
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 25, No 6, November/December 2014
AFRICA
271
=
0.57). However, after age adjustment, females seemed to have
a significantly higher SBP compared to males; 134.1 mmHg for
females and 132.1 mmHg for males (
p
=
0.042).
In the case of mean DBP, there was a small difference across
gender; 84.0 mmHg for females and 82.6 mmHg for males (
p
=
0.049). After age adjustment, there was a more significant
evidence of the difference in DBP; 84.3 mmHg for females and
82.2 mmHg for males (
p
=
0.001).
For HTN, the
χ
2
-test showed no difference across gender (
p
=
0.26). However, after age adjustment using the multivariable
model, it seemed that females had higher odds and hence risk of
HTN than males (odds ratio
=
1.25,
p
=
0.016).
SBP, DBP and HTN trends
From the total number of subjects with known age in the study (
n
=
2 348), a subdivision of this population (
n
=
2 247) represented
individuals with known age
≥
20 years old. This subpopulation
was used to examine the SBP, DBP and HTN prevalence trends
with age decade (Table 2).
Mean SBP increased continually with age decade for males
and females (Fig. 1). The rate of increase was similar between
the genders; the slopes of the regression lines for males and
females were 8.036 and 8.806, respectively. As in the case of SBP,
mean DBP increased continually with age decade for males and
females (Fig. 2). The rate of increase was very similar between
the genders; the slopes of the regression lines for males and
females were 3.696 and 3.824, respectively.
The Cochran–Armitage trend test showed significant
differences in the HTN prevalence between each age decade,
overall and gender-wise (
p
<
0.0001). This meant that within
males, females, or overall scores, there was evidence that HTN
prevalence increased with age decade (Fig. 3). Meanwhile, female
HTN prevalence appeared to be higher than that of males in the
age decades 40s, 50s, 60s, and
+
70s; however, the Fisher’s exact
test showed evidence for the difference only in the age decades
Table 1. Characteristics of patients with known age
≥
18 years
Variable
Overall
(
n
=
2 347)
F
(
n
=
1 236**)
M
(
n
=
1 111)
p
-value
unadjusted
p
-value
adjusted
Age (years)
39.6
±
16.1 38.9
±
15.9 40.5
±
16.4 0.018*
SBP (mmHg) 133.2
±
28.5 133.5
±
28.6 132.8
±
28.5 0.57*
0.042*
DBP (mmHg) 83.3
±
16.7 84.0
±
17.1 82.6
±
16.1 0.049* 0.001*
HTN (%)
44.5
45.6
43.3
0.26
†
0.016
††
Values: mean
±
SD or %.
**Females:
n
=
1 237 for SBP and age, and
n
=
1 236 for DBP and HTN.
p
-values for M vs F: *Student’s
t
-test,
†
χ
2
-test,
††
multivariable model (odds ratio
=
1.25). Adjustment: for age.
F
=
females, M
=
males, SD
=
standard deviation, SBP
=
systolic blood pressure,
DBP
=
diastolic blood pressure, HTN
=
hypertension.
Table 2. Characteristics of patients with known age
≥
20 years
Age
decade
(years) N Gender n
SBP
±
SD
(mmHg)
DBP
±
SD
(mmHg)
HTN
% (n/N)
HTN
Overall
% (n/N)
20s
694
F 386 119.3
±
19.1 76.0
±
14.0 21.8 (84/386)
22.3
(155/694)
M 308 118.6
±
16.9 74.9
±
11.7 23.1 (71/308)
†
30s
531
F 284** 125.4
±
23.1 80.2
±
15.4 33.8 (96/284)
33.9
(180/531)
M 247 124.7
±
21.0 79.2
±
13.5 34.0 (84/247)
†
40s
373
F 190 143.0
±
27.6 92.6
±
16.8 66.3 (126/190)
58.4
(218/373)
M 183 136.3
±
29.1 85.9
±
16.8 50.3 (92/183)*
50s
312
F 159 151.3
±
30.5 92.7
±
16.3 71.7 (114/159)
69.9
(218/312)
M 153 150.1
±
32.1 91.2
±
15.3 68.0 (104/153)
†
60s
201
F 96 160.8
±
25.5 95.7
±
13.1 86.5 (83/96)
80.1
(161/201)
M 105 155.9
±
30.8 92.6
±
16.8 74.3 (78/105)*
≥
70s
135
F 65 158.0
±
30.5 93.4
±
17.9 81.5 (53/65)
75.6
(102/135)
M 70 153.3
±
27.5 91.7
±
14.8 70.0 (49/70)
†
Values: mean
±
SD or % (n/N).
**Females:
n
=
285 for SBP and age, and
n
=
284 for DBP and HTN.
Fisher’s exact test: *significant differences, and
†
insignificant differences.
F
=
females, M
=
males, SD
=
standard deviation, SBP
=
systolic blood pressure, DBP
=
diastolic blood pressure, HTN
=
hypertension.
