CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 24, No 7, August 2013
262
AFRICA
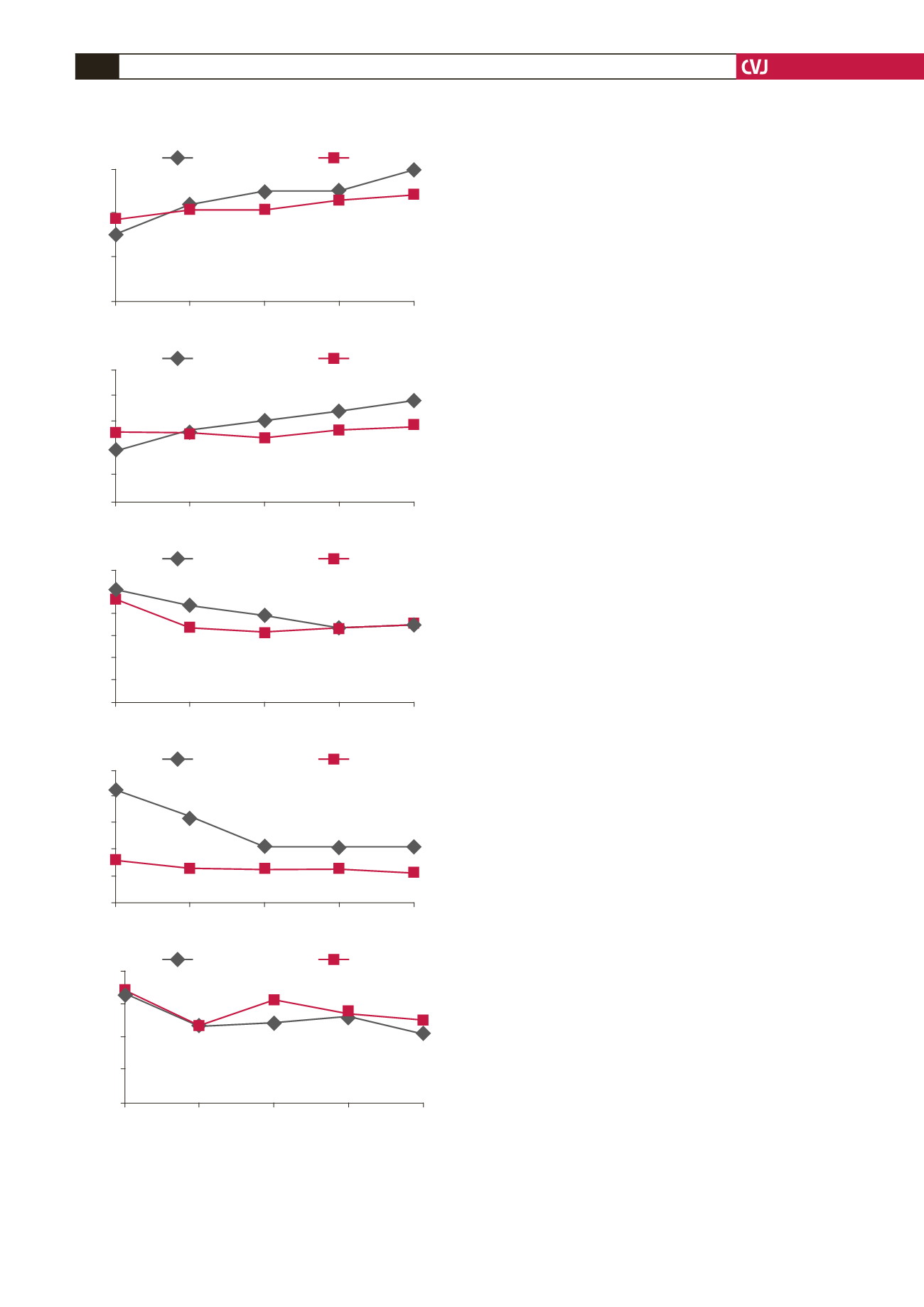
lower than those of group II (group I: 3.02
±
0.36 l/min vs group
II: 3.71
±
0.92 l/min;
p
=
0.001) (Fig. 1A). Considering all
measurements, CO
3
and CO
5
for group I were higher than those
of the control group, whereas there was no difference for the other
measurements [respectively for groups I and II; CO
2
: 4.39
±
1.56
vs 4.18
±
0.72 l/min (
p
=
0.804); CO
3
: 5.01
±
0.57 vs 4.11
±
1.00 l/
min (
p
=
0.024); CO
4
: 5.03
±
1.01 vs 4.62
±
0.61 l/min (
p
=
0.191);
CO
5
: 5.94
±
1.14 vs 4.87
±
0.34 l/min (
p
=
0.049)] (Fig. 1A).
