
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 1, January/February 2017
AFRICA
25
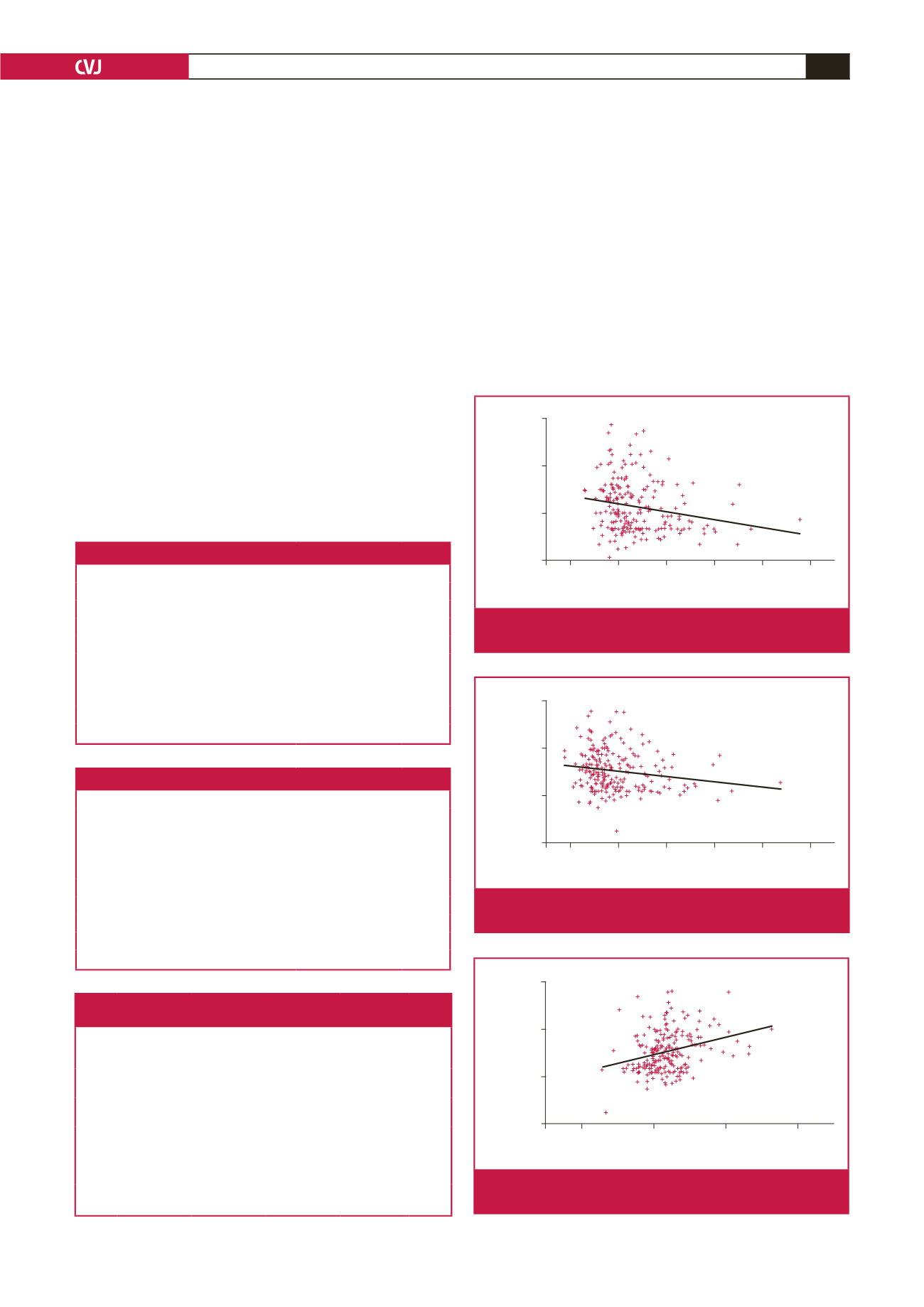
of risk factors for pre-eclampsia, as seen in Table 3. On multiple
regression analysis, there was a significant inverse correlation
between diastolic blood pressure and RHI (
r
=
–0.14,
p
<
0.05)
and mean arterial blood pressure and RHI (coeff
=
–4.95053, SE
=
2.29277;
p
<
0.05) as shown in Figs 1 and 2. The high diastolic
blood pressure and mean arterial pressure were associated with
lower RHI. Augmentation index was also positively associated
with mean arterial pressure, as shown in Fig. 3.
