CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 32, No 4, July/August 2021
206
AFRICA
CHD incidence in postmenopausal women is almost four
times higher than in men.
16
Although adipose tissues has
relatively low levels of aromatase and androgens (which are
often < 1% in any tissue), their influence on hormone function
may be high.
17
For this locally produced oestrogen, especially
with gonadal failure, there may be increased cause to exert a
cardiovascular protective effect.
Aromatase is involved in sex hormone transformation.
Differences in EAT aromatase expression may directly affect
local oestrogen levels, the oestrogen/androgen ratio and their
biological functions.
18
CYP19 polymorphisms are associated
with oestrogen inactivation and CYP19 mutations may alter
aromatase protein structure, affecting its activity.
19
It should be noted that adipose tissue is not homogeneous
and control of aromatase expression is tissue specific. For
example, while in the ovaries, aromatase expression is regulated
by cAMP, and in the breasts it is controlled by prostaglandins.
17
Some studies show that in breast adipose tissue, obesity and
low-grade inflammation upregulate aromatase gene expression
and oestrogen production.
20-22
In this study we did not find a correlation between aromatase
mRNA and protein levels in the control versus CHD groups.
This indicates that there may be other regulatory mechanisms
affecting aromatase protein synthesis. The regulatorymechanisms
of aromatase expression in EAT have not been studied as yet.
Numerous studies have examined the effects of oestrogen
on cardiovascular diseases and found that its protective effects
include reduced fibrosis, stimulation of angiogenesis and
vasodilation, improved mitochondrial function and reduced
oxidative stress.
6
Many of these oestrogen effects have been
associated with local EAT aromatase and atherosclerosis,
arrhythmia and ischaemia–reperfusion injury
.
Some patients with oestrogen-associated breast cancer may
require aromatase inhibitor chemotherapy. Cardiovascular