When within-group CO increase was evaluated, CO in the
levosimendan group showed a significant increase with time
compared to baseline values (CO
1
: 3.02
±
0.36 l/min vs CO
5
:
5.94
±
1.14 l/min;
p
=
0.018). On the other hand, increase in the
control group over time was not found to be significant (CO
1
:
3.71
±
0.92 l/min vs CO
5
: 4.87
±
0.34 l/min;
p
=
0.506).
Statistically significant differences in favour of group I were
recorded regarding the values of CI between the two groups. CI
in group I increased significantly compared to the control group
[respectively for groups I and II; CI
2
: 2.68
±
0.83 vs 2.54
±
0.47
l/min/m² (
p
=
0.273); CI
3
: 3.13
±
0.37 vs 2.40
±
0.54 l/min/m² (
p
=
0.229); CI
4
: 3.43
±
0.66 vs 2.74
±
0.31 l/min/m² (
p
=
0.006);
CI
5
: 3.84
±
0.81 vs 2.94
±
0.29 l/min/m² (
p
=
0.001)] (Fig. 1B).
When the within-group CI increase was evaluated, CI in
group 1 showed a significant increase over time compared to
baseline values (CI
1
: 1.89
±
0.30 l/min/m² vs CI
5
: 3.84
±
0.81 l/
min/m²;
p
=
0.014). Although the increase in group II over time
was found to be significant (CI
1
: 2.60
±
1.26 vs 2.94
±
029 l/
min/m²;
p
=
0.048) this increase was more apparent in group I.
Basal pulmonary arterial pressures were compared (PAP
1
)
between groups. PAP
1
in group I was higher compared to that
in group II (respectively for groups I and II; PAP
1
: 51.25
±
26.95 vs 47.00
±
9.00 mmHg;
p
=
0.001). PAP
1
was decreased
significantly in group I over time (PAP
1
: 51.25
±
26.95 mmHg
vs PAP
5
: 36.00
±
12.56 mmHg;
p
=
0.032). This decrease was not
significant in the control group (PAP
1
: 47.00
±
9.00 mmHg vs
PAP
5
: 35.85
±
8.29 mmHg;
p
=
0.595) (Fig. 1C).
When basal pulmonary vascular resistance values (PVR
1
)
were compared, values in group I were higher compared to
those in group II (respectively for groups I and II; PVR
1
:432.4
±
340.4 vs 164.2
±
79.5 dyne/s/cm
5
;
p
=
0.027). The decrease
in PVR over time was marked in group I (PVR
1
: 432.4
±
340.4
dyne/s/cm
5
vs PVR
5
: 218.7
±
163.2 dyne/s/cm
5
;
p
=
0.009). This
decrease was not significantly different with time in the control
group (PVR
1
: 164.2
±
79.5 dyne/s/cm
5
vs PVR
5
: 116.1
±
49.6
dyne/s/cm
5
;
p
=
0.445) (Fig. 1D).
Baseline systemic vascular resistance values (SVR
1
) were
compared between the groups. In group II, SVR
1
was higher than
that in group I (respectively for groups I and II; SVR
1
: 1681.2
±
422.6 vs 1740.0
±
698.5 dyne/s/cm
5
,
p
=
0.032). Decrease in
SVR with time was significant in group I (SVR
1
: 1681.2
±
422.6
dyne/s/cm
5
vs SVR
5
: 1039.2
±
354.2 dyne/s/cm
5
;
p
=
0.015).
In the control group, SVR
1
also showed a significant decrease
(SVR
1
: 1740.0
±
698.5 dyne/s/cm
5
vs SVR5: 1272.2
±
375.5
dyne/s/cm
5
;
p
=
0.036) (Fig. 1E).
Discussion
Nowadays many patients indicated for cardiac surgery are at
high peri-operative risk for increased risk of morbidity and
mortality. Pulmonary arterial hypertension and low ejection
fraction are among the key factors determining prognosis
Fig. 1. Course of measurements between the two groups
over time. A. cardiac output, B. cardiac index, C. mean
pulmonary artery pressure (MPAP), D. pulmonary vascu-
lar resistance (PVR), E. systemic vascular resistance
(SVR).
6
4
2
0
5
4
3
2
1
0
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
500
400
300
200
100
0
2000
1500
1000
500
0
CO
1
CO
2
CO
3
CO
4
CO
5
CI
1
CI
2
CI
3
CI
4
CI
5
MPAP
1
MPAP
2
MPAP
3
MPAP
4
MPAP
5
PVR
1
PVR
2
PVR
3
PVR
4
PVR
5
SVR
1
SVR
2
SVR
3
SVR
4
SVR
5
Study period
Study period
Study period
Study period
Study period
CO (l/min)
CI (l/min/m
2
)
MPAP (mmHg)
PVR (dyn/s/cm
–5
)
SVR (dyn/s/cm
–5
)
A
B
C
D
E
Levosimendan
Control
Levosimendan
Control
Levosimendan
Control
Levosimendan
Control
Levosimendan
Control


