CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 3, May/June 2018
136
AFRICA
dated CMR sequences as a comparator, Mutnuru
et al.
found
echocardiography to be a more reliable tool for diagnosis of
RHD.
15
Our group has recently reported on the role of CMR in
unravelling the pathophysiology of heart block and myocarditis
in a patient subsequently confirmed to have acute rheumatic
fever (Fig. 3).
16
Edwards and colleagues reported on a CMR cross-sectional
study of 35 patients (mean age 60 years) with asymptomatic
moderate and severe primary degenerative mitral regurgitation
but impaired VO
2 max
and found dilated left ventricular (LV)
volumes, preserved LV systolic function, evidence of impaired
longitudinal and circumferential strain, LGE in 30% of subjects,
and evidence of diffuse myocardial fibrosis from elevated ECV.
17
The authors concluded that patients with moderate to severe
mitral regurgitation have increased myocardial fibrosis, impaired
myocardial strain and reduced exercise capacity.
In this issue of the journal (page 150), Meel and colleagues
report, similarly, on a study of 22 patients with chronic rheumatic
mitral regurgitation and 14 age- and gender-matched controls
characterised by echocardiography, LGE-CMR (for assessment
of focal fibrosis) and serum biomarkers of collagen turnover.
18
The key findings were that 18% of the patients had evidence
of LGE, while none was observed in the controls. As expected,
on both CMR and echocardiography, patients with rheumatic
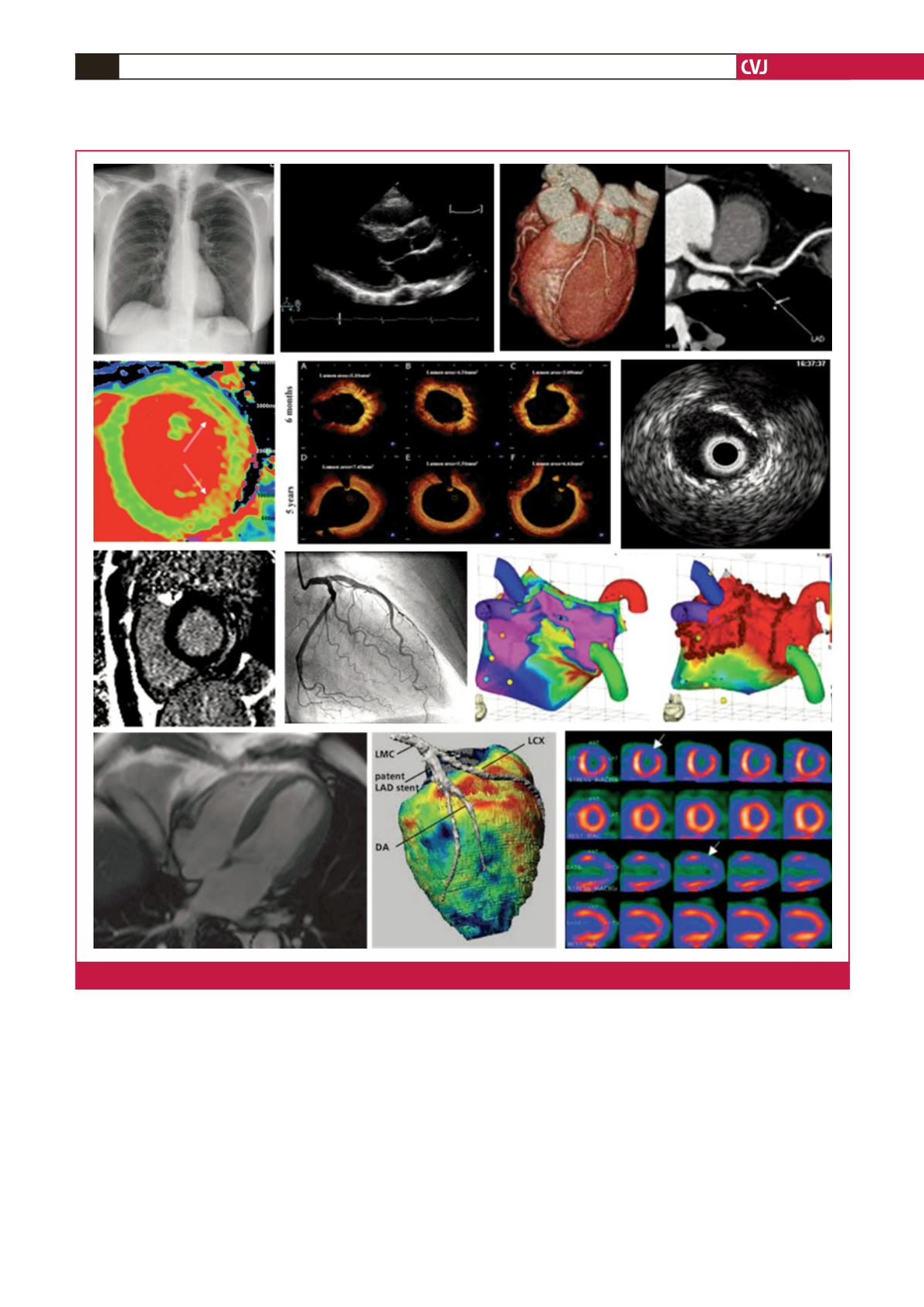
Fig. 1.
Different modalities of cardiovascular imaging.