CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 21, No 1, January/February 2010
AFRICA
39
These data showed that HIF-1
α
seemed to be partly responsi-
ble for the apoptosis in primary neonatal rat ventricular myocytes
cultured under hypoxic conditions.
Effect of HIF-1
α
inhibitor
To confirm that the apoptotic response to hypoxia in primary
neonatal rat ventricular myocytes was mediated specifically
by HIF-1
α
, the cells were treated with YC-1, a small-molecule
inhibitor of HIF-1
α
. Cells were cultured at 1% O
2
in the presence
of YC-1 (5
μ
mol/l) for 24 hours and were analysed by immuno-
blotting for HIF-1
α
expression. Under hypoxic condition of 1%
O
2
, HIF-1
α
activity in cells cultured in the presence of YC-1 was
significantly less than that in those cultured in the absence of
YC-1 (
p
<
0.01; Fig. 3).
On selective suppression of HIF-1
α
activity by YC-1, there
was a decrease in the degree of hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Under
hypoxic conditions, the rate of apoptosis in cells cultured in the
presence ofYC-1 was nearly 20% less than that in cells treated in
the absence ofYC-1 (58
±
7.9% and 38
±
2.6% in cells cultured in
the absence and presence ofYC-1, respectively) (
p
<
0.01; Fig.4).
These findings confirmed that a decrease in the rate of apopto-
sis was specifically due to a reduction in the level of HIF-1
α
.
Effects of hypoxia and HIF-1
α
inhibitor on pro-
apoptotic proteins
To further investigate the underlying mechanisms by which
HIF-1
α
enhances the hypoxia-induced apoptosis in primary
neonatal rat ventricular myocytes, we evaluated the expression
levels of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bnip3, Bax and Bad. The
Bnip3 expression level when the cells were cultured at 1% O
2
was significantly higher than that under normoxic conditions (
p
<
0.05; Fig. 5). When HIF-1
α
activity was inhibited by treating
the cells with YC-1 and there was a significant reduction in the
apoptotic rate of cells compared to that under hypoxic condi-
tions without YC-1, there was a simultaneous reduction in the
