CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 21, No 2, March/April 2010
116
AFRICA
Comparison of ivabradine plus
β
-blockers versus
β
-blocker therapy only
A study of patients with stable angina
and moderate left ventricular systolic
dysfunction has shown that the addition
of ivabradine to bisoprolol produced
additional anti-anginal and anti-ischae-
mic effects that were not achieved with
up-titration of bisoprolol.
1
This indicative
study is of importance to clinicians as
they are frequently faced with patients on
β
-blockers who are not able to tolerate the
full target dose, as defined from evidence-
based clinical trials.
Ivabradine is a novel agent that reduces
heart rate (HR) by selective and specific
inhibition of the I
f
current in sino-atri-
al cells, leading to prolongation of the
slow diastolic depolarisation phase of the
action potential.
Placebo-controlled studies in angi-
na patients have shown that ivabradine
improves exercise tolerance, lengthens
time to ischaemia, and has anti-anginal and
anti-ischaemic efficacy similar to that of
atenolol or amlodipine. The ASSOCIATE
study in stable angina patients receiv-
ing the beta-blocker atenolol has demon-
strated that ivabradine reduces HR and
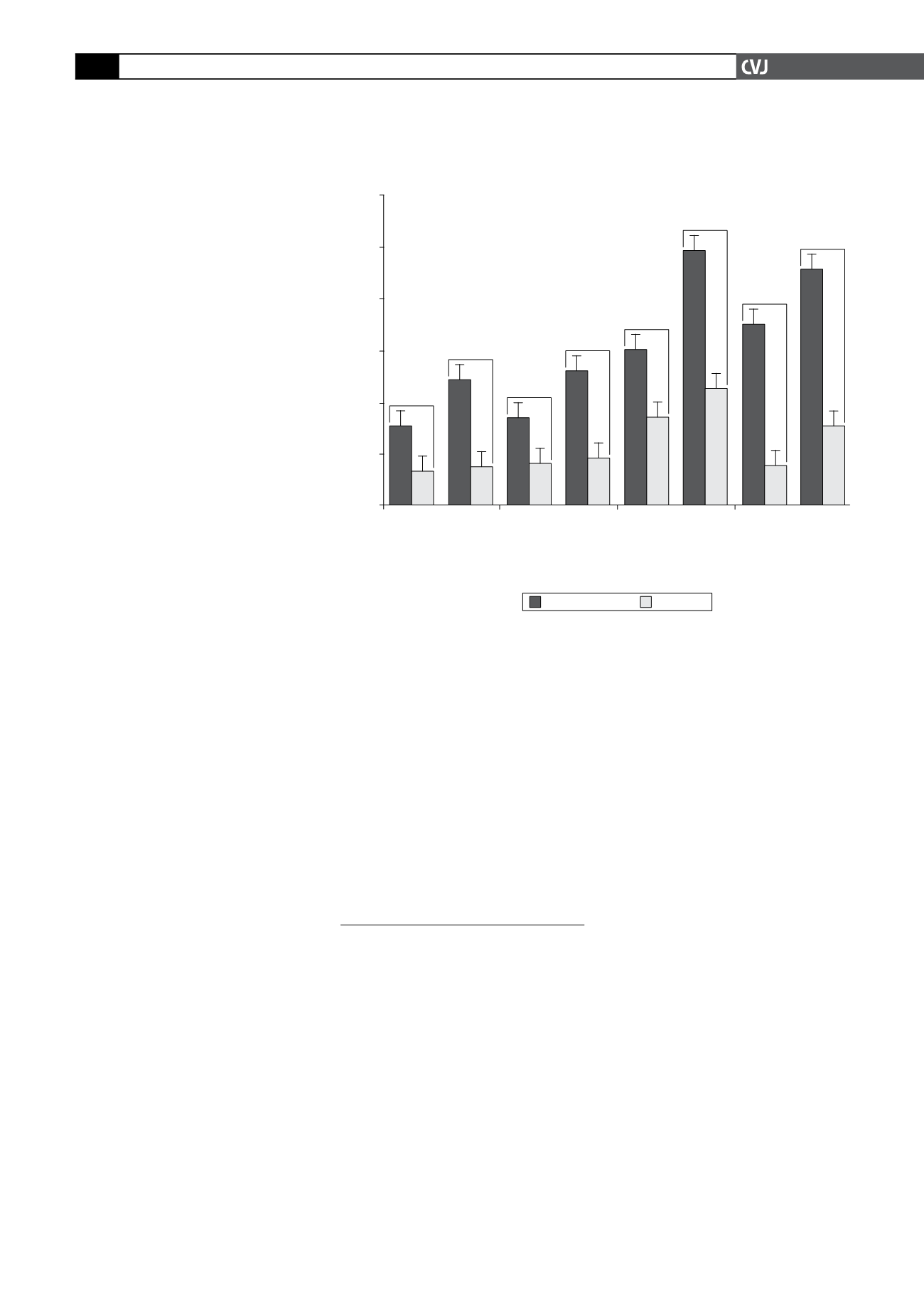
improves exercise capacity (Fig. 1).
