CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 32, No 2, March/April 2021
AFRICA
83
between hs-TNT and NT-proBNP
(r
=
0.65,
p
<
0.01)
(Table 4).
Also, there was a positive correlation between levels of hs-TNT
and fibrinogen, D-dimer, ferritin, procalcitonin and CRP (
r
=
0.24,
p
<
0.01;
r
=
0.37,
p
<
0.01;
r
=
0.25,
p
<
0.01;
r
=
0.34,
p
<
0.01;
r
=
0.31,
p
<
0.01) (Table 4).
Serum levels of hs-TNT, NT-proBNP, ferritin, D-dimer,
procalcitonin, CRP, fibrinogen, and neutrophil and lymphocyte
counts are shown in Table 5 and compared with each patient
grouped according to thorax CT scans, which were divided into
three categories: 1, mild pneumonia; 2, moderate pneumonia; and
3, severe pneumonia (Table 5). Mean plots of the comparisons
according to thorax CT scans are shown in Figs 2–5.
Discussion
By 19 April 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic had reached 2 241
359 cases and 152 551 deaths worldwide, according to the data
of the religious health organisation. In Turkey, there were 82 329
cases and 1 890 deaths by 18 April 2020.
This study reflects a general and cardiovascular perspective
on the current data of Istanbul University Medical Faculty
Hospital, where original treatment protocols and advanced
intensive care services are provided. In addition, our study
demonstrates the prognostic significance of cardiovascular
biomarkers in the follow up of COVID-19.
In general, our mortality rates and ICU admission rates
were lower than reported in other previous studies. We linked
this lower mortality and ICU admission rates to certain specific
applications in our treatment protocol. Favipravir treatment
was started in all patients with severe pneumonia and in those
whose treatment was unresponsive to the routine treatment
protocol, and/or in those with clinical deterioration of moderate
pneumonia. In addition, due to the increased tendency to
thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, antithrombotic and
anticoagulant therapy/prophylaxis was initiated unless contra-
indicated in all patients admitted to the hospital, with a regimen
of subcutaneous enoxaparin 4 000 IU once a day and oral
dipyridamole 75 mg twice a day.
In patients with severe pneumonia, enoxaparin 100 IU/kg
twice a day (at the treatment dose) was used subcutaneously
if serum ferritin levels were
>
1 000 ng/ml (or nearly two-fold
increase in follow up) or serum LDH levels were
>
400 U/l (or
increase in follow up) or serum D-dimer levels were
>
2 000
μ
g/l.
We believe that these treatment protocols (early favipravir usage
and routine anticoagulant/antiplatelet use) might have played a
role in our favourable treatment results.
A recent report on 138 patients hospitalised with COVID-
19 has shown that 7.2% had acute cardiac injury, and patients
admitted to ICU were more likely to have cardiac injury (22.2%)
than non-ICU patients.
1
This observation suggests that cardiac
injury is possibly associated with worse clinical outcomes of
COVID-19. In addition, another study also found 19.7% of
Table 3. Cardiovascular outcomes of the patients
Cardiovascular outcomes
Patients, n (%)
Acute myocardial injury
78 (25)
Acute coronary syndrome
2 (0.6)
Myocarditis
2 (0.6)
Arterial thrombosis
1 (0.3)
Venous thrombosis
3 (0.9)
Stroke
1 (0.3)
Malignant ventricular arrhythmia
1 (0.3)
Table 4. Correlations between hs-TNT,
inflammatory markers and NT-proBNP
hs-
TNT
Fibrin-
ogen
NT-pro-
BNP
D-dimer Ferritin Procal-
citonin
CRP
Correlation
co-efficient
(
r
)
0.24 0.65
0.37 0.25 0.34 0.31
p-
value
<
0.01
<
0.01
<
0.01
<
0.01
<
0.01
<
0.01
hs-TNT, high-sensitivity troponin T; NT-proBNP, N-terminal proB-type natri-
uretic peptide; CRP, C-reactive protein.
