CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 31, No 1, January/February 2020
30
AFRICA
not affect levels of Nrf2 or Keap1 mRNA in the myocardium
of exhausted rats. However, it decreased the Keap1 level in
the myocardium. Therefore more Nrf2 was transported to the
nucleus to induce the expression of antioxidant enzymes in
the heart, reduce oxidative stress reactions in the exhausted
myocardium, and protect the heart from exhaustion.
Under the high circulatory conditions observed during
exhaustive exercise, the strength of cardiac stroke volume must
increase to meet the needs of the increased metabolism of organs
throughout the body. Ved and Ves increased, ventricular diastolic
and systolic load both increased significantly, and the PV loop
shifted to the right. Pes and dP/dt
max
were both markedly reduced,
and cardiac systolic function decreased. Stroke volume is always
adapted to the Ved phase, and the EF therefore did not show a
significant difference. Notably, the –dP/dt
min
was reduced, while
Tau was noticeably longer in the exhaustive exercise groups,
suggesting that left ventricular diastolic function was decreased.
The results of this experiment are similar to the findings
described in the study by Alexiou.
23
After applying Sal, Ved
decreased, Pes increased, dP/dt
max
and –dP/dt
min
recovered, and
Tau was reduced. Based on these results, Sal improved systolic
and diastolic function in exhausted hearts.
On ECG, HR showed a compensatory increase, the RR
interval became shorter, and an increase in the ST-segment
height caused by myocardial ischaemia was observed during the
process of exhaustion. Myocardial ischaemia altered the activity
of the heart conduction system, prolonged the PR and QT
intervals and increased the risk of arrhythmia. The R amplitude
was clearly reduced in the Sal-treated groups. Sal reduced
the instability in cardiac electrical activity and conduction
dysfunction caused by myocardial ischaemia, and prevented the
occurrence of arrhythmias.
As shown in the study by Zhao investigating ECG data, the
levels of ST–T changes and arrhythmia differed after exhaustive
exercise.
24
In our experiments, the anaesthetised and awake states
exerted opposite effects on HR that are potentially related to the
inhibitory effect of anesthetic drugs on the exhausted heart.
Exhaustive exercise increased ROS levels, and the
accumulation of ROS in myocardial cells leads to structural
Table 3. Pearson’s correlation analysis for some parameters (
r
)
Control
ES
SLE SHE
Parameter
T ampli-
tude
(mV)
R ampli-
tude
(mV)
QT inter-
val
(ms)
dP/dt
max
(mmHg/s)
P ampli-
tude
(mV)
P ampli-
tude
(mV)
Nrf2
–0.944** 0.041
0.333 –0.362 –0.182 –0.817*
Nuclear Nrf2 0.157 0.921** 0.699 0.836* 0.875* 0.324
Keap1
0.445 0.453
0.934* 0.153 –0.724 –0.250
The data show Pearson’s correlation coefficients (
r
),
n
=
6 animals per group.
*
p
<
0.05 and
**
p
<
0.01.
ES: acute exhaustive swimming group; SLE: low-dose salidroside plus exhaus-
tive swimming group; SHE: high-dose salidroside plus exhaustive swimming
group; dP/dt
max
: peak rate of the increase in pressure.
0
15
30
0
2
4
6
Nrf2
Keap
Nrf2
Sal (mg/kg/d)
effect on targeted proteins
y
= 0.1195
x
+ 1.557
R
2
= 0.9500
y
= 0.0429
x
+ 1.112
R
2
= 0.9408
y
= –0.0068
x
+ 0.7592
R
2
= 0.9995
*
0
15
30
0
2
4
6
Nrf2 nuclear translocation
Keap1
Nrf2
Sal (mg/kg/d)
effect on targeted proteins
Effect on targete proteins
Sal (mg/kg/d)
Fig. 4.
The effects of different concentrations of Sal on the
inhibition of Keap1 and the activation and nuclear
translocation of Nrf2 in the myocardium were analysed
using a single-factor regression analysis (
n
=
6).
The level of target protein was divided by the level
observed in the control group, and the multiple of
change in inhibition or activation of the target protein
was obtained. Sal: salidroside; *
p
<
0.05.
