
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 25, No 6, November/December 2014
AFRICA
283
of 23.7% of the cohort.
Thirty-three patients in the cohort were male and 26 were
female. Age ranged from 16 to 82 years (mean: 51.9 years).
Thirty-four patients were of Indian descent, while 17 were
black and the remaining eight were white patients. The majority
(79.4%) of Indian patients had coronary surgery alone or in
combination with valve surgery. Fifty-four patients had elective
surgery and five had surgery on an emergency basis.
RGW ranged from the institutional norm of two days up to a
maximum of 24 days. The mean RGW duration was 6.6 days (
n
=
54). Six patients died during the index admission period, three
of whom had emergency surgery.
Twenty-four patients were diabetic and 35 had hypertension.
Twenty patients had both diabetes and hypertension.
Thirty-seven patients used
β
-blockers and 40 were on statin
therapy on a chronic basis. Thirty-two patients in the cohort
used a combination of statins and
β
-blockers prior to surgery.
β
-blockers were withdrawn in only three patients in the immediate
pre-operative period.
Miscellaneous risk factors were BMI, previous cardiac
surgery and smoking. The BMI ranged from 17 to 42 kg/m
2
,with
a mean of 26.4 kg/m
2
(
n
=
54). Three patients in the cohort had
prior cardiac surgery. Twelve patients were still smoking in the
immediate pre-operative period. The echocardiographic results
are reflected in Table 2.
An analysis of the subgroup of patients (
n
=
33) who
underwent coronary artery surgery alone or in combination
with valve surgery is as follows: mean age was 62.2 years, there
were 26 male and seven female, mean BMI (
n
=
31) was 26.9
kg/m
2
, 33 patients were on statins and 31 on
β
-blockers. Mean
echocardiographic parameters (
n
=
27): LVD
=
56.3 mm, LA
=
45.9 mm, EF
=
51.6%.
The coronary patients were a mean of 10.3 years older than
the whole cohort and 78.8% were male. The other parameters
closely resembled that of the entire cohort.
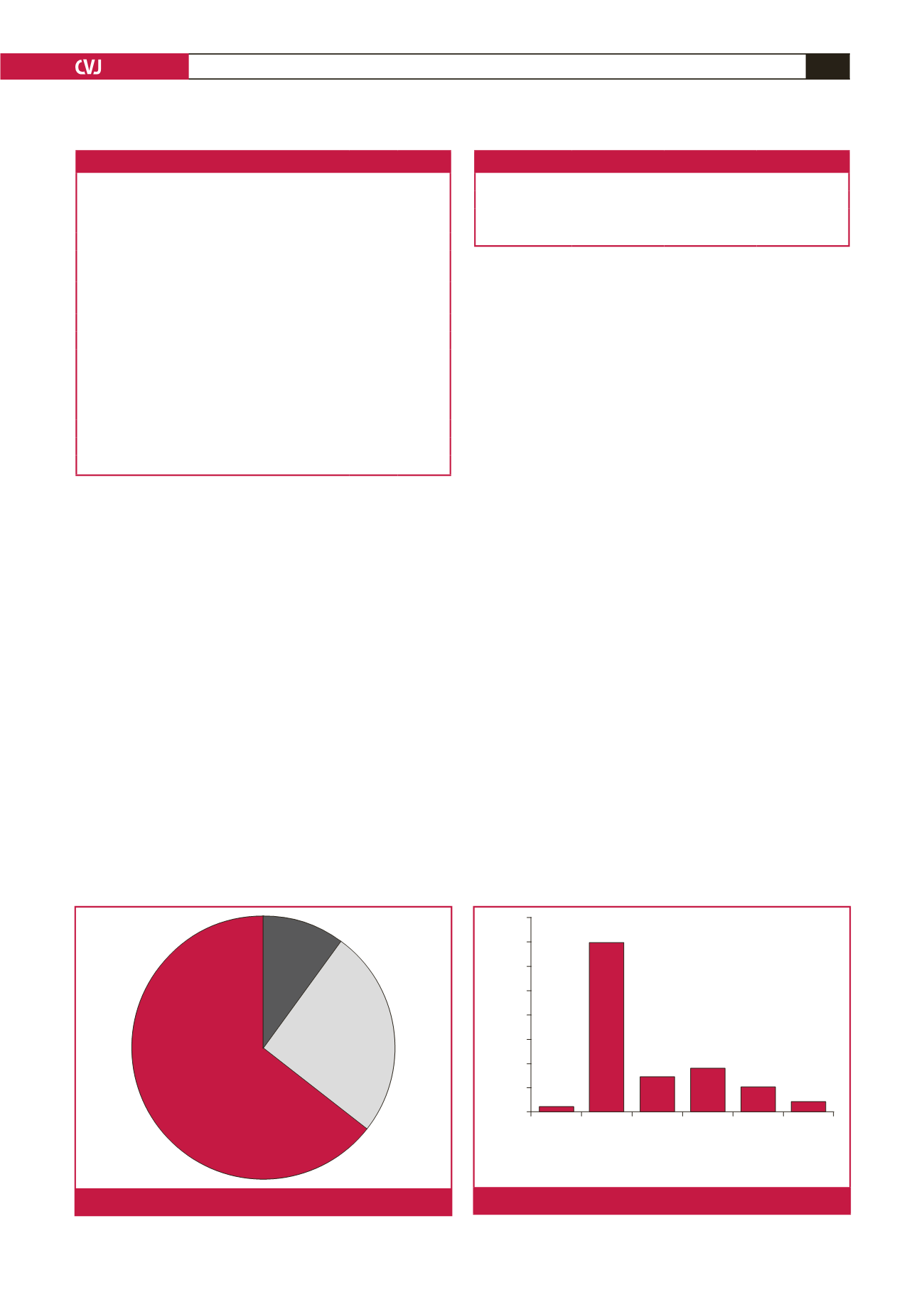
