
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 27, No 5, September/October 2016
AFRICA
301
Categorical variables are presented by frequency counts, and
differences between the groups with regard to categorised data
were compared with the chi-squared test. All calculations were
performed using a standard statistical package (SPSS 15.0, SPSS
Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). All
p
-values
<
0.05 were interpreted as
statistically significant.
Results
The groups were homogenous for baseline characteristics in the
pre-operative period (
p
>
0.05 for all comparisons) (Table 1).
Details of the surgery performed and the early postoperative
period is shown in Table 2.
For the whole group of patients, mean number of distal
anastomoses was 2.45
±
0.81, cardiopulmonary bypass time was
101.77
±
28.71 min, and aortic cross-clamping time was 54.93
±
16.19 min. The mean extubation time and length of stay in the
intensive care unit were 7.98
±
5.52 hours and 2.15
±
0.56 days,
respectively.
Off-pump CABG was performed in one patient in the
group with no previous MI, in four patients in the anterior MI
group and in two patients in the posterior/inferior MI group.
Two patients in the anterior MI group and one patient in the
posterior/inferior MI group underwent re-exploration due to
excessive mediastinal bleeding in the early postoperative period.
The left internal thoracic artery (ITA) was anastomosed to
the LAD in 57 patients and a saphenous vein graft was used for
the remaining patients. The right ITA was used as a graft in four
patients in the group with no previous MI, and in two patients in
the posterior/inferior MI group. The radial artery was used as a
graft in two patients in the posterior/inferior group.
Positive inotropic support was used in 21 patients, and
intra-aortic balloon pump was required in four in the early
postoperative period. There were two in-hospital deaths. The
patient in the anterior MI group died due to acute renal failure.
The patient in the posterior/inferior MI group died due to low
cardiac output and multiple organ failure.
There were no statistically significant differences between
the groups in terms of parameters of the intra-operative and
early postoperative periods (
p
>
0.05 for mean number of
distal anastomosis, cardiopulmonary bypass time, aortic cross-
clamping time, extubation time, length of stay in intensive care
unit, use of positive inotropic support, insertion of intra-aortic
balloon pump, incidence of acute renal failure and mortality).
Levels of adrenomedullin, IL-6 and TNF-
α
in the plasma
are shown in Fig. 1A. Levels of IL-1
β
and angiotensin-II in the
plasma are shown in Fig. 1B. The plasma level of adrenomedullin
in the anterior MI group (0.42
±
0.15 ng/ml) was significantly
higher than that in the group with no previous MI (0.30
±
0.07
ng/ml) and the posterior/inferior MI group (0.33
±
0.05 ng/ml) (
p
=
0.002 and
p
=
0.043, respectively) (Fig. 1A).
There were no statistically significant difference between the
plasma levels of IL-6 in the group with no previous MI, the
anterior MI and posterior/inferior MI groups (3.14
±
2.84, 3.62
±
2.93 and 3.53
±
2.91 pg/ml,
p
=
0.414) (Fig. 1A). There were
no statistically significant difference between the plasma levels of
TNF-
α
in the group with no previous MI, the anterior MI and
the posterior/inferior MI groups (4.48
±
2.93, 6.63
±
4.41 and
4.38
±
1.78 pg/ml,
p
=
0.322) (Fig. 1A).
There were no statistically significant differences between
the plasma levels of IL-1
β
in the group with no previous MI,
the anterior MI and the posterior/inferior MI groups (4.15
±
2.64, 4.62
±
3.83 and 4.46
±
2.86 pg/ml,
p
=
0.977) (Fig. 1B).
The plasma level of angiotensin-II in the anterior MI group was
significantly higher than that in the group with no previous MI
(91.30
±
26.40 vs 60.80
±
27.94 pmol/l,
p
=
0.002) (Fig. 1B).
Levels of adrenomedullin and IL-1
β
in the pericardial fluid
are shown in Fig. 2A. Levels of IL-6, TNF-
α
and angiotensin-
II in the pericardial fluid are shown in Fig. 2B. The level of
adrenomedullin in the pericardial fluid in the anterior MI group
was significantly higher than that in the group with no previous
MI (0.52
±
0.14 vs 0.42
±
0.08 ng/ml,
p
=
0.028) (Fig. 2A).
The level of IL-1
β
in the pericardial fluid in the anterior MI
group (10.54
±
5.17 pg/ml) was significantly higher than that in
both the group with no previous MI (5.96
±
3.68 pg/ml) and the
posterior/inferior MI group (6.08
±
4.10 pg/ml) (
p
=
0.008 and
p
=
0.005, respectively) (Fig. 2A).