0
0. 2
0. 4
0. 6
0. 8
1
1. 2
Con
EE
SLE
SHE
Ratio of Keap1/β-actin
SHE
Ratio of Nrf2/
β
-actin
Con
ES SLE
**
S
**
##
##
0
0. 2
0. 4
0. 6
0. 8
1
1. 2
Con
ES
SLE
SHE
Rat i o of Nr f 2/β - act i n
SHE
Ratio of nuclear Nrf2/
β
-actin
Con ES SLE
**
##
**
##
++
0
0. 1
0. 2
0. 3
0. 4
0. 5
0. 6
0. 7
0. 8
Con
ES
SLE
SHE
Ratio of Nrf2/β -actin in myocardial nucleus
SHE
Ratio of Keap1/
β
-actin
Con ES SLE
**
**
#
**
##
++
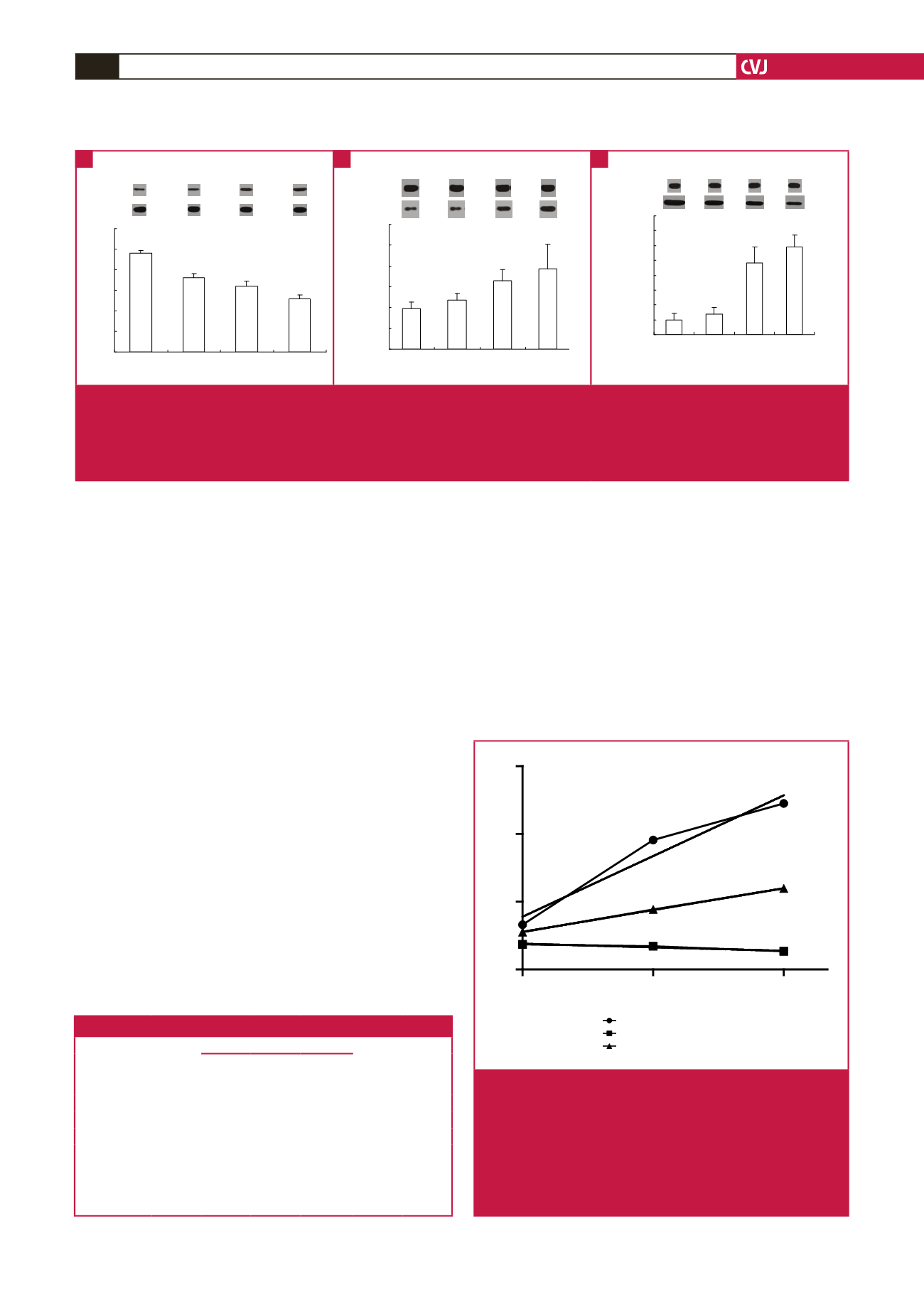
Fig. 3.
The effect of Sal on levels of total and nuclear Nrf2 and Keap1 proteins in rat myocardium after exhaustive exercise (
x
±
s,
n
=
6). A: Ratio of Nrf2/
β
-actin levels in rat myocardium. B: Ratio of nuclear Nrf2/
β
-actin levels in rat myocardium. C:
Ratio of Keap1/
β
-actin levels in rat myocardium. Con: control group; ES: acute exhaustive swimming group; SLE:
low-dose salidroside plus exhaustive swimming group; SHE: high-dose salidroside plus exhaustive swimming group.
**
p
<
0.01 compared with the control group;
##
p
<
0.01 compared with the ES group;
++
p
<
0.01 compared with the SLE group.
A
B
C