CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 21, No 4, July/August 2010
AFRICA
213
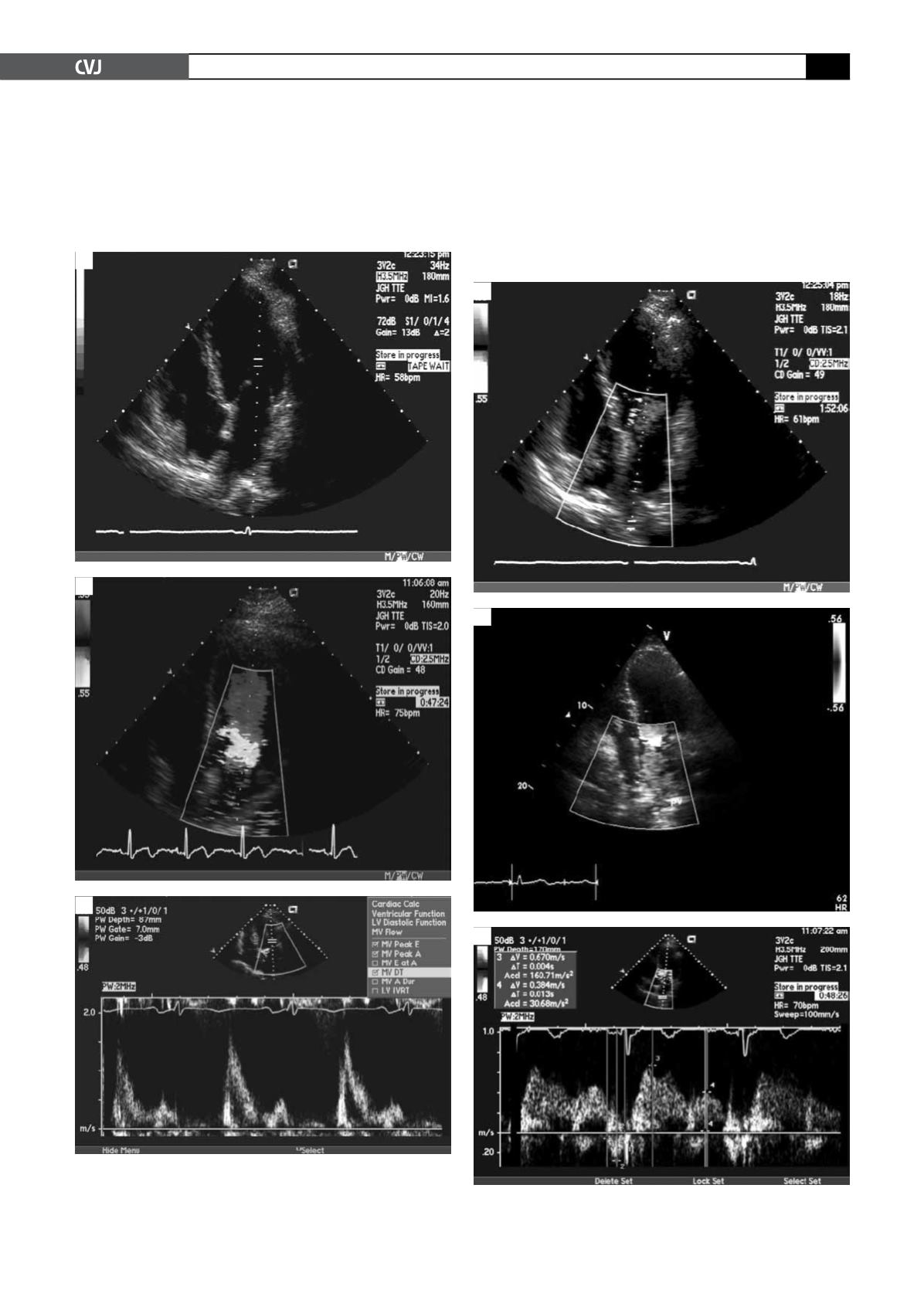
include assessment of the IVRT, peak E velocity, peak A veloc-
ity, E/A ratio, deceleration time (DT), and A duration, which
are obtained from the transmitral inflow velocities (Fig. 1).
Pulmonary vein (PV) flow velocities are then measured, which
include four components: two systolic velocities (PVs1 and
PVs2), diastolic velocity (PVd), and atrial flow reversal (PVa)
(Fig. 2).
7
Based on the echocardiographic parameters, diastolic dysfunc-
tion has been divided into three different grades of severity of
ventricular compliance, relaxation rate and filling pressures.
8
A
Fig. 1. Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography
with four-chamber view (A); colour Doppler (B); and
pulse-wave colour Doppler (C) showing normal mitral
inflow velocity pattern.
B
C
Fig. 2. Pulse-wave colour Doppler showing normal
pulmonary vein inflow velocity pattern.
A
B
C


