CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 25, No 2, March/April 2014
AFRICA
45
gamma camera and processed independently by three operators.
The second component examined the values and reproducibility
of estimates of LVEF calculated with the same software packages
using matched pairs of raw data acquired on both gamma
cameras (GE and Siemens) processed by one operator.
Methods
Since October 2007 the raw data of all GBP studies done in the
department have been stored in a Hermes electronic archive in
the original format. These studies, acquired on the GE camera,
were therefore available for reprocessing. All the patients were
referred to our department as part of their diagnostic work-up.
The majority of studies were done for patients receiving
cardiotoxic chemotherapy. A minority (
<
5%) of the studies were
done for patients who had heart transplants.
For the first component of the investigation, 200 studies
acquired on the GE camera were selected using random-number
tables to identify folder numbers of patient studies archived
between 1 October 2007 and 15 July 2009. There were 1 952
studies performed on 1 473 patients during this period.
For the second component, 200 patients were studied. Two sets
of data were acquired for each patient, the second immediately
after the first. One of the sets was acquired on the GE and
the other on the Siemens camera, the order depended on the
availability of the cameras. This produced 200 matched pairs of
data (Fig. 1).
Ethics approval for the study was obtained from the Research
Ethics Committee, Health Sciences Faculty, University of Cape
Town.
Imaging protocol
An
in-vivo
method for labelling the red blood cells was used.
One red blood cell labelling vial (Nuclear Technology Products,
Pelindaba, SA) containing 20 mg sodium pyrophosphate and
4 mg tin dichloride was reconstituted with 5 ml NaCl and 3.5
ml was injected intravenously, followed 20 minutes later by an
injection of 800–900 MBq of Tc-99m sodium pertechnetate
eluted from a NovaTec P generator manufactured by NTP
Radioisotopes (Pty) Ltd of Pelindaba. The dose administered was
in accordance with the Society of Nuclear Medicine guidelines.
8
For all patients, anterior, left lateral and left anterior oblique
images were recorded in a 64 × 64 matrix with the patient supine.
For the left anterior oblique image, the angle of the detector
head relative to the patient was adjusted to give the best septal
delineation. The ECG–RR interval was divided into 24 frames,
the beat acceptance window set at 30% and the energy window
at 15%.
A low-energy general purpose (LEGP) collimator
manufactured by GE and zoom of 1.5 were used with the
GE Starcam 400 AC single-head camera and acquisition was
stopped when 8 000 kilocounts had been acquired. The GE
camera was interfaced to an Alfanuclear acquisition system
(IM512P Data and Image Processor version 2.0). A LEHR
collimator manufactured by Siemens and a zoom of 2 were
used on the Siemens Signature Series e.cam dual-head camera
and acquisition was stopped when 8 000 kilocounts had been
acquired. The Siemens camera was interfaced to a Siemens
acquisition system (Version A4OA, Siemens Medical Solutions,
Chicago USA).
Processing
The studies were processed using the two methods available;
one provided by Siemens (Gated Blood Pool Activity version
7.0.7.2, Siemens Medical Solutions, Chicago, USA) and one
by Hermes (Functional Gated Analysis, FUGA version V4.7,
Hermes Medical Solutions, Stockholm, Sweden ).
Semi-automated programs were used because the automated
programs of both vendors placed the background region of
interest (ROI) in the bottom left-hand corner of the field of view.
This results in a background ROI that is not periventricular. It
overlies the spleen, aorta or other soft tissue structures.
The default settings of the Siemens method was: a zoom of
2 was used; a Butterworth filter with a cut-off of 0.40 of the
Nyquist frequency and order 5 was applied; the background ROI
was placed on the end-systolic frame; X and Y shifts were 2 and
the offset 4 pixels; height and width were 50%.
The default settings of the Hermes method was: no zoom
was used; a Butterworth filter with a cut-off of 5 as defined
by Hermes and order 70 was applied; the background ROI was
placed on the end-diastolic frame.
In the first component of the study, the data acquired on the
GE camera were processed three times by three independent
operators. These were the senior author (operator 1), and two
experienced radiographers (operators 2 and 3). The operators
adjusted the position, shape and size of the background ROI.
While processing, the operators recorded the number of
beats rejected, whether the labelling of the red blood cells was
good, satisfactory or poor (this was done using visual analysis),
whether the quality of the tracking of the left ventricle was good,
satisfactory or poor (this was done using visual analysis), where
the program placed the background ROI, where the operator
placed the background ROI, the size of the background ROI, as
well as the mean counts within it.