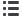
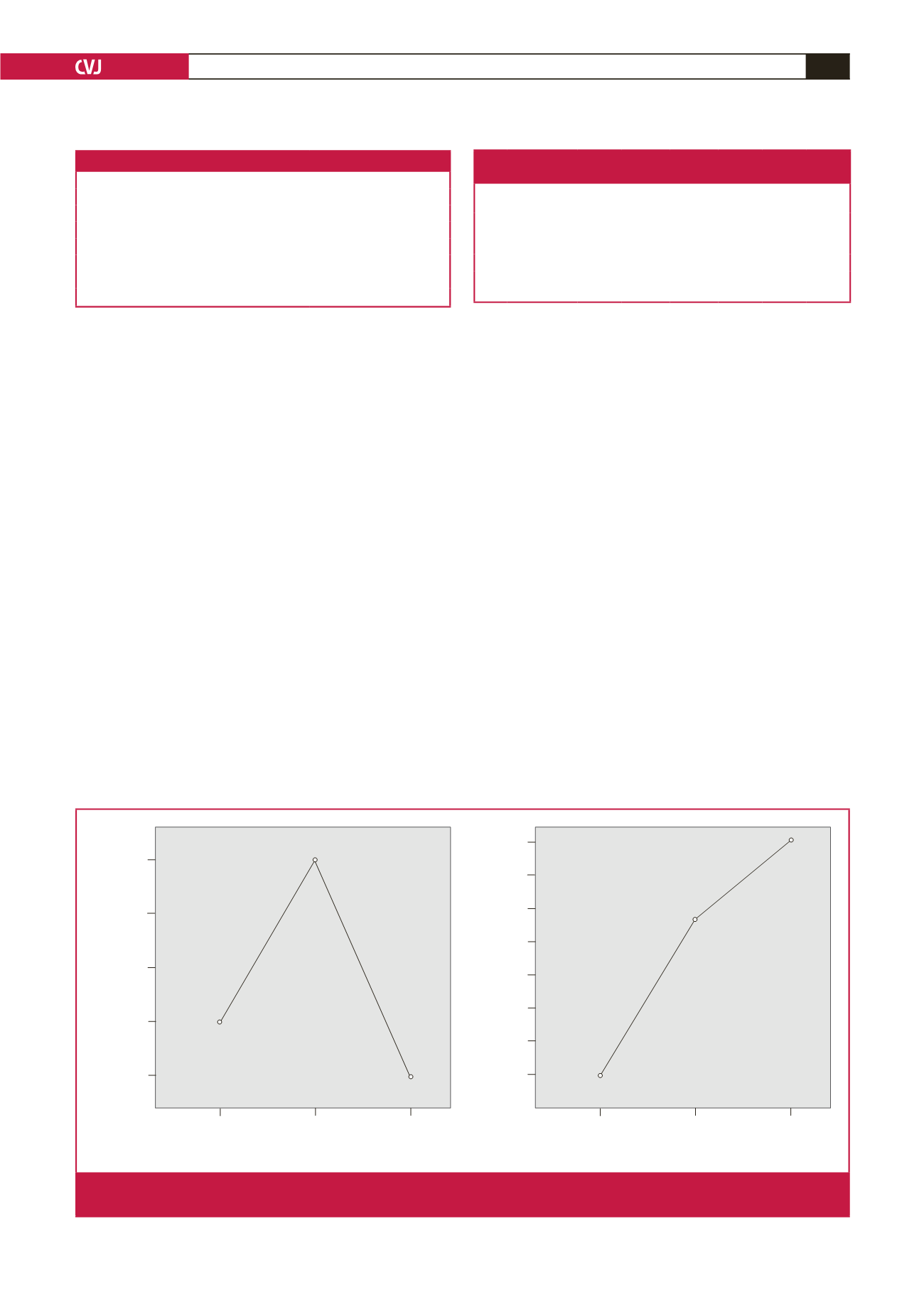
2 100.00
1 800.00
1 500.00
1 200.00
900
1.00 2.00 3.00
Thorax CT
Mean of lympthocytes/
μ
l
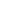
6 000.00
5 800.00
5 600.00
5 400.00
5 200.00
5 000.00
4 800.00
4 600.00
1.00 2.00 3.00
Thorax CT
Mean of neutrophils/
μ
l
Thorax CT: 1 (mild pneumonia), 2 (moderate pneumonia), 3 (severe pneumonia)
Fig. 2.
Mean plots of neutrophil and lymphocyte counts compared with patients grouped according to thorax CT scans, which were
divided into three categories: 1, mild pneumonia; 2, moderate pneumonia; and 3, severe pneumonia.