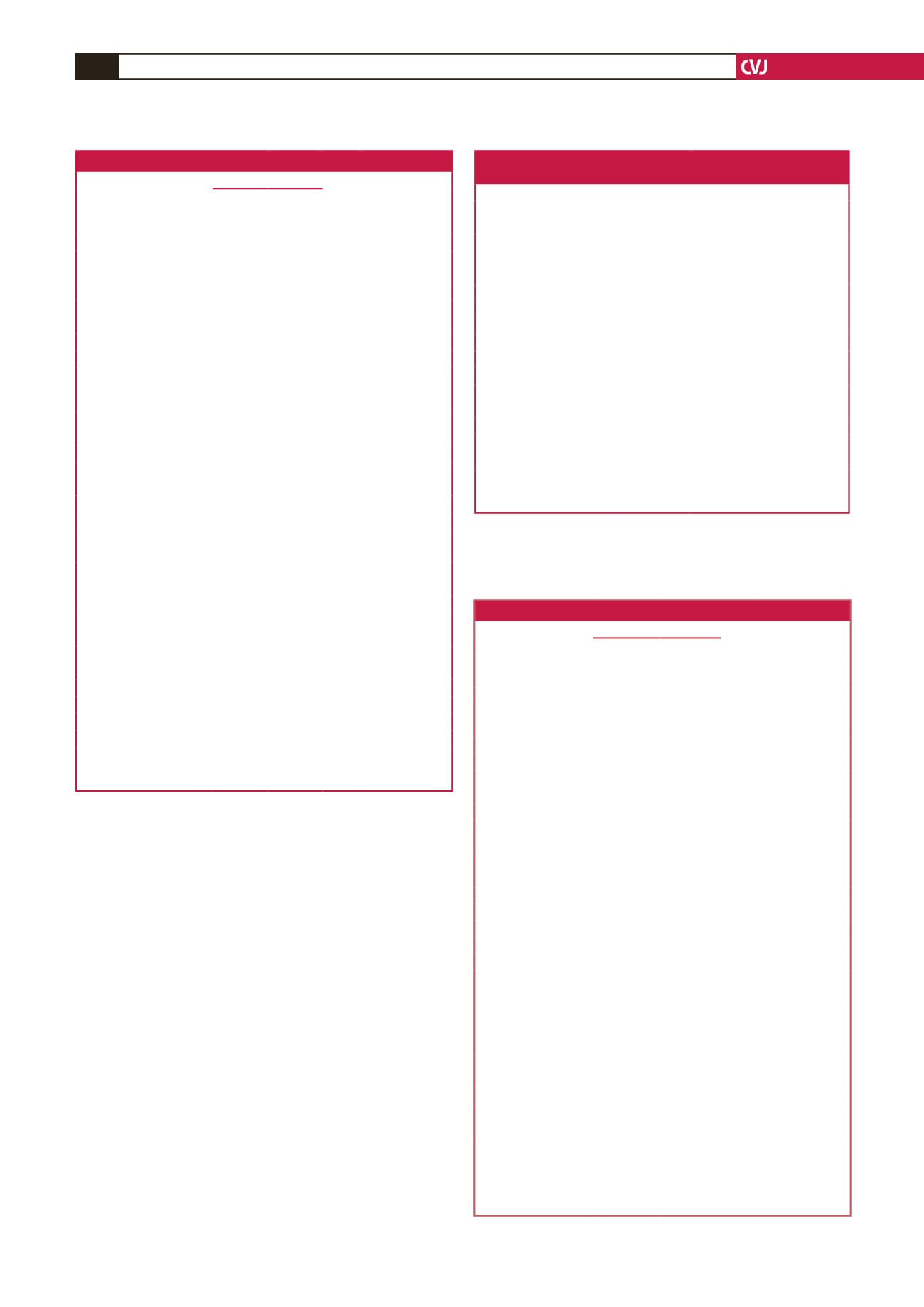
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 1, January/February 2018
48
AFRICA
Discussion
The average age of the HF patients in this study was 52.49
±
13.89 years, which is similar to the pattern seen in other African
countries but at variance with that of patients in Western
countries where HF remains predominantly a disease of the
elderly.
27,28
In Spain, Permanyer
et al
.
29
found that almost 40% of
HF patients were over 80 years and more than 70% were over 70
years. This is also the pattern in the United States of America
where average age was about 70 years for HF patients.
30
The lower average age in our study and that of other studies
emanating from Africa may be attributable to the fact that the
major causes of HF in sub-Saharan Africa, such as hypertension,
rheumatic heart disease, idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and
HIV-related heart disease affect mainly young and middle-aged
people.
31,32
Also hypertension detection, treatment and control in
Nigeria, as in other African countries, is poor and complications
such as heart failure is expected to occur earlier. The major
aetiologies of heart failure in this study were hypertension,
dilated cardiomyopathy and rheumatic valve disease, which is in
keeping with studies from other parts of Africa.
31,32
Late presentation of patients to hospital was a significant
finding in this study; 57.5% of the patients presented in NYHA
class III and 15.6% in class IV. This late presentation is similar
to findings from other studies documented by investigators on
the African continent.