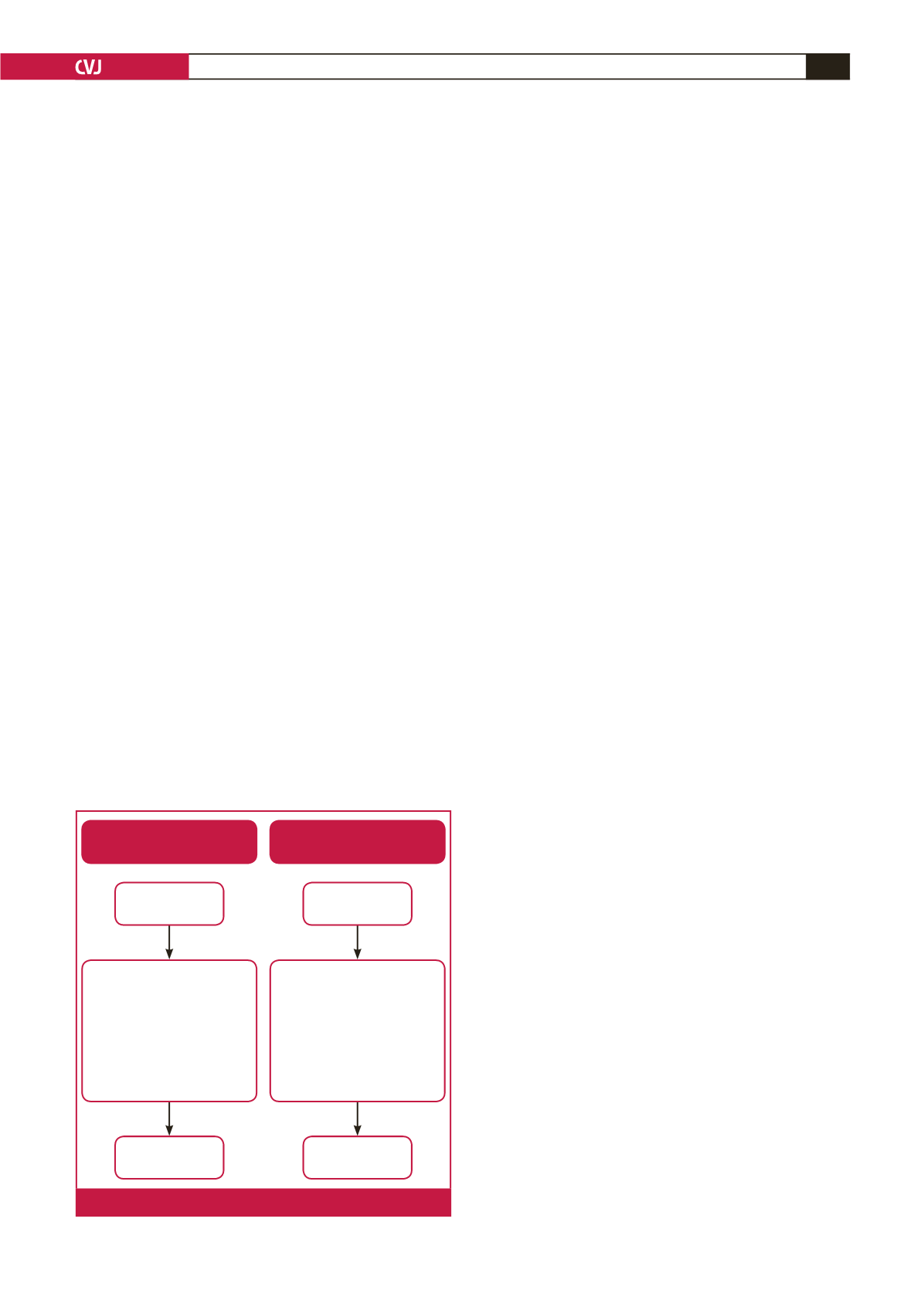
FIRST COMPONENT
SECOND COMPONENT
Two studies were from the
same patient, the second
study was excluded
One study was not
captured, one study was
a duplicate and seven
patients had two studies
(baseline and follow up).
The duplicate study and
the seven follow-up studies
were excluded
200 studies
199 studies
200 studies
191 studies
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of studies excluded.


