
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 2, March/April 2018
AFRICA
77
16.3–31.1).
1
More recently, a cross-sectional study conducted in
Uganda, South Africa, Tanzania and Nigeria encountered an
overall age-standardised prevalence of hypertension of 25.9%.
24
The estimated 9.2% prevalence of diabetes (9.8% in urban
and 6.8% in rural areas) was higher than previous reports from
Angola of 5.7% among an urban population (aged 20 to 72 years)
in 2010,
15
and 2.8% for a rural community (aged 30 to 69 years)
in 2009.
17
The value of 9.8% estimated in individuals older than
18 years is in the middle range of prevalence levels encountered
in STEPS surveys, with values from 3.0% in Benin to 22.5% in
Niger.
25,26
This value also falls within the confidence intervals of
the WHO estimate of 12.1% (95% CI: 5.6–18.9) for increased
Table 4. Prevalence of diabetes and relation with other factors by gender (Caxito, 2016)
Associated factor
All participants (
n
=
2 348)
Female (
n
=
1 220)
Male (
n
=
1 128)
Prevalence
% (95% CI)*
Prevalence
% (95% CI)*
Adjusted OR
a,b
(95% CI)*
Prevalence
% (95% CI)*
Adjusted OR
a,b
(95% CI)*
Total
9.2 (8.1–10.4)
8.9 (7.4–10.6)
1
9.6 (8.0–11.4)
1.4 (1.0–1.8)
Age (years)
15–24
4.4 (3.2–6.0)
4.4 (2.7–7.0)
1
4.4 (2.9–6.6)
1
25–34
5.6 (4.0–7.7)
3.2 (1.8–5.9)
0.8 (0.3–1.7)
8.0 (5.4–11.6)
1.9 (1.0–3.5)
35–44
13.2 (10.2–17.0)
12.7 (9.0–17.7)
3.3 (1.7–6.2)
13.9 (9.3–20.3)
3.4 (1.8–6.5)
45–54
19.3 (15.2–24.2)
17.6 (12.9–23.7)
4.8 (2.6–9.0)
22.2 (15.4–30.9)
6.2 (3.3–11.6)
55–64
17.2 (12.8–22.8)
15.5 (10.3–22.7)
4.0 (2.0–8.0)
20.7 (13.5–30.4)
5.6 (2.8–11.0)
Residence
Urban
9.8 (8.5–11.2)
9.2 (7.5–11.1)
1.6 (0.9–2.8)
10.4 (8.6–12.6)
2.6 (1.4–4.9)
Rural
6.8 (4.8–9.5)
7.4 (4.7–11.6)
1
6.0 (3.6–10.1)
1
Education (years completed)
None
11.5 (7.9–16.5)
11.9 (8.1-17.1)
–
6.7 (1.2-29.8)
–
1–4
11.7 (9.2–14.6)
10.0 (7.5-13.3)
–
17.2 (11.5-24.9)
–
5–9
8.3 (6.7–10.1)
7.1 (5.1–9.9)
–
9.0 (6.9–11.6)
–
> 10
7.7 (5.9–10.2)
6.2 (3.4–11.1)
–
8.3 (6.1–11.3)
–
BMI class (kg/m
2
)
Underweight (
<
18.5)
7.5 (4.9–11.4)
4.0 (1.7–9.0)
1
10.7 (6.6–16.9)
1
Normal (18.5–24.9)
7.8 (6.6–9.2)
7.7 (5.9–9.9)
2.0 (0.7–5.1)
7.9 (6.3–9.9)
0.7 (0.4–1.2)
Overweight (25.0–29.9)
12.4 (9.4–16.1)
10.4 (7.2–14.7)
2.4 (0.9–6.5)
16.5 (11.0–24.2)
1.1 (0.5–2.3)
Obese (
≥
30)
18.6 (13.4–25.4)
17.1 (11.5–24.5)
3.9 (1.4–11.1)
24.2 (12.8–41.0)
1.7 (0.6–4.5)
Abdominal obesity
No
7.0 (5.9–8.3)
3.5 (2.3–5.2)
1
7.5 (6.0–9.3)
1
Yes
15.9 (13.1–19.0)
8.8 (6.4–12.2)
1.5 (1.0–2.3)
24.3 (17.9–32.0)
2.3 (1.4–3.8)
Tobacco smoking
Non-current
8.8 (7.6–10.0)
8.6 (7.2–10.4)
–
8.9 (7.3–10.8)
–
Current
14.4 (9.6–21.0)
17.6 (8.3–33.5)
–
13.3 (8.2–20.8)
–
Alcohol consumption
No consumption
8.9 (7.6–10.5)
8.7 (6.9–10.8)
–
9.2 (7.2–11.7)
–
Occasional (
<
3 days per week)
10.5 (8.0–13.7)
10.1 (6.9–14.6)
–
11.0 (7.4–16.1)
–
Frequent (
≥
3 days per week)
8.8 (6.4–12.0)
8.3 (4.7–14.3)
–
9.1 (6.2–13.0)
–
*Post-stratification weights used as described in the methods section;
a
Adjusted for age (categorical: 15–23, 25–34, 35–44, 45–54, and 55–64);
b
Only variables with rela-
tions with statistical significance shown.
