CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 6, November/December 2018
AFRICA
353
replacement therapy, orthostatic hypotension and fall secondary
to hypotension were not approached to initiate sacubitril/
valsartan treatment.
When patients were already treated with an ARB, sacubitril/
valsartan was started the day after the cessation of the ARB.
Patients receiving an ACEI waited 36 to 48 hours after their last
dose before starting sacubitril/valsartan, ensuring a proper wash-
out period, to avoid angioedoema. The product monograph
recommends 36 hours for the wash-out period but it was
extended to 48 hours in this study for patients on once-daily
ACEI to facilitate adherence. According to the algorithm,
titration was subsequently based on ACEI or ARB doses and
baseline systolic blood pressure.
This prospective study was done with the agreement of
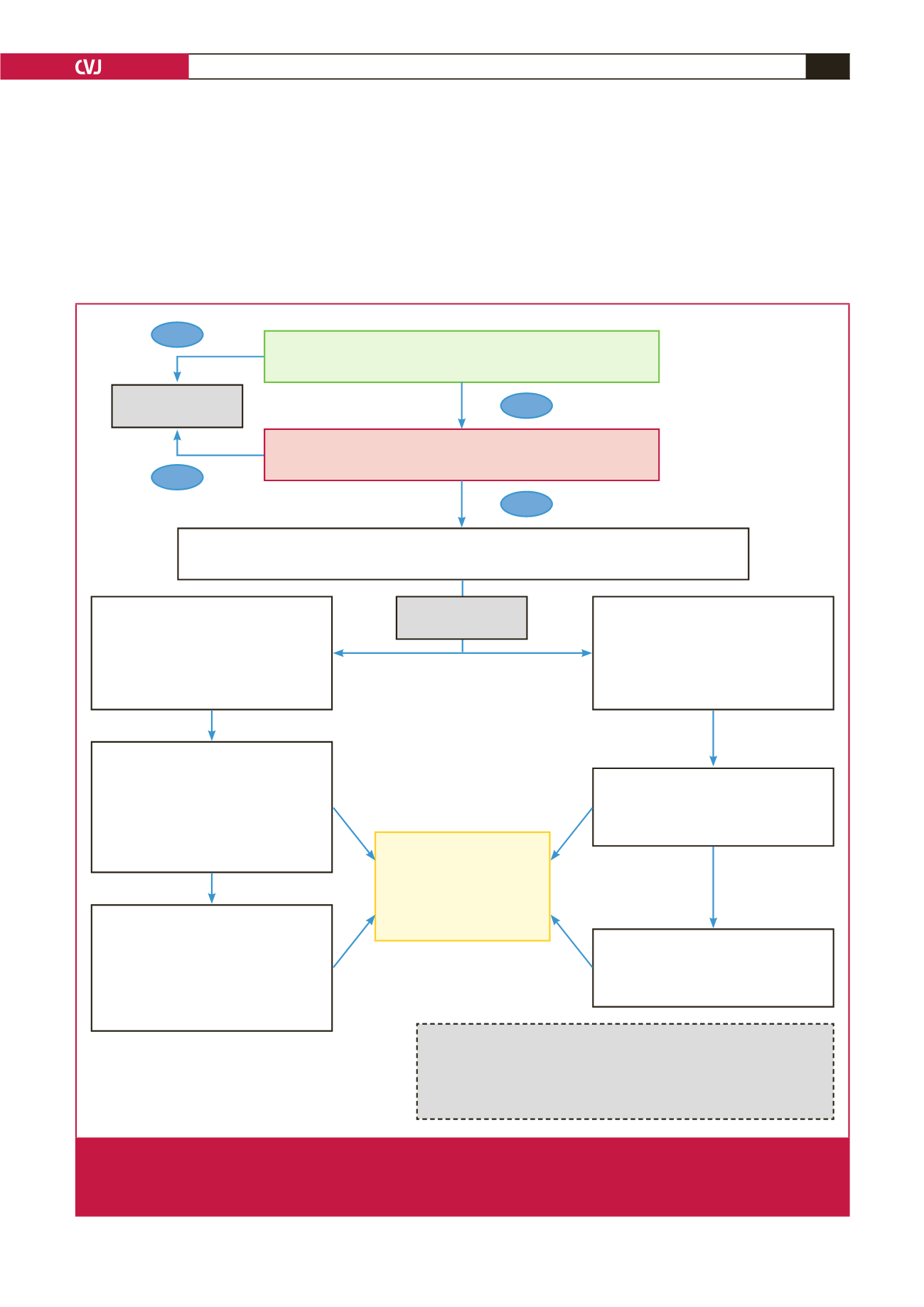
Excluded
Treated with ARB:
stop
ARB
and start
sacubitril/valsartan
24/26 mg
†
BID
THE DAY AFTER
Treated with ACEI:
stop
ACEI
and start
sacubitril/valsartan
24/26 mg
†
BID
TWO DAYS LATER
†
Consider starting sacubitril/valsartan at 49/51 mg BID if SBP
≥
140 mmHg
AND
if treated with
>
50% of the ACEi/ARB target dose*
Consider SLOW titration if:
• Actual ACEI/ARB dose
≤
50% of target dose*
• Labile BP or creatinine
• Borderline BP
• Altered kidney function
• Previous recurrent AKI or hyper K
+
while being
on RAAS inhibitor(s)
• Elderly or frail patient
7 to 14 days later (depending on Creat/K
+
):
• Serum BUN, Creat, K
+
21 to 28 days later:
•
↑
Sacubitril/valsartan 49/51 mg BID
†
if labs &
BP allow it and if well tolerated
†
Consider intermediate dose (ex: 24/26 mg AM +
49/51 mg PM) if needed and continue titration
7 to 14 days later (depending on Creat/K
+
):
• Serum BUN, Creat, K
+
21 to 28 days later:
•
↑
Sacubitril/valsartan 97/103 mg BID
††
if labs
