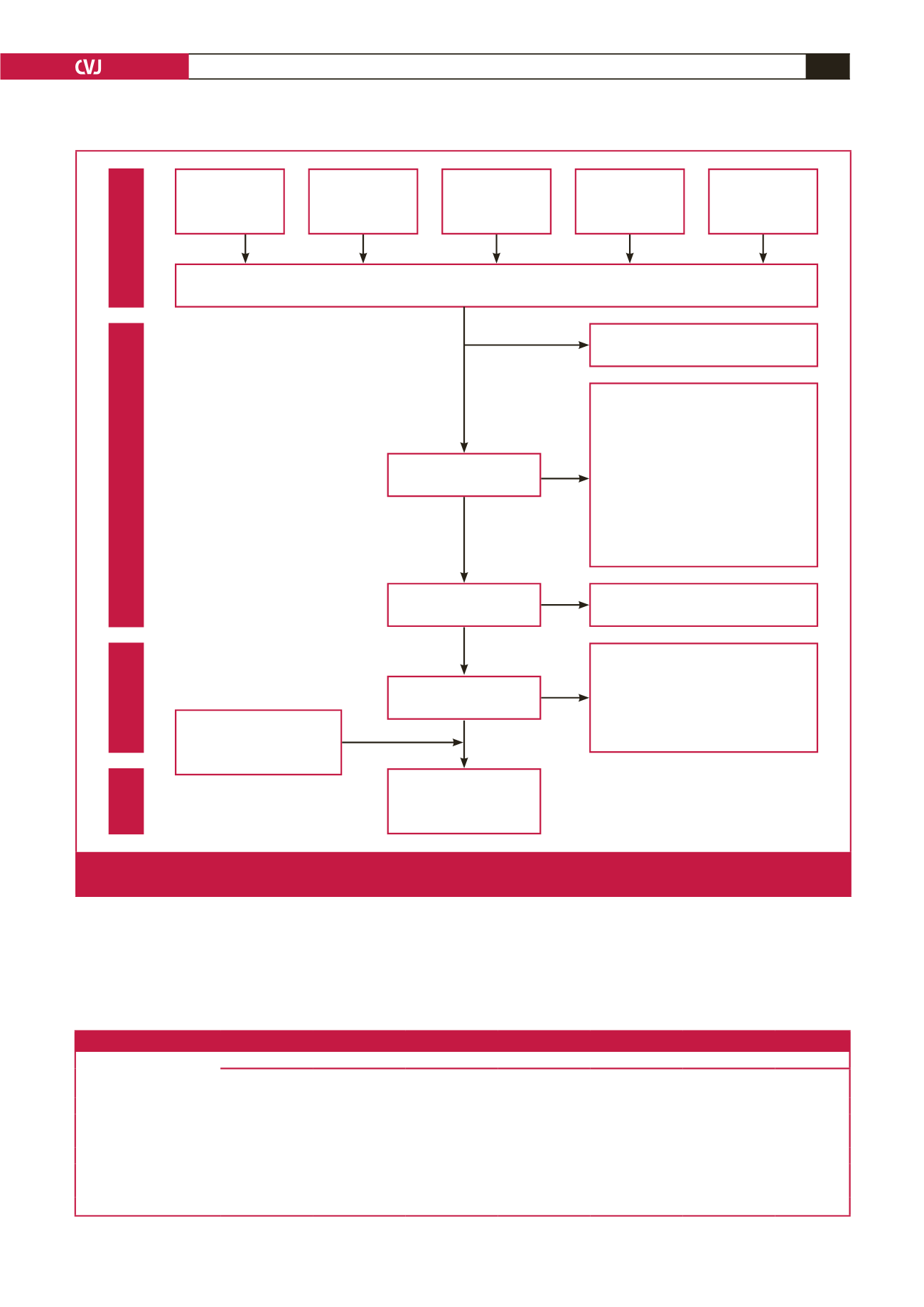
Total records identified
(
n
=
6988)
Duplicates removed
(
n
=
5280)
Titles screened
(
n
=
1708)
Abstracts screened
(
n
=
73)
Abstracts excluded
(
n
=
50)
Full text articles excluded
(
n
=
22)
• review studies/position statements/
guidelines/reports
• epidemiological/prevalence studies
• studies performed in high-income
countries
Abstracts of titles identified by
hand-searching whose full-text
articles were read (
n
=
6)
Full-text articles included in
systematic review
(
n
=
7)
Full-text articles screened
(
n
=
23)
Identification
Screening
Eligibility
Included
Records through
Pubmed
(
n
=
155)
Records through
Cochrane Library
(
n
=
445)
Records through
Scopus
(
n
=
5253)
Records through
Cinhal
(
n
=
22)
Records through
BioMed Central
(
n
=
1113)
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram illustrating the number of included and excluded studies in the systematic review on lifestyle interventions for
obesity/overweight during pregnancy in developing countries