CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 4, July/August 2017
AFRICA
217
Hypertension was the most important co-morbidity, present
in 52% of patients. Concomitant HIV infection occurred in 26%
of patients and 19% were on highly active antiretroviral therapy.
The majority of patients (85%) were on varying combinations of
medical therapy for either hypertension or HF and AF, with only
15% not on any drug therapy. None of the eight patients who
underwent coronary angiography during their surgical work-up
had occlusive coronary artery disease.
The mean LVEF was 58
±
12.7% with 43% of patients having
a LVEF
<
60%. The EDV and ESV were 93.8
±
31.4 and 39.7
±
22.3 ml/m
2
, respectively. Pulmonary hypertension was present
in 38 (45%) subjects with no patients having contributing
pulmonary abnormality. Concomitant organic rheumatic
tricuspid valve (TV) disease was present in 29% of patients, with
the mean tricuspid annulus diameter 38
±
7.2 mm. Tricuspid
regurgitation (TR) was present in 64% of patients with moderate
or severe TR present in 31% of cases (Table 1).
The mean mitral annulus diameter was 43
±
8.5 mm, with
71 (84.5%) patients having an annulus diameter greater than
35 mm. A Wilkins score of 4–8 and 8–12 was present in 26
and 74% of patients with chronic rheumatic MR, respectively.
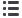
Subvalvular apparatus thickening contributed the most to the
total score (34.4%), followed by leaflet calcification (27%) (Fig.
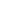
1). Fig. 2 depicts the overall distribution of subjects in each
component of the Wilkins score. Chordae were not elongated
and echocardiographic features suggestive of calcification within
the leaflets were found in all subjects. Significant commissural
fusion was present in 30% of cases.
Eighty per cent of cases were classified as having restrictive
Carpentier type IIIa leaflet dysfunction, while the remaining 20%
of patients had a mixed lesion that was a combination of type 2
(excessive leaflet motion) and type IIIa dysfunction. All patients had
a greater degree of restriction of the posterior mitral leaflet (PML),
