CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 3, May/June 2018
AFRICA
197
in 2:1 block, approximately 100 in 3:1 block, and approximately
75 in 4:1 block). In patients with AV node disease or who take
drugs that slow AV conduction, the ventricular response to
atrial flutter may be irregular, though less erratic than in atrial
fibrillation.
9,10
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is a rare condition
that occurs in patients with advanced pulmonary disease or
who are receiving theophylline treatment.
11
In multifocal atrial
tachycardia there is random firing of different atrial ectopic foci.
MAT is defined as a rhythm with an atrial rate
>
100 beats per
minute with at least three morphologically distinct P waves (Fig.
5), irregular P-P intervals, and an isoelectric baseline between P
waves (distinguishing MAT from AF and AFL).
9,10
The correct treatment depends on the correct
diagnosis
The correct distinction between AF, AFL and MAT is of
paramount importance, since the three conditions require
different therapeutic approaches.
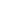
Variable AV conduction
3:1
2:1
3:1
V1
Regular and uniform morphology of flutter waves
Variable AV conduction
300
Variable
AV conduction
Regular
atrial activity
Regular and uniform morphology of flutter waves
Fig. 4.
In atrial flutter with a variable block, the re-entry circuit results in uniform flutter waves.
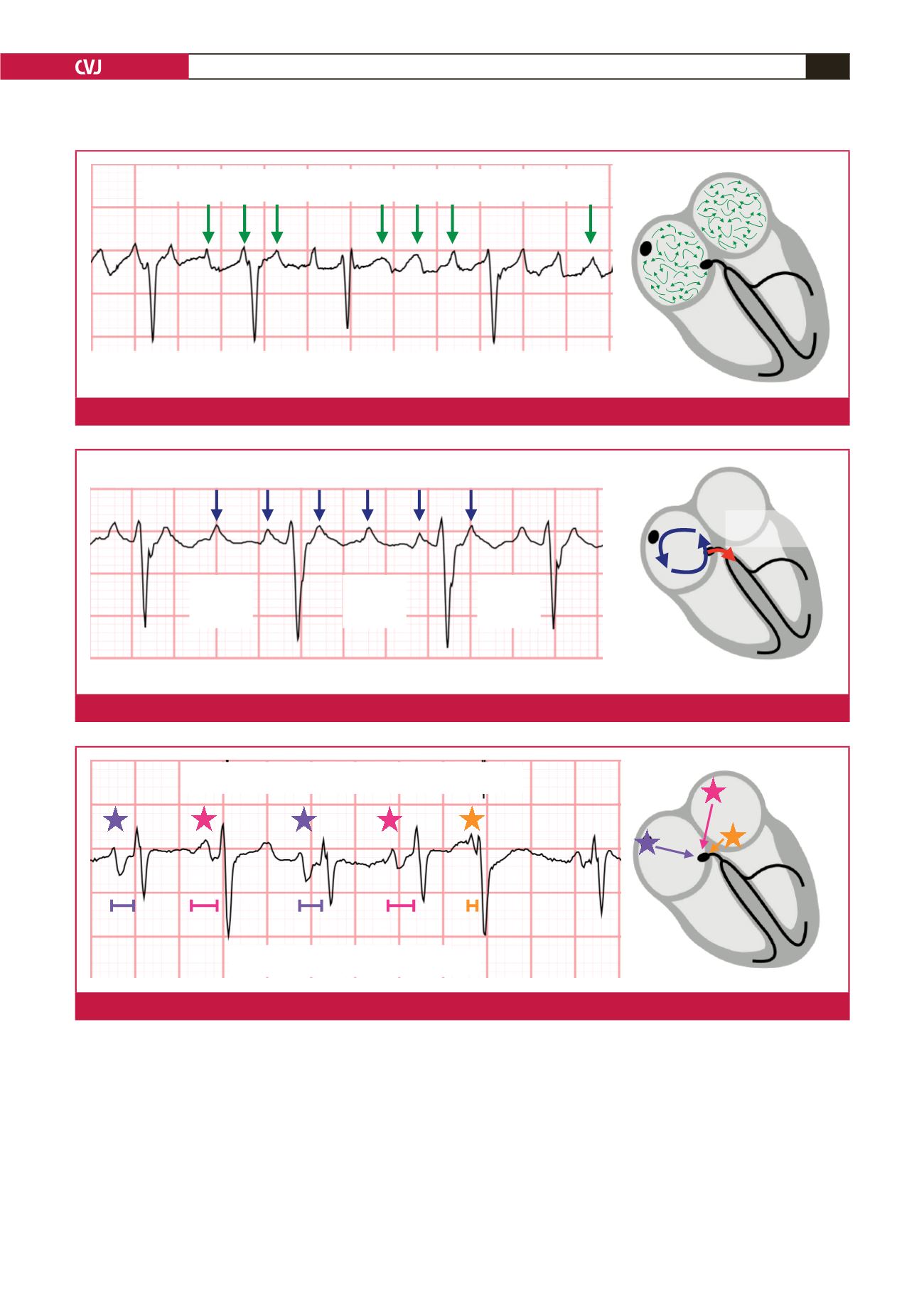
V1
Variable PR intervals
Variable P wave morphologies
Variable P-wave morphologies
Variable PR intervals
Fig. 5.
In multifocal atrial tachycardia, there are recognisable P waves with at least three different morphologies.
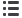
Fibrillatory waves have a variable morphology
V1
No pattern to the irregularity of the RR interval
No pattern to the irregularity of the RR interval
Fibrillatory waves have a variable morphology
Fig. 3.
In atrial fibrillation, the chaotic atrial activity translates to irregular fibrillatory waves.