CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 31, No 1, January/February 2020
42
AFRICA
wall at the end-ventricular systole (just before the opening of the
mitral valve) when the LA chamber is at its greatest dimension.
Measurements were indexed to body surface area (BSA).
LA surface and volume were obtained on an apical four-
chamber view at end-systole. The inner border of the LA,
excluding the area under the mitral valve annulus and the inlet of
the pulmonary veins was traced, giving the LA a shape roughly
like a square. The LA volume was calculated using the biplane
area–length method and the formula is given by
0.85(A1 × A2)/L.
15
where A1 and A2 are the areas of the LA in four- and
two-chamber views and L is the shortest of the lengths obtained
from the orthogonal views and indexed to BSA (Fig. 2).
The LA length (major axis) and width (minor axis) were
also measured in the apical four-chamber view. The length was
measured from the plane of the mitral annulus to the roof of the
atrium and the width was defined as the distance between the
lateral LA wall and inter-atrial septum, at the mid-atrial level,
defined by half of the LA long axis.
In the parasternal long-axis view, left ventricular (LV)
parameters were measured using the leading edge-to-leading
edge convention of the recommendations by the American
Society of Echocardiography. End-diastolic and end-systolic
LV internal diameters, interventricular septum thickness and
posterior wall thickness were measured from two-dimensionally
guided M-mode tracings recorded at 50 to 100 cm/s speed
during three or more consecutive cycles, according the American
Society of Echocardiography guidelines.
14
Relative wall thickness was defined by the ratio of posterior
wall plus interventricular septum thickness to LV internal
diastolic diameter. Left ventricular mass (LVM) was calculated
using the Devereux-modified Penn formula
16
and was indexed to
BSA (calculated using the formula of Dubois).
0.8 {1.04[(LVEDD + PWTd + IVSTd)3 – (LVEDD)3]} + 0.6
where LVEDD is left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, PWTd
is posterior wall thickness in diastole, IVSTd is interventricular
septal thickness in diastole.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was calculated using
the Teichholz formula. Fractional shortening was calculated
from LV internal dimensions in diastole and systole:
LVIDd – LVIDs
_____________
LVID
×
100
where LVIDd is left ventricular internal diameter in diastole and
LVIDs is left ventricular internal diameter in systole.
Diastolic function parameters
From the apical four-chamber view, trans-mitral echo-Doppler
velocity flow profile was recorded in all patients, positioning
the sample volume at the level of the leaflet tips; the highest
discernible signal was determined as velocity. The diastolic filling
indices were measured: peak flow velocity of early (peak E) and
late (peak A) diastole, E/A ratio and deceleration time (DT),
defined as the time interval required for the E velocity to decline
from its peak to the baseline. The isovolumetric relaxation time
(IVRT) was also considered, measured from the aortic valve
closure to the beginning of trans-mitral flow.
The pulsed-wave Doppler tissue imaging (DTI) sample volume
was placed on the mitral annuli at the apical four-chamber view.
The spectral longitudinal velocity of the myocardium, normally
consisting of a positive systolic wave and two diastolic peaks,
notably the S
′
, E
′
and A
′
, respectively, were measured in the
lateral and septal mitral annuli.
LAR was defined as changes in LA structure (as evidenced
by increased anterior–posterior diameter, surface or volume)
or function (increased atrial contraction measured from the
late diastolic wave velocity, A) induced by hypertension. Left
structural changes were defined as increase in LA volume index
(LAVI
>
34 ml/m
2
). Mild LA enlargement was 35–41 ml/m
2
,
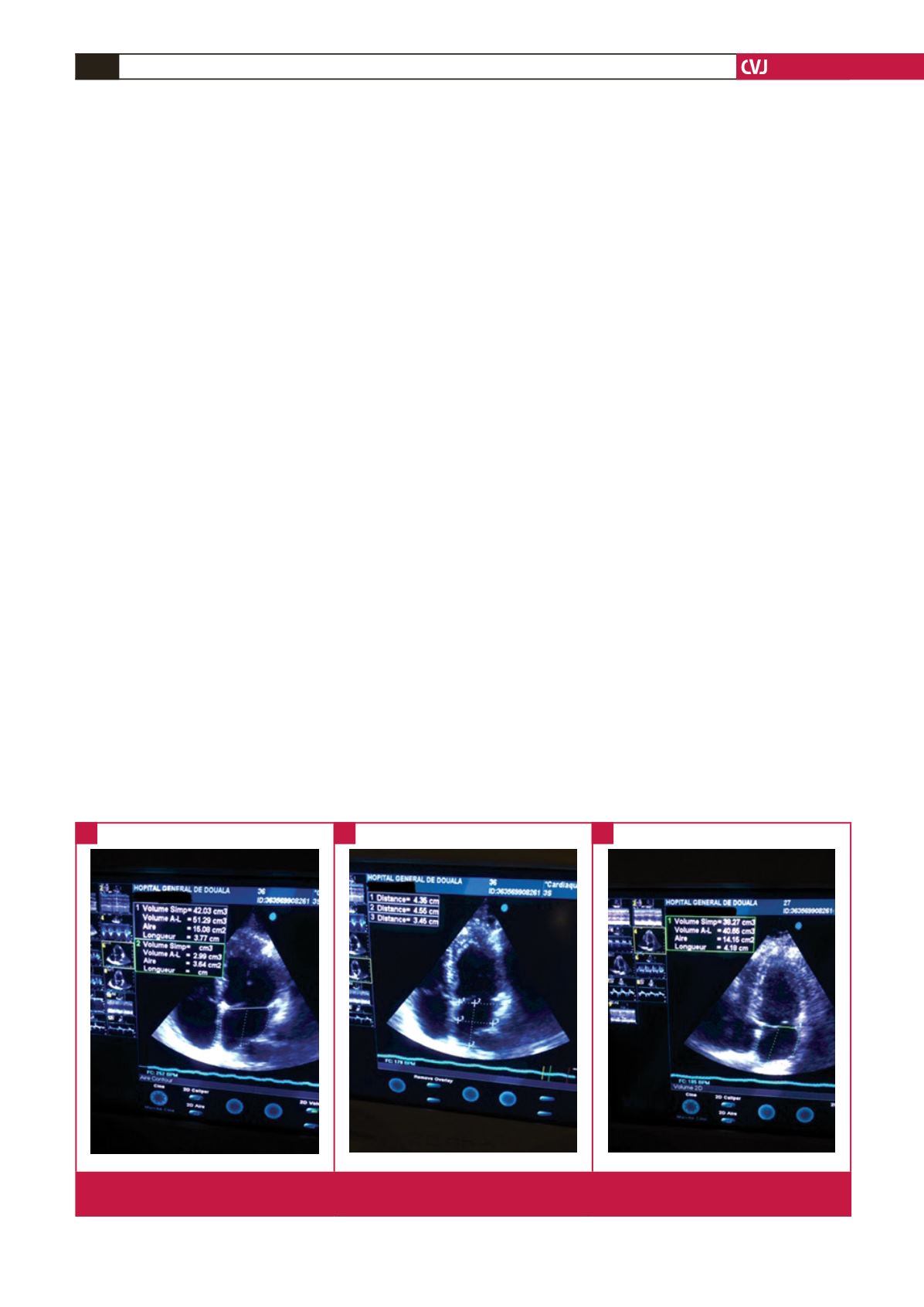
Fig. 2.
Measurement of LA volume from the biplane area–length method, using apical four- and two-chamber views to obtain A1,
A2 and the longitudinal diameter (L) (distance 2 in B) (courtesy of Doula General Hospital).
A
B
C