BPWA was positively related to maternal age, BMI, parity,
pulse pressure, weight and systolic blood pressure on univariate
correlation, as seen in Table 4. On multiple regression analysis,
systolic blood pressure was the only variable independently
correlated with BPWA (
r
=
0.22,
p
=
0.0166), as seen in Fig.
4. Higher systolic blood pressure was therefore significantly
associated with arterial stiffness.
Differences in the study variables as per HIV status
The participants were divided into four groups, namely, (1)
HIV-negative normotensive (A) (
n
=
83); (2) HIV-positive
normotensive (B): (
n
=
27); (3) HIV-positive pre-eclamptic (C):
(
n
=
38); and (4) HIV-negative pre-eclamptic (D) (
n
=
67) (Table
5). The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to analyse the differences
between the four groups and Dunn’s multiple comparison post-
test was used to check significance between the individual groups.
For mean arterial pressure, significant differences were
evident between HIV-positive normotensive and HIV-positive
pre-eclamptic pregnant mothers (
p
<
0.001), HIV-positive
normotensive and HIV-negative pre-eclamptic pregnant mothers
(
p
<
0.001), HIV-negative normotensive and HIV-positive
pre-eclamptic pregnant women (
p
<
0.0001), and between
HIV-negative normotensive and the HIV-positive pre-eclamptic
Table 3. Relationship between RHI and maternal risk factors
Factor
Coefficient (
r
)
p
-value
Maternal age
–0.095
0.171
Baseline heart rate
–0.022
0.756
BMI
–0.122
0.078
Diastolic blood pressure
–0.210
0.0022
Parity
–0.138
0.045
Mean arterial pressure
–0.187
0.0066
Pulse pressure
0.051
0.461
Weight
–0.121
0.081
Systolic blood pressure
–0.124
0.072
RHI
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
4.8
Diastolic BP (mmHg)
130
100
70
40
Fig. 1.
Relationship between diastolic blood pressure and RHI
(
p
<
0.05).
RHI
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
4.8
Mean arterial pressure (mmHg)
150
110
70
30
Fig. 2.
Relationship between mean arterial pressure and RHI
(
p
=
0.0328).
Augmentation index @ 75 (%)
–50
0
50
100
Mean arterial pressure (mmHg)
150
110
70
30
Fig. 3.
Relationship between mean arterial pressure and
augmentation index @ 75 bpm (
p
=
0.0372).
Table 4. Relationship of BPWA and maternal risk factors
Factor
Coefficient (
r
)
p
-value
Maternal age
0.141
0.0416
Baseline heart rate
–0.137
0.0475
BMI
0.238
0.0005
Diastolic blood pressure
0.079
0.2556
Parity
0.192
0.0052
Mean arterial pressure
0.123
0.076
Pulse pressure
0.169
0.014
Weight
0.209
0.0024
Systolic blood pressure
0.170
0.0136
Table 5. Differences in study parameters between
four HIV groups in the study population
Charac-
teristic
Normotensive
HIV
+
(
n
=
27)
Normotensive
HIV–
(
n
=
83)
Pre-eclamptic
HIV
+
(
n
=
38)
Pre-eclamptic
HIV
–
(
n
=
67)
p
-value
MAP
(mmHg)
76.7
(64.0– 99.3)
78.7
(0– 103.3)
103.7
(64.3– 141.7)
102.4
(73.3– 142.0)
<
0.0001
RHI
(au)
1.79
(1.18–3.21)
1.84
(1.22–4.62)
1.67
(1.22–3.61)
1.70
(1.04–2.84)
0.1195
BPWA
(au)
527.08
±
68.272 417.69
±
34.867 593.55
±
64.295 601.78
±
43.92 0.0072
AIx @
75 (%)
8.02
(–19.18–22.8)
0.82
(–50.7–23.6)
15.09
(–35.8–51.9)
10.53
(–27.9–81.6)
<
0.0001
MAP, mean arterial pressure; RHI, reactive hyperaemia index; BPWA, baseline
pulse-wave amplitude; Aix, augmentation index @ 75 bpm.

