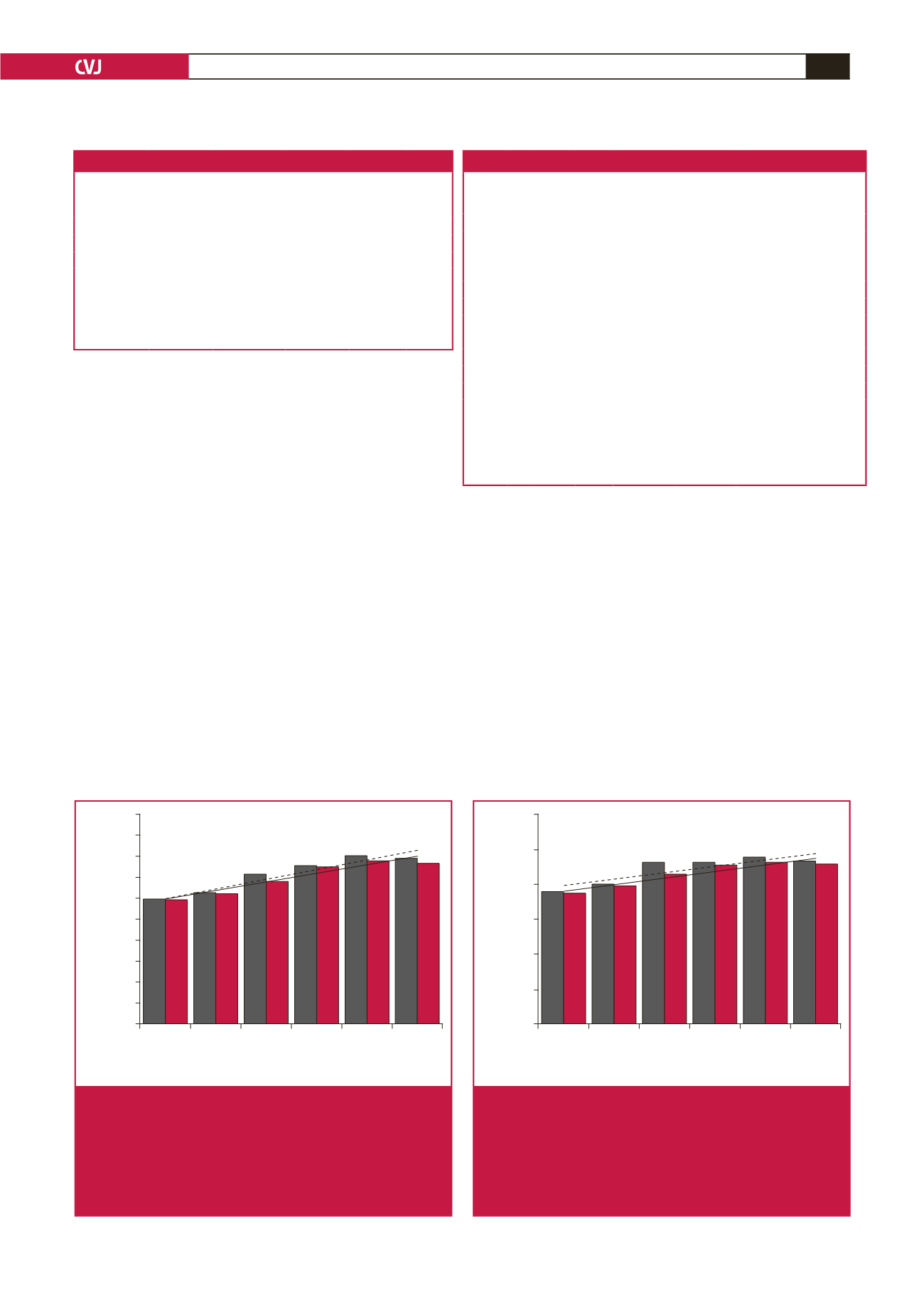
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
F M F M F M F M F M F M
20s 30s 40s 50s 60s
≥
70s
Age decade by gender
Systolic blood pressure (mmHg)
119.3
±
19.1
125.4
±
23.1
143.0
±
27.6
151.3
±
30.5
160.8
±
25.5
158.0
±
30.5
118.6
±
16.9
124.7
±
21.0
136.3
±
29.1
150.1
±
32.1
155.9
±
30.8
153.3
±
27.5
Fig. 1.
Mean SBP of patients with known age
≥
20 years.
Histogram of mean SBP
±
SD. Females
=
grey bars
and dashed line, males
=
red bars and solid line.
Regression equations:
y
=
8.806
x
+
112.1 (
R
=
0.956)
for females and
y
=
8.036
x
+
111.6 (
R
=
0.954) for
males. F
=
females, M
=
males, SD
=
standard devia-
tion, SBP
=
systolic blood pressure.
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
F M F M F M F M F M F M
20s 30s 40s 50s 60s
≥
70s
Age decade by gender
Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg)
76.0
±
14.0
80.2
±
15.4
92.6
±
16.8
92.7
±
16.3
95.7
±
13.1
93.4
±
17.9
74.9
±
11.7
79.2
±
13.5
85.9
±
16.8
91.2
±
15.3
92.6
±
16.8
91.7
±
14.8
Fig. 2.
Mean DBP of patients with known age
≥
20 years.
Histogram of mean DBP
±
SD. Females
=
grey bars
and dashed line, males
=
red bars and solid line.
Regression equations:
y
=
3.824
x
+
75.03 (
R
=
0.872)
for females and
y
=
3.696
x
+
72.97 (
R
=
0.938) for
males. F
=
females, M
=
males, SD
=
standard devia-
tion, DBP
=
diastolic blood pressure.



















