CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 27, No 6, November/December 2016
376
AFRICA
(IFS)
30
and increases cell viability,
31
while others have found
no effect on IFS and cell survival.
29,32
There seems to be more
consensus regarding function following I/R. FTY720 given at the
onset of reperfusion increases functional ability.
30,32
The effect of
acute pre-ischaemic administration of FTY720 to the heart has
not yet been described.
Clinical interest in FTY720 has however not centred
on its postulated cardioprotective effects, but rather on its
immunosuppressant effects, which led to the approval of a
commercial form of the drug for use as an oral treatment for
multiple sclerosis (MS).
33,34
One of the proposed explanations for
the mechanism by which FTY720 suppresses the autoimmune
response associated with MS is by binding to S1P1 in the
lymphoid tissue. This initiates a paradoxical reduction in the
effects linked to S1P1 activation, including the egress of lymphoid
cells from the lymph nodes. This ‘functional antagonism’, as
Brinkmann
26
puts it, can be explained by the down-regulation of
S1P1 receptors due to sustained activation by P-FTY720. The
end-effect is the specific suppression of lymphocyte release from
the lymph tissue.
25-27
In addition to its immuno-modulatory effects, FTY720 has
also received attention as a possible tumour suppressor.
35
Studies
have shown that FTY720 induces cell death in cancerous cells,
while not eliciting any toxic effects in other tissues.
35-37
One of the
proposed mechanisms by which FTY720 induces cell death in
these cells entails the FTY720-mediated activation of the serine/
threonine protein phosphatase, protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A),
which, when activated, favours the de-phosphorylation and
inactivation of pro-survival proteins such as protein kinase B
(PKB/Akt), extracellular signal-regulated kinase p42/p44 (ERK
p42/p44), Bad and others.
36-39
FTY720 is therefore a drug with both existing and potential
clinical applications in divergent fields: MS, cancer and
cardioprotection following I/R, although the precise nature of its
influence in the latter context is still controversial. Consequently
it is important to clarify its effects on the heart since, on one
hand, FTY720 could present as a clinically feasible drug for the
treatment of myocardial I/R injury, while on the other hand, it
also has clinical potential in other scenarios, making it important
to better illuminate the ‘off-target’ effects of this drug on organs
such as the heart.
The controversies associated with FTY720 administration in
the context of myocardial I/R injury highlight questions regarding
the effects of different doses of the drug, administered at different
time points relative to sustained ischaemia, on different endpoints
associated with I/R injury. The aim of this study was therefore to
investigate and describe the effects of FTY720 administration at
two different concentrations (1 and 2.5
µ
M) prior to ischaemia or
at the onset of reperfusion in two different models of ischaemia (20
minutes’ global ischaemia and 35 minutes’ regional ischaemia) on
different endpoints (functional recovery and IFS) in the isolated,
working rat heart model. In view of the immunomodulatory
effects of FTY720, the isolated heart preparation allows for the
study of direct cardiac effects independent of systemic, in this case
specifically, immune interactions and effects.
40
Regional ischaemia (RI) of the isolated heart is an accepted
model of ischaemia of only a portion of the left ventricle, thereby
simulating myocardial infarction. Global ischaemia (GI) on the
other hand is of scientific interest, as it is well characterised and
commonly used in basic research studies requiring relatively
large amounts of homogenous tissue where biochemical analysis
of tissue is required, or in instances where functional recovery
is the primary endpoint of interest, for example in studies
investigating stunning.
40,41
Methods
Male Wistar rats were allowed free access to food and water prior
to experimentation. Rats weighing between 250 and 350 g were
anaesthetised by intraperitoneal injection of 60 mg pentobarbital
per rat. All experimental protocols were approved by the Animal
Ethics committee of the University of Stellenbosch (Faculty of
Medicine and Health Sciences) and were executed in accordance
with the revised South African National Standard for the care
and use of laboratory animals for scientific purposes (SABS,
SANS 10386, 2008).
For all experimentation, the isolated, working rat heart
preparation was used as described previously.