except in three cases where the anterior mitral leaflet (AML) was
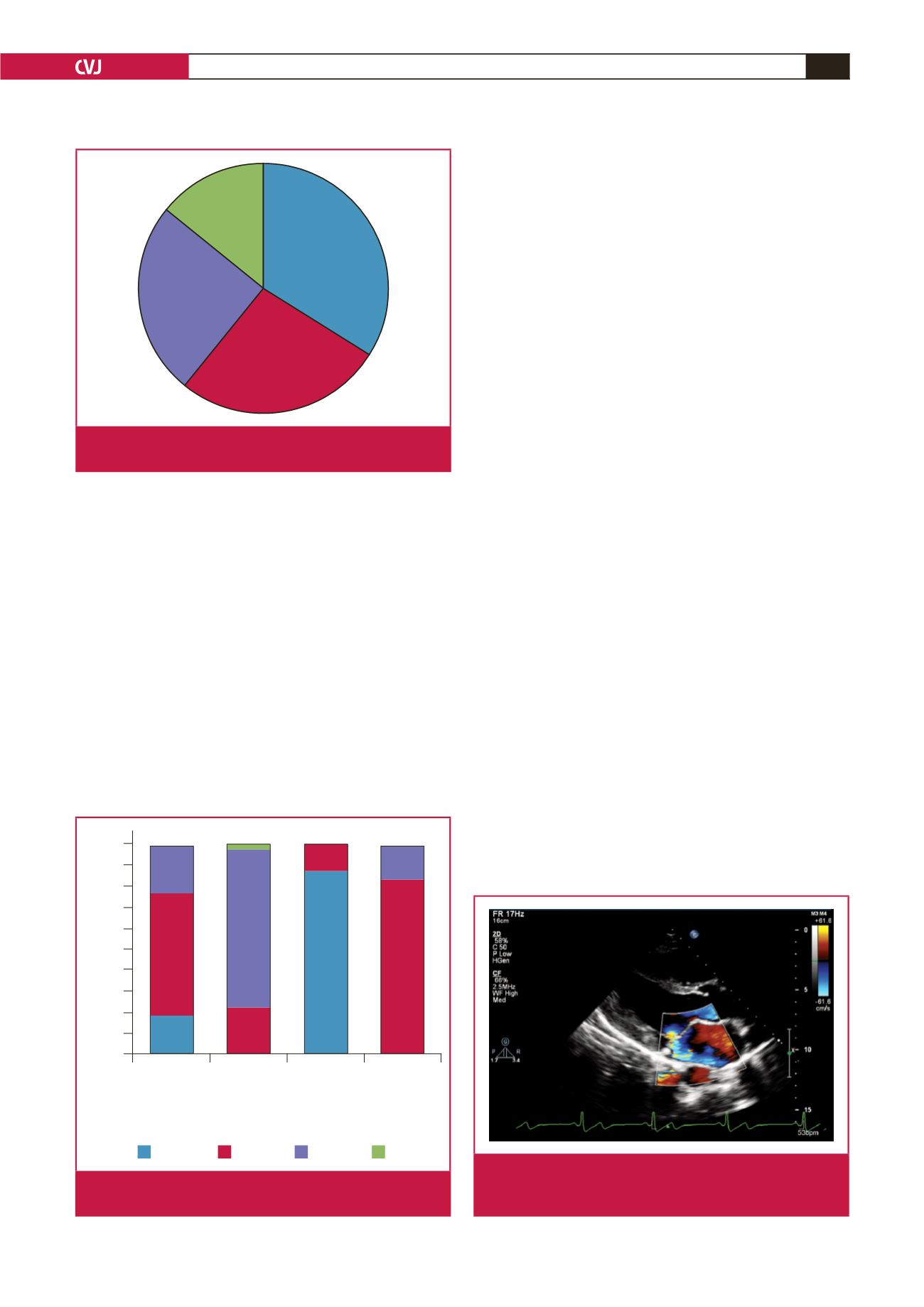
restricted to a greater degree than the PML. A posteriorly directed
eccentric MR jet was present in 96% of cases, except for the three
subjects who had an anteriorly directed jet secondary to posterior
mitral leaflet prolapse (Fig. 3). A comparison between the clinical
characteristics and mitral valve morphology of our cohort with
those of Marcus
et al
. is depicted in Table 2.
Patients younger and older than 30 years of age were
compared (Table 3). Twenty-six per cent of patients were
younger than 30 years of age. There was no significant difference
in the proportion of individuals with moderate or severe MR (
p
>
0.05). The remodelling parameters of the LV, LVEF and LA
volume were similar in both groups (
p
>
0.05). Older patients
were more likely to have co-morbidities, including hypertension
(69 vs 9%,
p
<
0.01) and HIV (32 vs 9%,
p
=
0.03), and a greater
degree of impairment of early diastolic relaxation (E
′
=
11.4
±
3.3 vs 7.6
±
2.3,
p
<
0.01).
Comparative analysis of the morphology of the mitral valve
revealed no significant differences in overall Wilkins score
between the two groups (8.31
±
1.2 vs 8.1
±
1.0,
p
=
0.33). No
statistically significant difference was noted in the degree of
calcification of the leaflets, mobility, subvalvular apparatus
thickening and commissural abnormality (
p
>
0.05).
Compared to normotensive patients with MR, patients with
hypertension were older (51.7
±
11.1 vs 35.1
±
14.2 years,
p
<
Leaflet calcification
27%
Subvalvular
apparatus
34%
Leaflet mobility
25%
Leaflet
thickness
14%
Fig. 1.
Distribution of abnormality according to the compo-
nents comprising the Wilkins score.
Category
Mobility Subvalvular
apparatus
thickening
Leaflet
thickening
Leaflet
calcification
Percentage
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Score 1
Score 2 Score 3 Score 4
Fig. 2.
Distribution of patients according to each component
of the Wilkins score.
Fig. 3.
Parasternal long-axis view showing an eccentric mitral
regurgitation jet due to restricted anterior and posterior
leaflet motion.