CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 31, No 3, May/June 2020
AFRICA
157
and willingness of patients, as well as the experience and skill of
the clinician should be taken into consideration before making
a decision.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation
of China (81770334, 81970281) and the Taishan Scholar Engineering
Construction Fund of Shandong Province (ts201511104).
J Li, M Gao, M Zhang and D Liu contributed equally to the work.
References
1.
Du X, Dong J, Ma C. Is atrial fibrillation a preventable disease?
J Am
Coll Cardiol
2017;
69
(15): 1968–1982.
2.
Lip GY, Tse HF, Lane DA. Atrial fibrillation.
Lancet
2012;
379
(9816):
648–661.
3.
Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K,
et al
. Worldwide epidemiology
of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study.
Circulation
2014;
129
(8): 837–847.
4.
Rahman F, Kwan GF, Benjamin EJ. Global epidemiology of atrial fibril-
lation.
Nat Rev Cardiol
2014;
11
(11): 639–654.
5.
Passman R. Atrial fibrillation and stroke: The more we learn, the less we
understand.
Am Heart J
2018;
201
: 158–159.
6.
Saksena S, Slee A. Atrial fibrillation and its pernicious role in heart
failure with preserved ejection fraction: a new frontier in interventional
electrophysiology.
J Interv Card Electrophysiol
2018;
51
(2): 89–90.
7.
Soliman EZ, Safford MM, Muntner P,
et al
. Atrial fibrillation and the
risk of myocardial infarction.
J Am Med Assoc Intern Med
2014;
174
(1):
107–114.
8.
Bansal N, Fan D, Hsu CY,
et al
. Incident atrial fibrillation and risk of
end-stage renal disease in adults with chronic kidney disease.
Circulation
2013;
127
(5): 569–574.
9.
Schoonderwoerd BA, van Gelder IC, van Veldhuisen DJ,
et al
. Electrical
and structural remodeling: role in the genesis and maintenance of atrial
fibrillation.
Prog Cardiovasc Dis
2005;
48
(3): 153–168.
10. Nattel S, Harada M. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: recent
advances and translational perspectives.
J Am Coll Cardiol
2014;
63
(22):
2335–2345.
11. Xu D, Murakoshi N, Igarashi M,
et al
. PPAR-
γ
activator pioglitazone
prevents age-related atrial fibrillation susceptibility by improving anti-
oxidant capacity and reducing apoptosis in a rat model.
J Cardiovasc
Electrophysiol
2012;
23
(2): 209–217.
12. Orso F, Fabbri G, Maggioni AP. Upstream treatment of atrial fibril-
lation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: myth or reality?
Arrhythm
Electrophysiol Rev
2015;
4
(3): 163–168.
13. Savelieva I, Kakouros N, Kourliouros A, Camm AJ. Upstream therapies
for management of atrial fibrillation: review of clinical evidence and
implications for European Society of Cardiology guidelines. Part I:
primary prevention.
Europace
2011;
13
(3): 308–328.
14. Liu T, Korantzopoulos P, Xu G, Shehata M, Li D, Wang Z,
et al
.
Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion
gene polymorphism and atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis.
Europace
2011;
13
: 346–354.
15. Shiroshita-Takeshita A, Schram G, Lavoie J, Nattel S. The effect of
simvastatin and antioxidant vitamins on atrial fibrillation-promotion by
atrial tachycardia remodeling in dogs.
Circulation
2004;
110
: 2313–2319.
16. Sakabe M, Shiroshita-Takeshita A, Maguy A,
et al
. Omega-3 polyun-
saturated fatty acids prevent atrial fibrillation associated with heart
failure but not atrial tachycardia remodeling.
Circulation
2007;
116
(19):
2101–2109.
17. Prystowsky EN, Padanilam BJ, Fogel RI. Treatment of atrial fibrilla-
tion.
J Am Med Assoc
2015;
341
(3): 278–288.
18. Andrade JG. MY APPROACH to atrial fibrillation: rate vs rhythm
control.
Trends Cardiovasc Med
2017;
27
(3): 226–227.
19. Pellman J, Sheikh F. Atrial fibrillation: mechanisms, therapeutics, and
future directions.
Compr Physiol
2015;
5
(2): ae649–665.
20. Piccini JP, Fauchier L. Rhythm control in atrial fibrillation.
Lancet
2016;
388
(10046): 829–840.
21. Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D,
et al
. 2016 ESC guidelines for the
management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with
EACTS.
Europace
2016;
18
(11): 1609–1678.
22. Law SWY, Lau WCY, Wong ICK,
et al
. Sex-based differences in
outcomes of oral anticoagulation in patients with atrial fibrillation.
J
Am Coll Cardiol
2018;
72
(3): 271–282.
23. Prystowsky EN, Padanilam BJ. Preserve the brain: primary goal in the
therapy of atrial fibrillation.
J Am Coll Cardiol
2013;
62
(6): 540–542.
24. Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E,
et al
. Comparison of the efficacy
and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with
atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials.
Lancet
2014;
383
(9921): 955–962.
25. Freedman B, Potpara TS, Lip GY. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrilla-
tion.
Lancet
2016;
388
(10046): 806–817.
26. Ben Freedman S, Gersh BJ, Lip GY. Misperceptions of aspirin efficacy
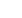
Management of AF
Prevention of
stroke
Rate control
Rhythm control
Prevention of AF
Pharmacological
therapy/Table 2
(≥ 1 of the following):
β
-blockers
ND-CCBs
digoxin
amiodarone
Pharmacological
therapy
(1 of the following):
warfarin
dabigatran
apixaban
edoxaban
rivaroxaban
Pharmacological
therapy/Table 1
(1 of the following):
flecainide
propafenone
sotalol
amiodarone
ibutilide
dronedarone
Upstream treatment
ACEIs
ARBs
statins
n-3 PUFA
Rrisk factors
valvular diseases
hypertension
heart failure
hyperthyroidism
diabetes
obesity
smoking
alcohol abuse
Non-pharmacological
therapy
DDC
RFCA
catheter ablation
maze procedure
Non-pharmacological
therapy
LAAC
Fig. 1.
Overview of management of AF.