events are suggested as primary causes of the low quality of life
in breast cancer patients undergoing treatment with aromatase
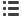
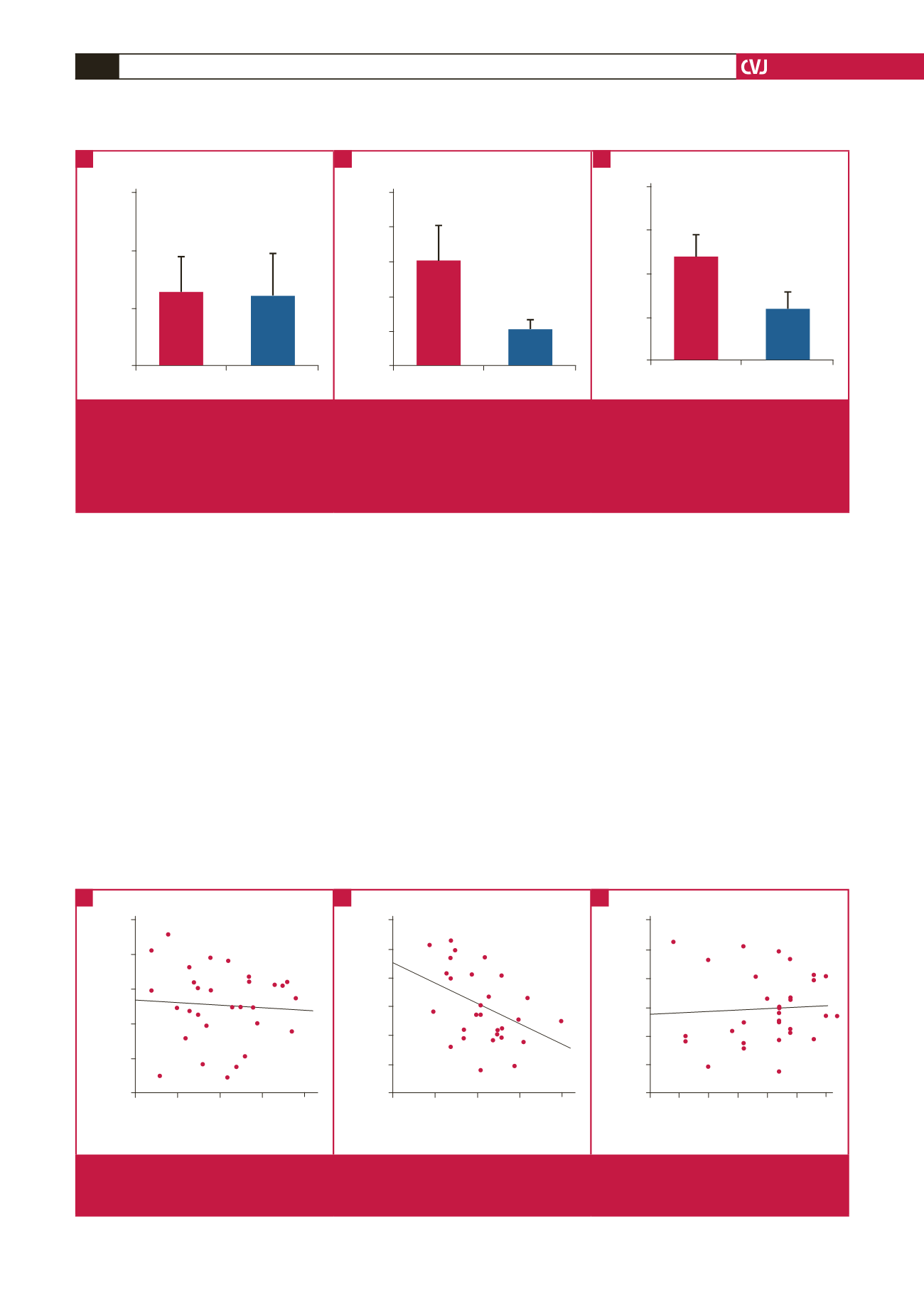
Non-CHD group CHD group
Level of oestrogen in serum (µmol/l)
150
100
50
0
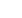
Non-CHD group CHD group
Aromatase mRNA expression
5
4
3
2
1
0
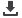
Non-CHD group CHD group
Aromatse protein content in EAT (pg/ml)
20
15
10
5
0
Fig. 1.
A. Comparison of oestrogen levels in the serum between the two groups. CHD group: 63.20
±
32.12 (μmol/l); non-CHD
group: 59.79
±
36.23 (μmol/l). There was no significant difference between the two groups (
p
> 0.05). B. Comparison of the
expression of aromatase mRNA in EAT between the two groups. CHD group: 1.0
±
0.37; non-CHD group: 3.05
±
0.99. The
mRNA expression of aromatase was significantly reduced (
p
< 0.05) in the CHD group. C. Comparison of aromatase protein
content in EAT using the
t
-test. CHD group: 5.74
±
1.97 (pg/ml); non-CHD group: 11.79
±
2.60 (pg/ml) (
p
< 0.0001). The differ-
ence was statistically significant (
p
< 0.05).
A
B
C
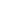
1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00
mRNA quantity of aromatse protein
in control group
r
= –0.069,
p
= 0.717
Level of oestrogen in serum (µmol/l)
17.50
15.00
12.50
10.00
7.50
0
10
20
30
40
50
Syntax score and aromatase
protein content in CHD group
r
= –0.430,
p
= 0.018
Aromatase protein content (pg/ml)
12.00
10.00
8.00
6.00
4.00
2.00
0
0 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 1.25 1.50
mRNA quantity of aromatase
protein in CHD group
r
= –0.057,
p
= 0.764
Level of oestrogen in serum (µmol/l)
12.00
10.00
8.00
6.00
4.00
2.00
0
Fig. 2.
A. Scatter diagram of aromatase mRNA quantity and aromatase protein content in the control group. B. Scatter diagram
of aromatase mRNA quantity and aromatase protein content in the CHD group. C. Scatter diagram of SYNTAX score and
aromatase protein content in the CHD group.
A
B
C