CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 32, No 1, January/February 2021
AFRICA
7
anticipation stress. Hereafter, registered clinical psychologists
supervised the completion of the depression questionnaire
25
and
participants were advised to go to bed at 22:00, fasting overnight.
The next morning, after the last 24-hour blood pressure
(BP) recording at 07:00, the Cardiotens CE120
®
apparatuses
were disconnected. BP and two lead ECG time-domain HRV
analyses
19
were done using theCardioVisions 1.19 personal edition
software (Meditech, Budapest, Hungary). Anthropometric and
total energy expenditure measures were performed according
to standardised procedures. Hereafter, participants were in a
AR
α
1a
α
2a
α
1b
D
2
R
GCR
Light
Inner BRB
Outer BRB
BV: Flicker-light-induced-provocation (FLIP)
BV: Calibre diameter
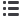
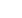
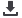
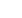
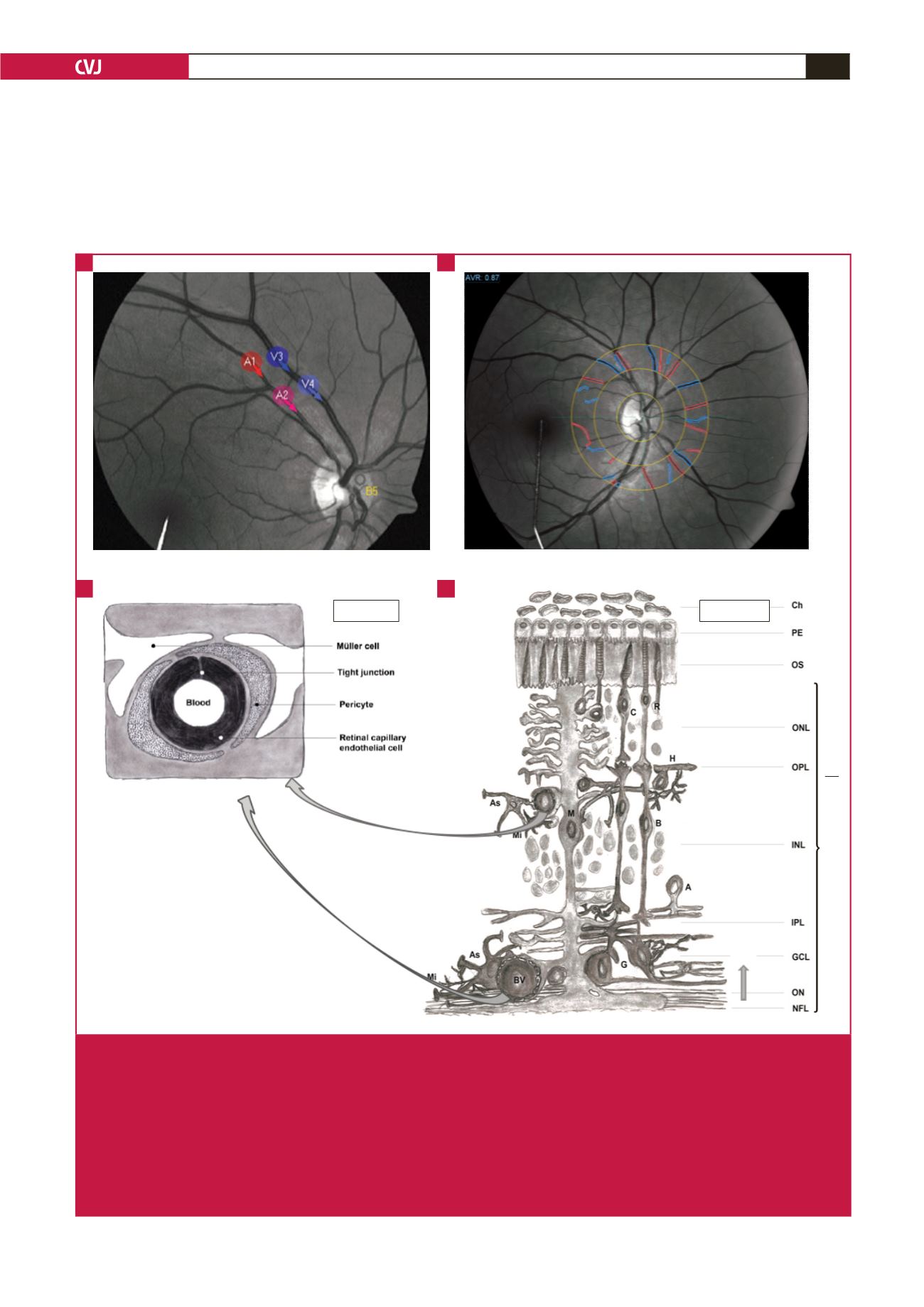
Fig. 1.
Presenting retinal haemodynamic assessment sites and neurovascular coupling between glial cells and blood vessels (BV).
A. The selected artery (A = red) and vein (V = blue) areas to determine BV responses upon flicker light-induced provoca-
tion. B. Retinal BV to determine arterial narrowing (red) and vein widening (blue). C, D. The blood vessel characteristics in
the inner and outer blood–retinal barrier (BRB). The inner BRB (C) contains capillary endothelial cells and the outer BRB
(D) contains pigment epithelial (PE) cells. D shows the inner and outer BRB retinal neural layers (bottom to top). NFL, optic
nerve fibre layer; ON, optic nerve; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer
plexiform layer with horizontal cells (H), bipolar cell dendrites (B), amacrine cells (A), astrocytes (As), microglia (Mi); Müller
cells (M); ONL, outer nuclear layer with rods (R) and cones (C); OS, outer segment layers; PE, pigment epithelial cells; Ch,
choroid; AR, adrenergic receptors in the OPL (
α
1a
-AR,
α
1b
-AR,
α
2a
-AR); D
2
R, dopamine
2
receptors; GCR, glucocorticoid recep-
tors (Malan
et al
.
4
Adapted by Louise Malan).
A
C
B
D