5,15,33
Presentation in an advanced NYHA
Table 1. Association of different variables with rehospitalisation
Rehospitalisation
Total
n
Chi
2
(
p
-value)
Variable
No
n
(%)
Yes
n
(%)
Gender
1.033 (0.309)
Male
52 (68.4) 24 (31.6)
76
Female
51 (60.7) 33 (39.3)
84
Age group (years)
4.95 (0.084)
18–45
26 (52.0) 24 (48.0)
50
45–65
56 (70.9) 23 (29.1)
79
>
65
21 (67.7) 10 (32.3)
31
Level of education
0.24 (0.623)
None/primary
29 (67.4) 14 (32.6)
43
Secondary/tertiary
74 (63.2) 43 (36.8) 117
NYHA class at
presentation
26.64 (
<
0.001)*
Class II
39 (90.7)
4 (9.3)
43
Class III
44 (47.8) 48 (52.2)
92
Class IV
20 (80.0)
5 (20.0)
25
Type of HF
6.05 (0.014)*
Diastolic HF
14 (93.3)
1 (6.7)
15
Systolic HF
89 (61.4) 56 (38.6) 145
BMI (kg/m
2
)
11.72 (0.003)*
≤
24.99
34 (64.2) 19 (35.8)
53
25–29.99
35 (52.2) 32 (47.8)
67
≥
30
34 (85.0)
6 (15.0)
40
Haemoglobin (g/dl)
5.51 (0.019)*
≥
10
84 (69.4) 37 (30.6) 121
<
10
19 (48.7) 20 (51.3)
39
LVEF (%)
7.52 (0.023)*
≥
40
48 (77.4) 14 (22.6)
62
25–39.99
40 (56.3) 31 (43.7)
71
<
25
15 (55.6) 12 (44.4)
27
eGFR (ml/min)
11.17 (0.001)*
≥
60
76 (73.8) 27 (26.2) 103
<
60
27 (47.4) 30 (52.6)
57
NYHA
=
New York Heart Association; BMI
=
body mass index; LVEF
=
left
ventricular ejection fraction; eGFR
=
estimated glomerular filteration rate;
n
=
number; %
=
percentage within variable; *significant
p
-value.
Table 2. Result of logistic regression analysis of
some variables with rehospitalisation
Variable
B
p
R
2
NYHA class
0.296
Class II
–
<
0.001
Class III
1.022
0.271
Class IV
2.819
<
0.001*
Type of HF
2.711
0.032*
BMI (kg/m
2
)
<
24.99
–
0.410
25–29.99
0.158
0.812
≥
30
0.635
0.285
Haemoglobin
<
10 g/dl
1.432
0.012*
LVEF (%)
≥
40
–
0.475
25–39.99
–0.879
0.225
<
25
–0.461
0.435
eGFR
<
60 ml/min
1.085
0.024*
NYHA
=
New York Heart Association; BMI
=
body mass index; LVEF
=
left
ventricular ejection fraction; eGFR
=
estimated glomerular filteration rate;
*significant
p
-value.
Table 3. Association of some variables with mortality
Variables
Mortality
Total
No.
Chi
2
(
p
-value)
No,
n
(%) Yes,
n
(%)
Gender
Male
63 (82.9)
13(17.1)
76 2.01 (0.156)
Female
76 (90.5)
8 (9.5)
84
Age group (years)
18–45
43 (86.0)
7 (14.0)
50 3.724 (0.155)
46–65
72 (91.1)
7 (89)
79
>
65
24 (77.4)
7 (22.6)
31
Level of education
Nursery/primary
36 (95.3)
7 (16.3)
43 0.513 (0.474)
Secondary/tertiary 103 (88.0)
14 (12.0)
117
NYHA class
Class II
41 (95.3)
2 (4.7)
43 57.10 (
<
0.001)*
Class III
88 (95.7)
4 (4.3)
92
Class IV
10 (40.0)
15 (60.0)
25
Type of HF
Diastolic HF
15 (100.0)
0 (0.0)
15 2.501 (0.114)
Systolic HF
124 (85.5)
21 (14.5)
145
BMI (kg|m
2
)
≤
24.99
45 (84.9)
8 (15.1)
53 5.49 (0.064)
25–29.99
55 (82.1)
12 (17.9)
67
≥
30
39 (97.5)
1 (2.5)
40
Haemoglobin (g/dl)
≥
10
110 (90.9)
11 (9.1)
121 7.09 (0.008)*
<
10
29 (74.4)
10 (25.6)
39
LVEF (%)
≥
40
60 (96.8)
2 (3.2)
62 8.72 (0.013)*
25–39.99
57 (80.3)
14 (19.7)
71
<
25
22 (81.5)
5 (18.5)
27
eGFR (ml/min)
≥
60
93 (90.3)
10 (9.7)
103 2.96 (0.085)
<
60
46 (80.7)
11 (19.3)
57
NYHA
=
New York Heart Association; BMI
=
body mass index; LVEF
=
left
ventricular ejection fraction; eGFR
=
estimated glomerular filteration rate;
n
=
number; %
=
percentage within variable; *significant
p
-value.