CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 27, No 6, November/December 2016
AFRICA
e1
A circumflex coronary artery-to-right atrial fistula in a
10-month-old child
Emrah
Ş
i
ş
li, Mehmet Fatih Ayık, Muhammet Akyüz, Münevver Dereli, Yüksel Atay
Abstract
A coronary fistula (CF) is a rare congenital cardiac anomaly
in which there is a connection between the coronary artery
and a cardiac chamber or a great vessel. In the paediatric
population, a CF is usually asymptomatic. While the circum-
flex coronary artery (Cx) is the least common source of a CF,
the right heart chambers are the most common location of
drainage. Herein, we present a symptomatic 10-month-old
boy with an atrial septal defect (ASD) in whom we inciden-
tally detected a CF, which stemmed from the Cx and drained
to the right atrium. Because the patient was symptomatic and
his small size was not appropriate for percutaneous closure of
the ASD, surgical closure of the ASD and CF was performed.
Keywords:
heart defects, congenital, atrial septal defect, vascular
fistula, cardiac surgical procedures
Submitted 25/7/15, accepted 3/4/16
Cardiovasc J Afr
2016; 27: e1–e3
www.cvja.co.zaDOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2016-044
A coronary fistula (CF) is a rare congenital cardiac anomaly
in which there is a connection between one or more coronary
arteries and a cardiac chamber or great vessel.
1-3
Herein, we
present a paediatric case with a CF between the circumflex
coronary artery (Cx) and the right atrium (RA).
Case report
In the follow up of a 10-month-old boy (weight 8 kg and height
70 cm) with a prenatal diagnosis of atrial septal defect (ASD),
apart from the fixed splitting of the second heart sound, a
prominent increase in the severity of the mid-systolic murmur
at the pulmonary auscultation area was incidentally detected.
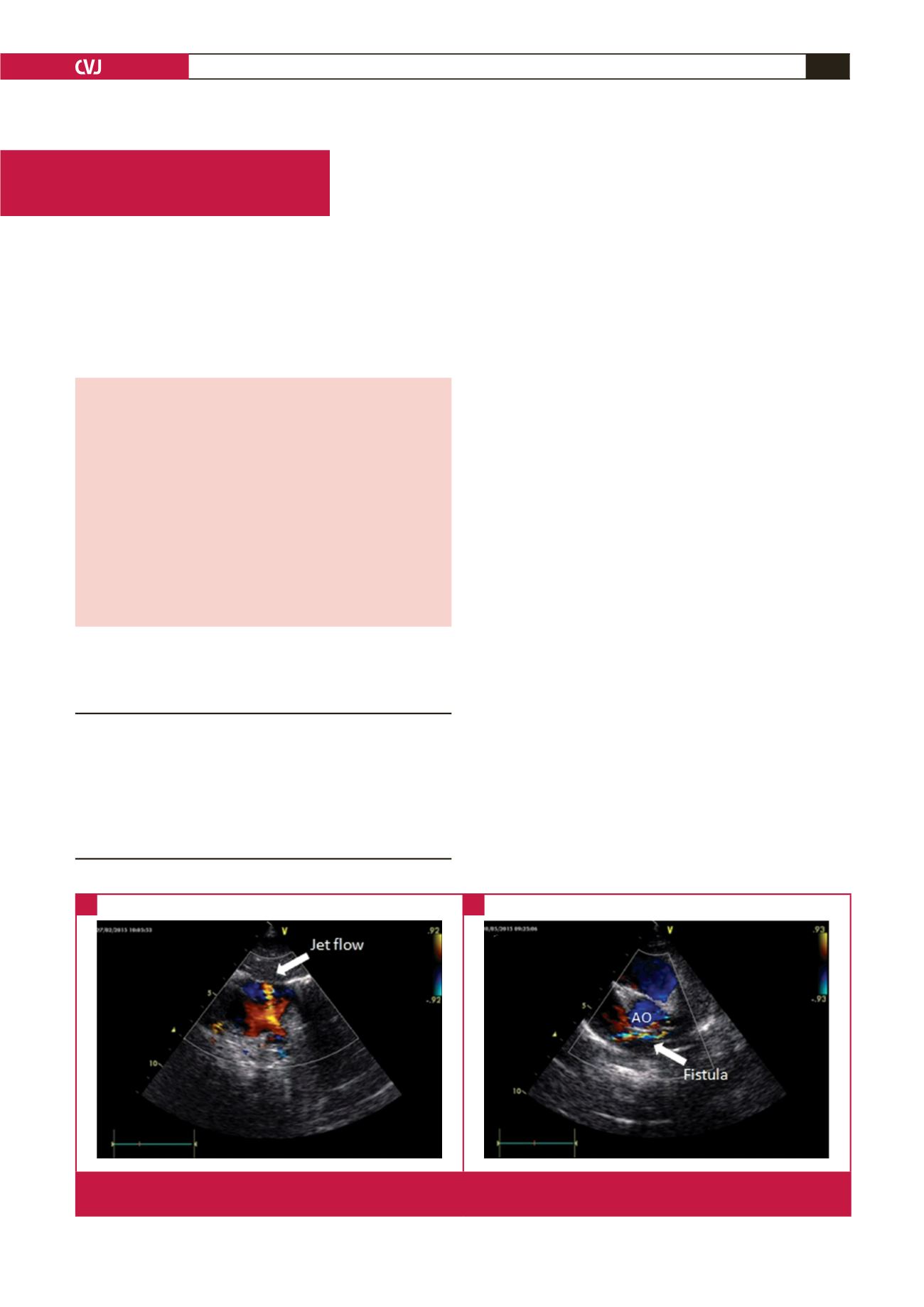
On echocardiography, a new continuous jet flow into the RA
indicative of a CF was detected.
His history showed he had had recurrent upper respiratory
infection and failure to thrive so that both the weight and height
of the patient were within the third and 10th percentiles. There
was no evidence of myocardial ischaemia on electrocardiography.
On echocardiography, the ASD (5 mm) was secundum type. The
opening of the jet was sited adjacent to the superior cavo-atrial
Section of Paediatric Cardiovascular Surgery, Department
of Cardiovascular Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Ege
University, Izmir, Turkey
Emrah
Ş
i
ş
li, MD,
dresisli@gmail.comMehmet Fatih Ayık, MD
Muhammet Akyüz, MD
Münevver Dereli, MD
Yüksel Atay, MD
Case Report
Fig. 1.
Pre-operative subcostal (A) and modified parasternal short-axis (B) echocardiographic views demonstrating the jet flow and
trajectory of the coronary fistula.
A
B