& BP allow it and if well tolerated
• Plan a final lab control in 7 to 14 days
††
Consider intermediate dose if needed and continue
titration at target dose
Consider FAST titration if:
• Actual ACEI/ARB dose
>
50% of target dose*
• SBP
≥
120 mmHG
• Treated with CCB/
α
-blocker or any other
antihypertensive therapy
• Adequate renal function & kalaemia
ALL
these criteria present?
• LVEF
≤
40%
•
K
+
<
5.4 mmol/l under ACEI/ARB
• NYHA II–III
or K
+
<
5.2 mmol/l without ACEi/ARB
ONE
or more of these criteria present?
• Previous angioedema
•
Orthostatic hypotension
• Renal replacement therapy
•
Fall due to hypotension
YES
YES
NO
NO
7 to 14 days later (depending on Creat/K
+
):
• Serum BUN, Creat, K
+
•
↑
Sacubitril/valsartan 49/51 mg BID if labs &
BP allow it and if well tolerated
* ACEI/ARB recommended target dose according to practice guidelines:
ACEI:
Enalapril 20 mg/d
ARB:
Candesartan 32 mg/d
Lisinopril 20 mg/d
Irbesartan 300 mg/d
Perindopril 8 mg/d
Losartan 100 mg/d
Ramipril 10 mg/d
Telmisartan 80 mg/d
Trandolapril 4 mg/d
Valsartan 320 mg/d
If K
+
>
5,5 mmol/l
OR
if serum
creat
≥
30% vs baseline =
medical evaluation
Consider
↓
diuretic dose or
antihypertensive treatment
depending on volaemia and BP
7 to 14 days later (depending on Creat/K
+
):
• Serum BUN, Creat, K
+
•
↑
Sacubitril/valsartan 97/103 mg BID if labs &
BP allow it and if well tolerated
• Plan a final lab control in 7 to 14 days
TITRATION
Fig. 1.
Titration algorithm. ACEI: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; AKI: acute kidney injury; ARB: angiotensin receptor
blocker; BID: twice daily; BP: blood pressure; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; CCB: calcium channel blocker; Creat: creatinine
level; K
+
: potassium level; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; NYHA: New York Heart Association; RAAS: renin–angioten-
sin–aldosterone system; SBP: systolic blood pressure.