The level of IL-6 in the pericardial fluid in the anterior MI
group (193.51
±
62.29 pg/ml) was significantly higher than that in
both the group with no previous MI (105.25
±
69.71 pg/ml) and
the posterior/inferior MI group (139.91
±
54.18 pg/ml) (
p
=
0.000
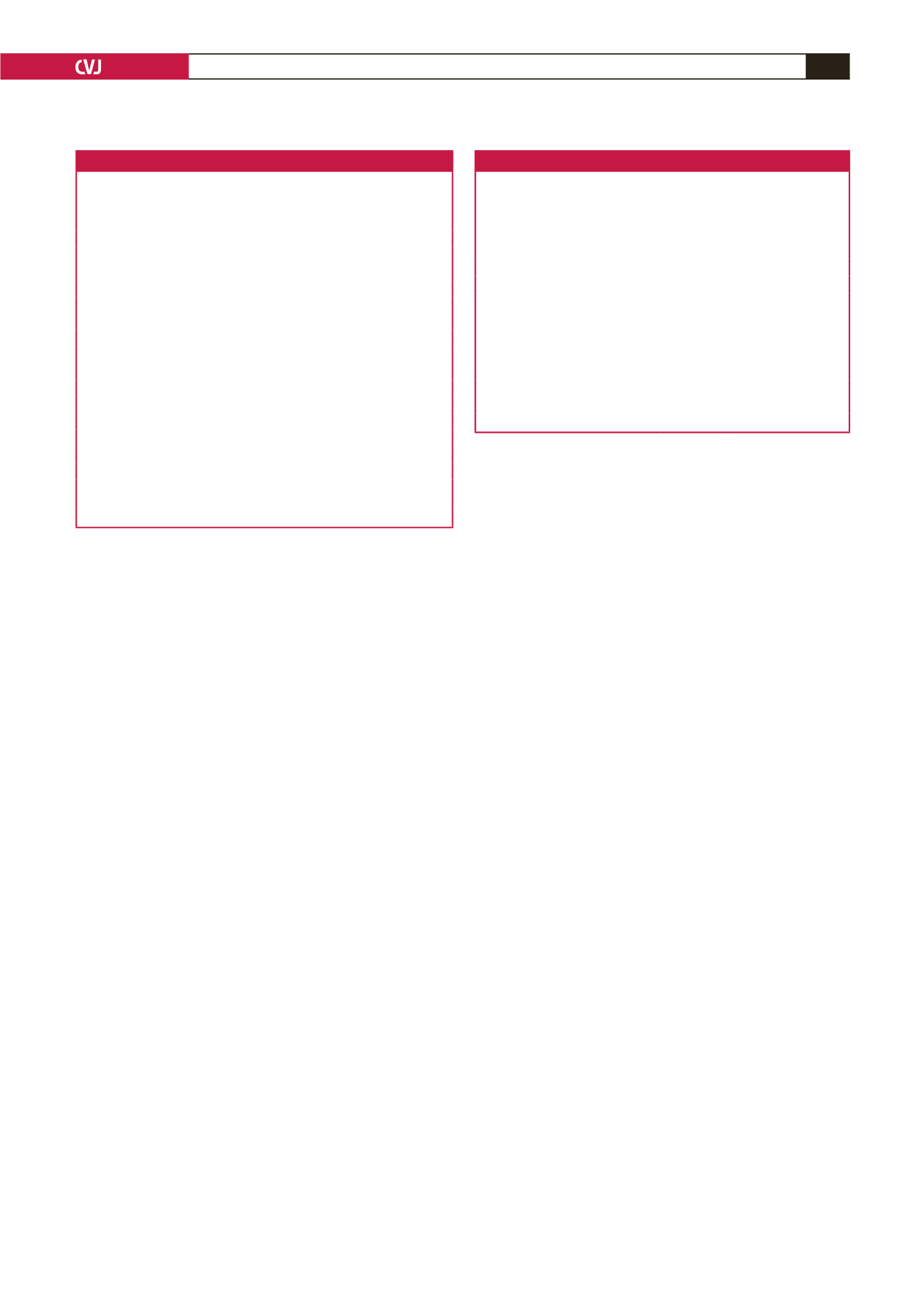
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the patients
Parameters
No previous
MI
(
n
=
20)
Anterior MI
(
n
=
20)
Posterior/
inferior MI
(
n
=
20)
p-
value
Male/female
18/2
18/2
18/2
1.00
Age (years)
57.65
±
8.15 63.26
±
9.90 61.90
±
9.60 0.097
Body mass index (kg/m
2
)
26.03
±
8.31 27.10
±
7.86 26.81
±
9.02 0.842
Drugs
Beta-blockers
8
9
4
0.054
ACE inhibitors
8
7
4
0.061
Nitrates
20
20
20
1.00
Calcium channel blockers
5
2
3
0.062
Hypertension
11
11
5
0.089
Hyperlipidaemia
13
9
12
0.414
Smoking
13
12
17
0.189
Diabetes mellitus
4
7
3
0.298
COPD
2
2
3
0.851
Peripheral artery disease
1
1
1
1.00
Cerebrovascular event
0
0
0
1.00
Coronary artery stenting
1
0
1
0.596
Left main coronary artery
disease
3
1
2
0.574
COPD
=
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 2. Details of surgery and the early postoperative period
No previous
MI
(
n
=
20)
Anterior MI
(
n
=
20)
Posterior/
inferior MI
(
n
=
20)
p
-value
Number of distal
anastomoses
2.62
±
0.80 2.54
±
0.82 2.66
±
0.48 0.136
CPB time (min)
99.25
±
25.08 94.81
±
25.47 111.44
±
33.59 0.254
ACC time (min)
55.93
±
16.57 51.81
±
15.08 57.11
±
16.57 0.740
Extubation time (h)
6.88
±
1.48 9.11
±
8.29 8.02
±
4.79 0.642
Stay in intensive care
unit (days)
2.00
±
0.00 2.11
±
0.32 2.35
±
0.87 0.190
Positive inotropic
drugs
3
9
9
0.072
Intra-aortic balloon
pump
1
2
1
0.765
Acute renal failure
–
1
–
0.437
Exitus
–
1
1
0.382
CPB
=
cardiopulmonary bypass, ACC
=
aortic cross-clamping time.

















