
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 27, No 3, May/June 2016
e10
AFRICA
defect (ASD). The systolic pulmonary arterial pressure was 63
mmHg, calculated from tricuspid regurgitation velocity.
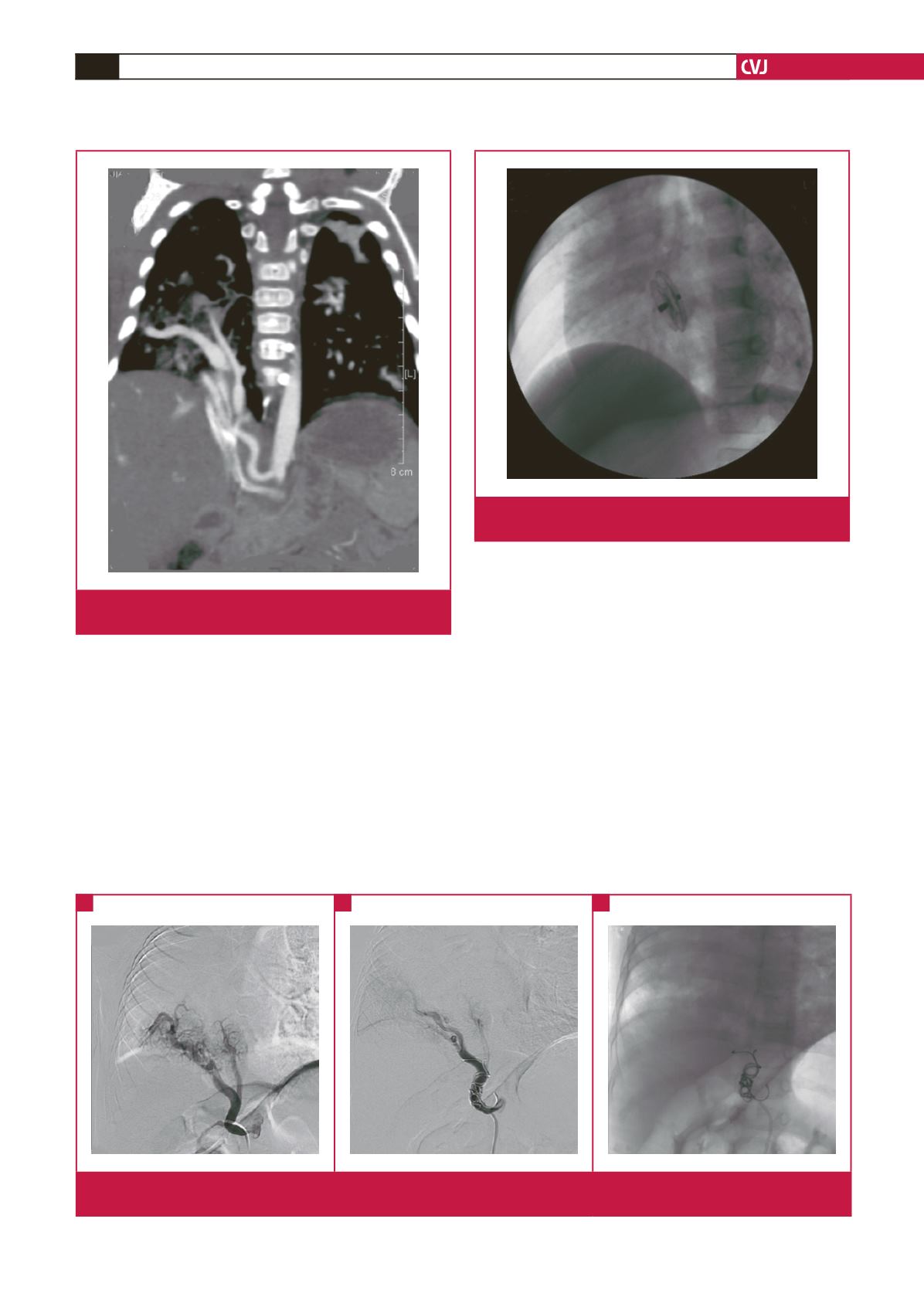
The computerised tomography angiography (CTA) revealed
partially anomalous pulmonary venous drainage to the IVC,
APC originating from the abdominal aorta, and hypoplasia of
the right lung (Fig. 2), which confirmed the diagnosis of scimitar
syndrome. The patient’s parents refused conventional surgical
intervention, considering the high risk of postoperative events.
As an alternative, stepwise transcatheter intervention
and coil embolisation of the APC and closure of the ASD
were selected to decrease the left-to-right shunt and reduce
pulmonary arterial hypertension. The patient proceeded to
have cardiac catheterisation under general anaesthesia. A 4-F
Cobra cathether (Cook, Bloomington, IN) was delivered to the
APC via the femoral artery and then two 8
×
50-mm MReye
embolisation coils (Cook, Bloomington, IN), five 5
×
30-mm
MReye embolisation coils and two 5
×
30-mm Cook coils (Cook,
Bloomington, IN) were deployed for occlusion (Fig. 3A, B).
After percutaneous entry of the femoral vein, a sizing
balloon 8-F MPA2 catheter was introduced over an extra-stiff
guide wire positioned in the left upper pulmonary artery to
measure the pulmonary arterial pressure (pathway: IVC
→
RA:
right atrium
→
RV: right ventricule
→
MPA: main pulmonary
artery). Using an exchange 260-cm Cordis guidewire, an
occlusion balloon catheter was introduced into the left atrium
to determine the stretched diameter of the ASD (pathway:
MPA
→
RV
→
RA
→
ASD
→
LA). A 10-mm Amplatzer septal
occluder (AGA Medical, MN) was implanted after balloon sizing
the defect (diameter: 8 mm) (Fig. 4). The procedure was successful.
Fig. 4.
Catheterisation showing complete occlusion of the
atrial septal defect by the Amplatzer septal occluder.
Fig. 2.
CTA showing right pulmonary vein drainage to the
inferior vena cava.
Fig. 3.
(A) Catheterisation showing systemic arterial collaterals arising from the abdominal aorta and supplying the right lung. (B)
and (C) Catheterisation showing coil embolisation of the systemic arterial collaterals supplying the right lung.
A
B
C

