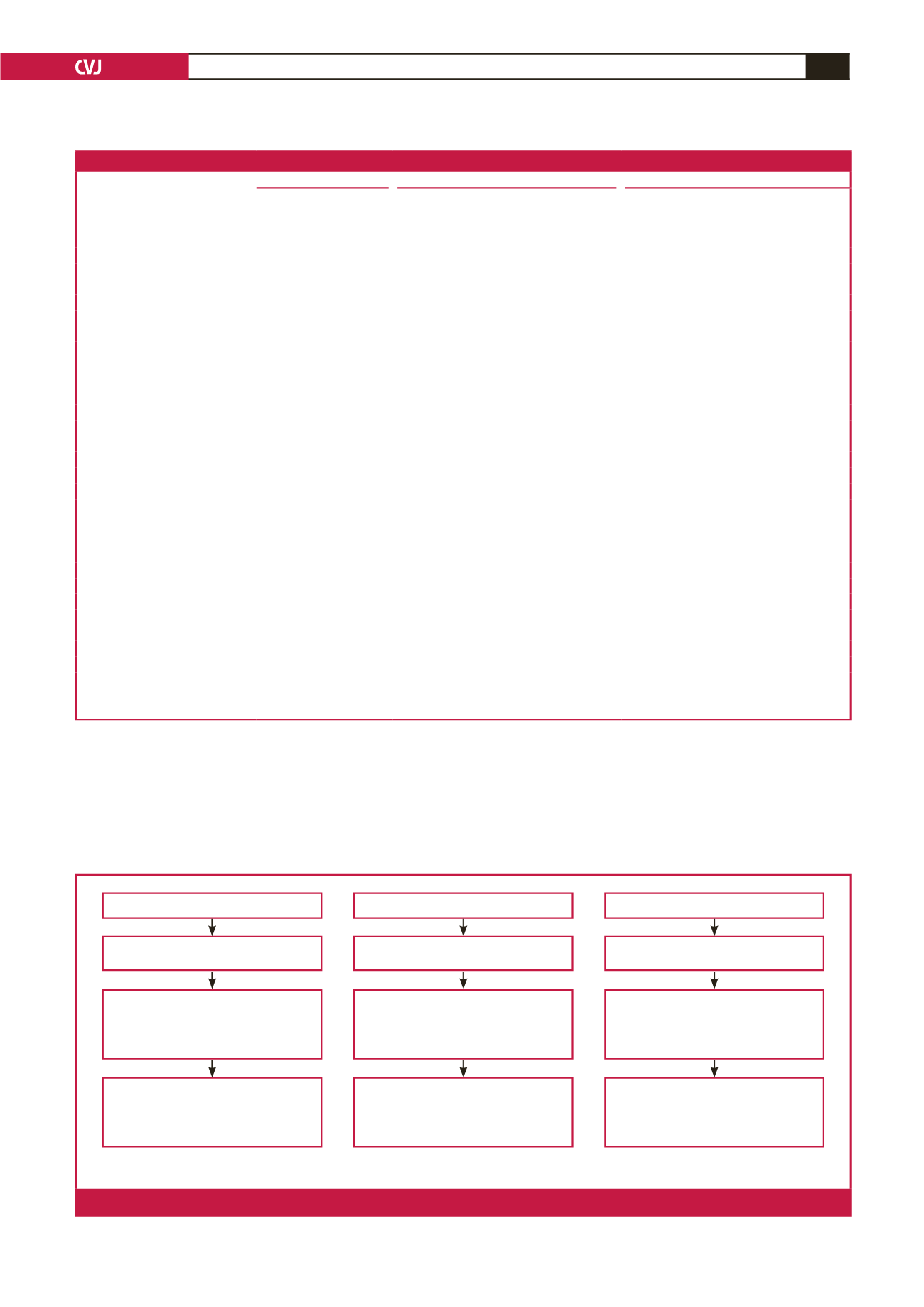
Hypertensive (
n
=
431)
Aware (
n
=
209)
48.5% (95% CI 43.8–53.2)
Treated (
n
=
68)
32.5% (95% CI 26.6–39.2)
among the aware
15.8% (95% CI12.6–19.5)
among the hypertensive
Controlled (
n
=
39)
57.7% (95% CI 46.2–68.6)
among the treated
9.1% (95% CI 6.7–12.1)
among the hypertensive
Diabetic (
n
=
223)
Aware (
n
=
24)
10.8% (95% CI 7.3–15.5)
Treated (
n
=
10)
41.7% (95% CI 24.5–61.2)
among the aware
4.5% (95% CI 2.5–8.1)
among the diabetic
Controlled (
n
=
6)
60.0% (95% CI 31.3–83.2)
among the treated
2.7% (95% CI 1.2–5.7)
among the diabetic
Hypercholesterolaemic (
n
=
71)
Aware (
n
=
3)
4.2% (95% CI 1.5–11.7)
Treated (
n
=
1)
33.3% (95% CI 6.1–7.9)
among the aware
1.4% (95% CI 0.3–7.6)
among the hypercholesterolaemic
Controlled (
n
=
1)
100% (95% CI 20.7–100)
among the treated
1.4% (95% CI 0.3–7.6)
among the hypercholesterolaemic
Post-stratification weights used as described in the methods section.
Fig. 1.
Frequencies, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension, diabetes and hypercholesterolaemia.

















