CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 31, No 2, March/April 2020
e2
AFRICA
prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day) treatment was started from the
second day in hospital, with a possible diagnosis of eosinophilic
granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) or hyper-eosinophilic
syndrome. After intravenous steroid treatment, the patient’s
clinical conditions, including body temperature, skin rash and
numbness of the feet, improved rapidly.
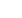
On the fourth day in hospital, the patient had an operation for
resection of the mass-like lesions in the left ventricle. Pathological
gross findings showed fragments of pinkish-gray soft tissue
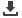
measuring 3.0 × 1.0 and 2.5 × 1.0 cm (Fig. 2). Microscopic
findings revealed non-infective vegetations that comprised a
thrombus, granulation tissue, eosinophils, lymphoplasmic cells,
neutrophils and histiocyte infiltrations (Fig. 3).
Based on these pathological findings, namely hyper-
eosinophilia, history of asthma, chronic sinusitis and
polyneuropathy, a diagnosis of EGPA was made. Seven days
after starting intravenous steroid treatment, all the laboratory
results, including eosinophil count, C-reactive protein and
cardiac markers, were normalised. The patient was discharged
and is on oral methyl-prednisolone treatment at the out-patient
clinic.
Discussion
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis or EGPA,
previously named Churg-Strauss syndrome, which was first
described in 1951, is a rare form of systemic, necrotising
small-vessel vasculitis with accompanying bronchial asthma,
eosinophilia and eosinophilic tissue infiltration of various tissues
with granuloma formation.
1,2
The pathogenesis is not well
known, however it is considered a T-helper type 2 (Th2)-
mediated disease.
2-4
The immune response may be triggered by
genetic or environmental factors such as allergens, infections,
drugs or nutrition.
2,5
Eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes
and various cytokines may also play a role in the process.
2-4
The most commonly involved organ is the lung, followed by
the skin and nervous system; however it can affect any organ
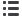
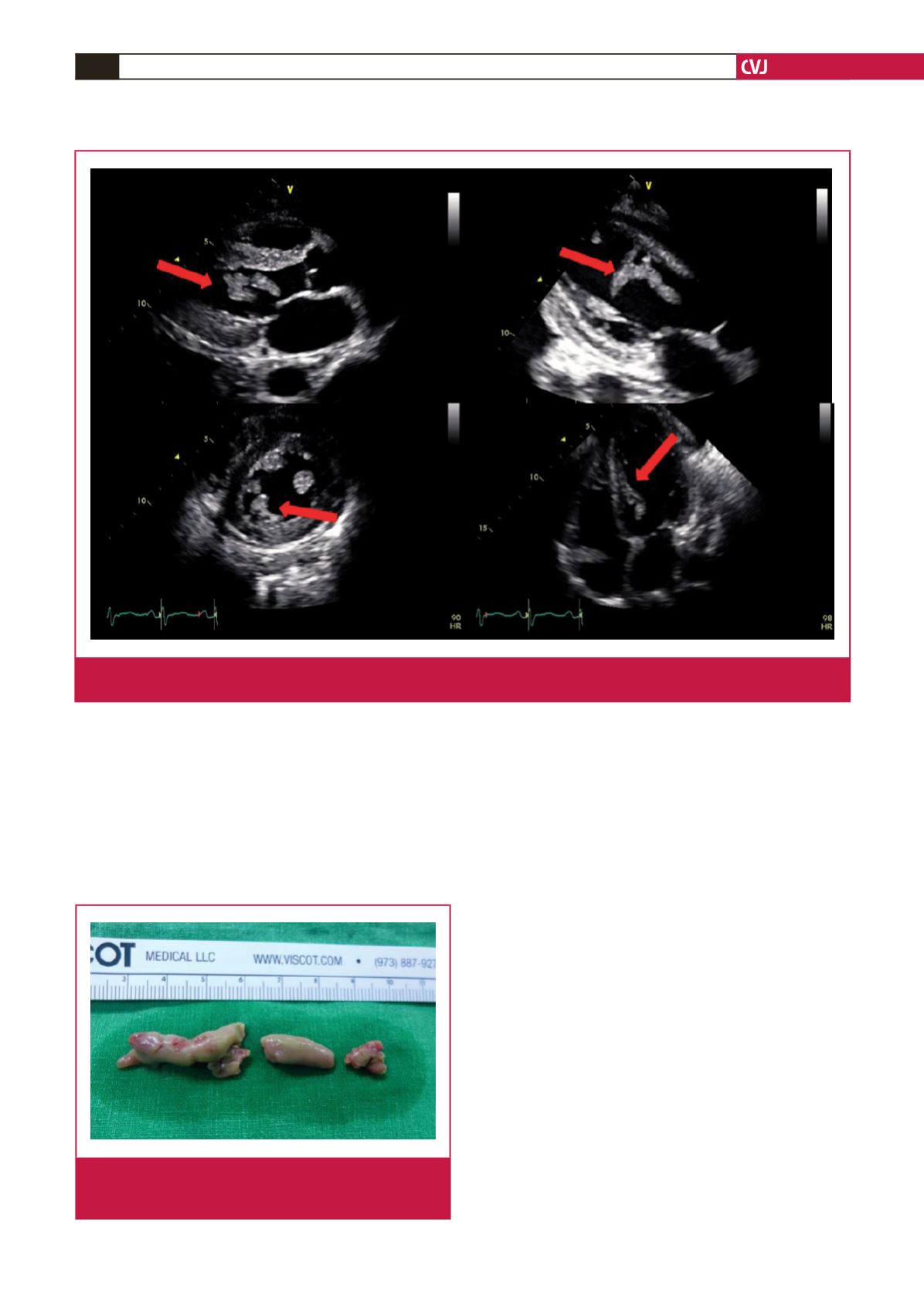
Fig. 1.
Transthoracic echocardiography showing oscillating mass-like lesions at the mid anteroseptal wall of the left ventricle
(arrows). The heart chamber size and systolic function were normal.
Fig. 2.
Pathological gross findings showing fragments of
pinkish-gray soft tissue measuring 3.0 × 1.0 and 2.5
× 1.0 cm.