The majority of patients (64.4%) developed AF from day
three onwards. The incidence of AF in the individual post-
operative time periods is reflected in Fig. 1. The various
individual and combination treatment modalities used to treat
AF after cardiac surgery is shown in Fig. 2.
Follow-up data was available for 40 patients at the time
of data presentation. Follow-up duration ranged from 1.5 to
38 months after surgery, with a mean of 16.1 months. At the
follow-up visit, all 40 patients were in sinus rhythm. Twenty-two
patients were at that stage noted to be using
β
-blocker therapy
for underlying chronic cardiac conditions.
Discussion
De novo
atrial fibrillation post cardiac surgery is a post-
operative complication associated with significant morbidity
and mortality.
3
Hakala
et al.
demonstrated, in a retrospective
study of 3 676 Finnish patients, an increase in peri-operative
cardiovascular accidents (CVA), confusion, ICU LOS and ICU
re-admission rates.
4
Almassi
et al.
showed significantly higher
Table 1. Incidence of AF per surgical procedure
Type of surgery
Number
develop-
ing AF
Total
number
of
surgeries
Percent-
age of
cohort
(%)
Coronary surgery
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery
(CABG)
13
270 45.8
Off-pump coronary bypass surgery
(OPCAB)
14
251
Valve surgery
Mitral valve replacement (MVR)
7
251 44.1
Aortic valve replacement (AVR)
11
85
Double valve replacement (DVR)
8
113
Combination coronary and valve surgery
CABG + MVR
0
12 10.2
CABG + AVR
6
12
CABG + DVR
0
3
Total
59
997
Table 2. Echocardiographic parameters
Parameter
Patient number
Range
Mean
LVD (mm)
50
42–75
56.1
LA (mm)
50
33–90
51
EF (%)
52
25–66
52.8
<
24 hours
(
n
=
6)
>
48 hours
(
n
=
38)
24–48 hours
(
n
=
15)
Fig. 1.
Timing of AF presentation.
Spont-
aneous
resolution
Cardio-
version
and amio-
darone
Amio-
darone
only
Cardio-
version
only
Cardio-
version and
other anti-
arrythmic
drug
Other anti-
arrythmic
drug only
Modality
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Number of patients (
n
= 59)
1
35
7
9
5
2
Fig. 2.
Modalities used to treat AF.



