This study, presented at the ACC
congress, included 29 patients with
chronic stable angina (class II) who had
had a myocardial infarction more than
three months before and had moderate
left ventricular systolic dysfunction on
stable therapy, including bisoprolol 5 mg
once daily. Therapy included aspirin, and
statins enalapril and furosemide in cases
with congestive heart failure.
Over a period of two months, resting
heart rate was reduced in both groups to
similar levels (60 bpm). However more
patients in the ivabradine-treated group
(7.5 mg twice daily) showed improve-
ments in angina and more patients moved
from angina class II to angina class I
than those who received the up-titrat-
ed bisoprolol dose (10 mg once daily).
Importantly, walking distance and exer-
cise tolerance improved in the ivabradine
group while no improvement occurred in
the bisoprolol-treated group.
J Aalbers, Special Assignments Editor
Ekaterina N,
1.
et al
. Anti-ischemic efficacy of
ivabradine in combination with bisoprolol
versus up-titration of bisoprolol. E-Abstract
1217-1322, ACC congress 2010.
Fig. 1. Change in exercise tolerance test criteria between baseline and M2
visit and between baseline and end of study (M4) in the full analysis set.
(Ammended from
Eur Heart J
9 Jan, 2009).
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
M2
M4
M2
M4
M2
M4
M2
M4
Change in ETT criteria (s)
p
=
0.017
Total exercise
duration
Time to
limiting angina
Time to
angina onset
Time to 1-mm
ST depression
Ivabradine
Placebo
p
<
0.001
p
=
0.018
p
<
0.001
p
=
0.005
p
<
0.001
p
<
0.001
p
<
0.001
ACCORD LIPID study results strengthen guideline approach of adding fenofibrate to therapy of
dyslipidaemic type 2 diabetic patients
Type 2 diabetic patients treated with
statins but still experiencing elevated
serum levels of triglycerides (2.3 mmol/l
or higher) and low HDL cholesterol
(0.8 mmol/l or lower), a pre-specified
subgroup, benefited from the addition of
fenofibrate to their treatment regimen.
Risk of cardiovascular events was reduced
by 31% in those patients, translating to a
need-to-treat 20 patients for five years to
prevent one cardiovascular event.
1
Prof Frank Sacks, Harvard School of
Public Health and Brigham and Women’s
Hospital, Boston, USA pointed out that
the ACCORD LIPID study has reinforced
the residual-risk hypothesis. ‘Interestingly,
those patients whose LDL cholesterol was
below 3 mmol/l, essentially at target,
showed a tendency to receive greater
benefit from the addition of fenofibrate.
Importantly, the atherogenic dyslipidae-
mia group was a pre-specified group in
this trial.’
‘Previous studies had raised possible
concerns about the importance of the
observed increase in serum creatinine
levels in patients on fenofibrate. The
ACCORD LIPID trial has shown convinc-
ingly that fenofibrate is safe, with no
significant difference in the incidence of


