CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 5, September/October 2018
298
AFRICA
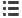
0.81,
p
=
0.03) and WBC count (
r
=
0.47,
p
=
0.001) (Fig. 1).
However, there was no significant difference in lymphocyte
count and red blood cell distribution width between the groups
(
p
>
0.05).
Mitral regurgitation (MR) existed in 68 patients, aortic
regurgitation (AR) in 16, and combined valve involvement in 36
patients. There were 38 patients with severe valve regurgitation.
Twenty-eight patients had severe MR, six had severe AR, and
four had severe combined valve regurgitation. We found a
positive correlation between NLR and the severity of valvular
regurgitation (
r
=
0.34,
p
<
0.001), and a negative correlation
between MPV and the severity of valvular regurgitation (
r
=
–0.38,
p
<
0.05). The MPV and NLR values according to valve
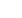
involvement in the groups are shown in Fig. 2.
Clinical and echocardiographic variables, which were
correlated with NLR and MPV values in the Student’s
t
-test
(severe valvular regurgitation), were included in multiple linear
regression analysis to detect the determinants of possible platelet
volume decrease and NLR increase in the patient group. In
regression analysis, NLR (OR
=
0.51, 95% CI: 0.32–0.68,
p
=
0.006) and MPV (OR
=
–0.78, 95% CI: –0.72–0.98,
p
=
0.008)
were found to be independent predictors for the presence of
severe valvular regurgitation (Table 2).
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this study showed for the first time
that increased NLR and decreased MPV levels can be associated
with severity of valvular involvement in patients with ARC.
Furthermore, NLR values were correlated with WBC count,
ESR and CRP during ARF.
In the case of ARF, several inflammatory cells such as
neutrophils, macrophages, and T and B lymphocytes infltrate
both the myocardium and the valves. Activated lymphocytes
and macrophages secrete tumour necrosis factor cytokines, and
interleukins play an important role in the pathogenesis of ARC.
The healing process of rheumatic carditis results in varying
degrees of fibrosis and valve damage. Kumar
et al
. reported that
macrophages and neutrophils, which infiltrate the myocardium,
may through the generation of oxygen free radicals, play a role
in the pathogenesis of cardiac damage seen in patients with
rheumatic heart disease. Also, they showed that the enzymatic
Severe MR/AR
MR/AR
Control
NLR
12.00
10.00
8.00
6.00
4.00
2.00
0.00
Severe MR/AR
MR/AR
Control
MPV
14.00
12.00
10.00
8.00
6.00
4.00
Fig. 2.
Box plot showing neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios (NLR) and mean platelet volume (MPV) in the controls and in acute rheu-
matic carditis patients (the severity of mitral and aortic regurgitation was defined as mild and moderate or severe). MR: mitral
regurgitation, AR: aortic regurgitation.
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
NLR
ESR
120.00
100.00
80.00
60.00
40.00
20.00
0.00
r
= 0.81
p
= 0.03
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
NLR
CRP
250.00
200.00
150.00
100.00
50.00
0.00
r
= 0.377
p
= 0.001
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
NLR
WBC
25.00
20.00
15.00
10.00
5.00
0.00
r
= 0.47
p
= 0.001
Fig. 1.
The relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios (NLR) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein
(CRP) and white blood cell (WBC) count. The same numerical valves are shown once on the figures.