expression level of Bnip3 (
p
<
0.05; Fig. 5). No clear-cut trends
in the expression levels of the other pro-apoptotic proteins Bax
and Bad were identified. These results suggest that HIF-1
α
prob-
ably mediated the occurrence of hypoxia-induced apoptosis by
enhancing the activation of Bnip3.
Discussion
In many cell types, HIF-1
α
is rapidly degraded and cannot
be detected under normoxic conditions. Hypoxia can induce
HIF-1
α
protein accumulation and mediate a hypoxia-adaptation-
al response. Hypoxia is a characteristic feature of cardiac ischae-
mia. We cultured primary neonatal rat ventricular myocytes
under different levels of hypoxia and examination of these cells
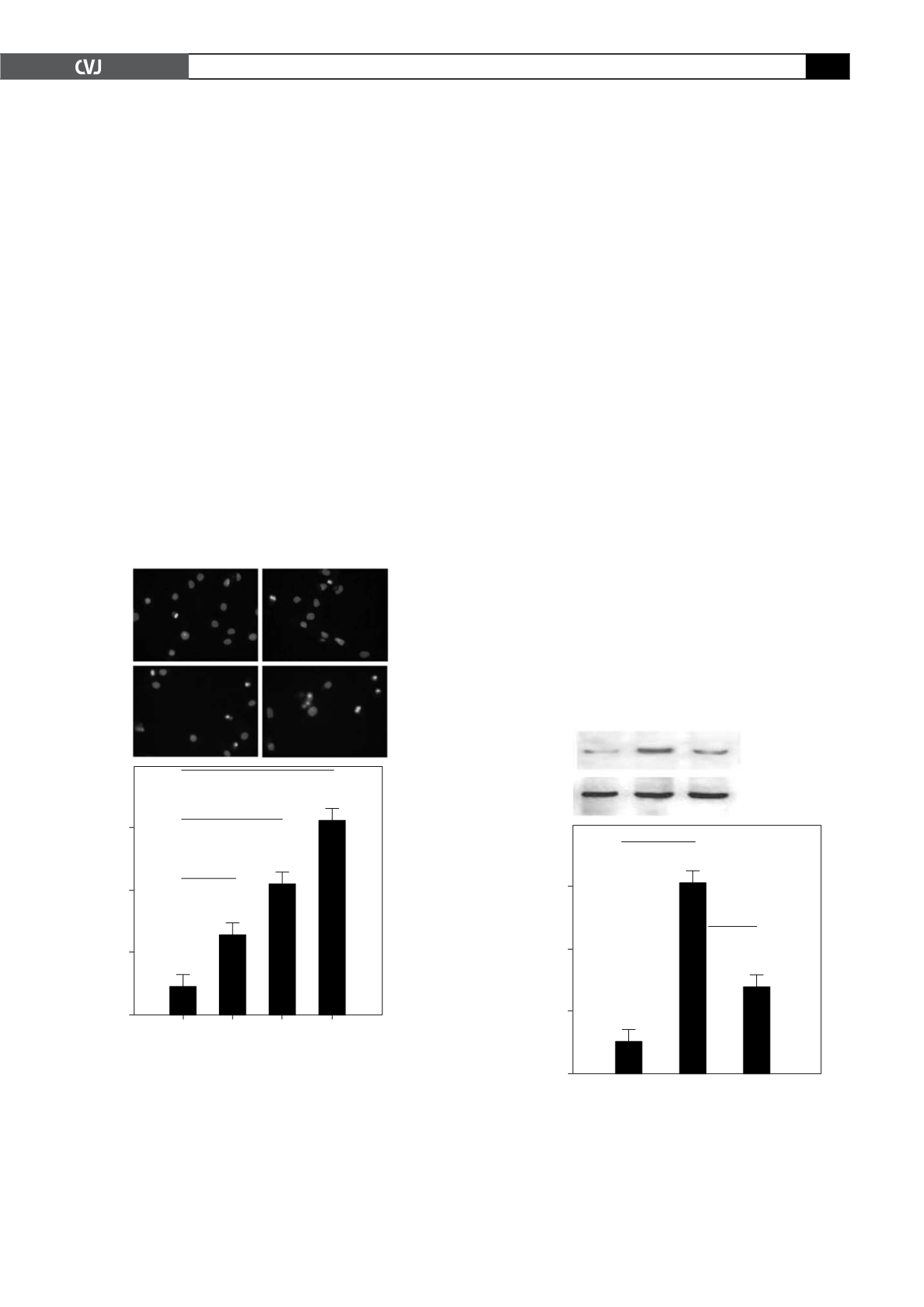
Fig. 3. YC-1 mediated downregulation of HIF-1
α
protein.
Cells were subjected to normoxic (20% O
2
), hypoxic
(1% O
2
) and hypoxic (1% O
2
) conditions in the presence
of YC-1 for 24 hours. The cells were then harvested.
(A) Western blot analysis was carried out with HIF-1
α
proteins isolated from these cells.
β
-actin was used to
monitor equal protein loading. (B) Quantification of the
expression level of HIF-1
α
protein (#
p
<
0.01).
A
B
Normoxia Hypoxia YC
HIF-1
a
120 kD
b
-actin
42 kD
Relative density
(HIF-1
a
/
b
-actin)
Normoxia Hypoxia YC
0.60
0.40
0.20
0.00
#
#
Fig. 2. Hypoxia strongly induced apoptosis in primary
neonatal rat ventricular myocytes in a degree-dependent
manner. Apoptosis in cells cultured for 24 hours under
normoxic (20% O
2
) conditions and different degrees of
hypoxia (5% O
2
, 2% O
2
and 1% O
2
). (A) Hoechst 33258
staining results. Nuclei of apoptotic cells appeared to be
intensely fluorescent, fragmented and condensed. (B)
Hoechst 33258-positive apoptotic cells were quantified in
terms of cells per high-power field. Original magnification
was
×
400. Hypoxia treatment significantly increased the
number of apoptotic cells (#
p
<
0.01).
A
B
% Apoptic cells
20% 5% 2% 1%
Oxygen concentration
60.00
40.00
20.00
0.00
*
#
#
Hoechst 33258 staining
20% 0
2
5% 0
2
2% 0
2
1% 0
2
1
3
2
4