42
Following the
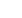
Retrograde Work Retrograde Ischaemia Retrograde Work
Control
15
15
20
20 GI
20
15
PreFTY
15
15
15 FTY
20 GI
20
15
PostFTY
15
15
20
20 GI
15 FTY
15
0
15
30
50
70
90
105
*
*
Time duration (minutes)
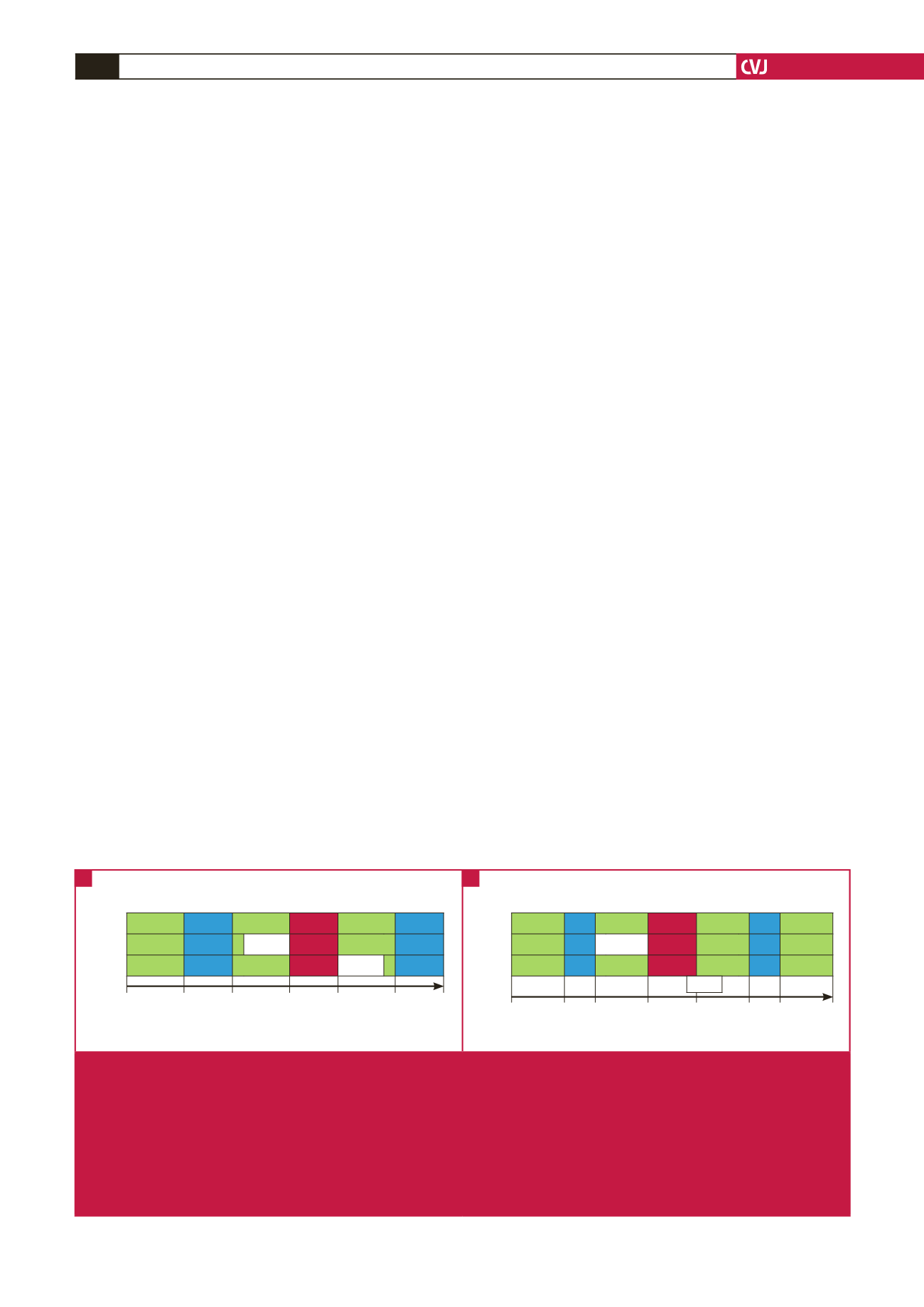
Retrograde Work Retrograde Ischaemia Retrograde Work Retrograde
Control
15
15
15
35 RI
20
20
20
PreFTY
15
15 15 FTY
35 RI
20
20
20
PostFTY
15
15
15
35 RI
20
20
20
0
15 30
45
80
100 120
140
*
*
#
Time duration (minutes)
15 FTY
Fig. 1.
Isolated working rat heart perfusion protocols used to investigate the effects of different concentrations of FTY720, adminis-
tered at different time points relative to sustained ischaemia, in different models of ischaemia and their respective endpoints.
FTY720 (1
μ
M or 2.5 μM) was administered for a period of 15 minutes either immediately prior to sustained ischaemia
(PreFTY), or directly at the onset of reperfusion (PostFTY). Two models of ischaemia were used: (A) 20 minutes’ global
ischaemia (GI), followed by a total of 35 minutes’ reperfusion; and (B) 35 minutes’ regional ischaemia (RI), followed by 60
minutes’ reperfusion. In the RI model, the reperfusion administration of FTY720 already commenced during the final five
minutes of RI. Functional recovery was measured in both groups at the end of the last episode of work during reperfusion.
Infarct size (IFS) was the primary endpoint for this model of ischaemia. *Determination of functional ability both pre- and post
ischaemia.
#
Determination of infact size.
A
B