CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 21, No 1, January/February 2010
40
AFRICA
revealed that the protein levels of HIF-1
α
in rat ventricular
myocytes increased significantly under hypoxic conditions,
depending on the degree of hypoxia (Fig. 1). In addition, as with
others culturing cell types, our data showed that there was low
accumulation of HIF-1
α
under normoxic conditions in primary
neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (Fig. 1). This accumulation
may be associated with the growth factor present in the medium
and serum. Previous studies have suggested that some growth
factors could stimulate expression of HIF-1
α
under normoxic
conditions.
12-15
Some studies have indicated that HIF-1 plays both an anti-
apoptotic and pro-apoptotic role, depending on the cell type.
In our experiment, Hoechst 33258 DNA staining revealed that
hypoxia could induce apoptosis in primary neonatal rat ventricu-
lar myocytes and that the degree of apoptosis depended on the
degree of hypoxia (Fig. 2). These findings suggested that there
might be an association between hypoxia-induced apoptosis and
the accumulation of HIF-1
α
.
To elucidate the effect of this factor on hypoxia-mediated
apoptosis in primary neonatal rat ventricular myocytes, we
cultured these cells in the presence of YC-1, an inhibitor of
HIF-1
α
. YC-1 blocked the expression of HIF-1
α
, which was
induced by hypoxia, iron chelation and proteasomal inhibition,
and also degraded ectopically expressed HIF-1
α
.
11
YC-1 inhibits
HIF-1
α
activity
in vitro
, and
in vivo
and has no serious toxic
effects;
16
5
μ
mol/l YC-1 could have resulted in approximate
reduction of HIF-1
α
proteins compared with short hairpin
RNAs (hrRNAs) against HIF-1
α
.
17
Therefore, in our experiment,
instead of genetic manipulation, we chose YC-1 for the inhibi-
tion of HIF-1
α
. It has been shown that, whenYC-1 was added to
hypoxia-treated cells, the level of HIF-1
α
expression decreased
(Fig. 3), with a simultaneous decrease in the apoptotic rate of
cells (Fig. 4). These data demonstrated that HIF-1
α
mediated
apoptosis induced by hypoxia in cultured primary neonatal rat
ventricular myocytes.
Some reports have described a possible role of HIF-1
α
in the
modulation of apoptosis by inducing the transcription of differ-
ent Bcl-2 pro-apoptotic members and other proteins involved in
apoptosis. Bnip3 is a member of the Bcl-2 family proteins, which
display pro-apoptotic activity. This protein contains the Bcl-2
homology (BH3) and a single carboxy-terminal membrane-
anchoring domain (TM), which targets specific intracellular
organelles, especially mitochondria.
Recent studies have shown that BNIP3 undergoes a dual
Fig. 5. Expression of Bnip3, Bax and Bad under normoxia,
hypoxia and hypoxia with inhibition of HIF-1
α
. Cells were
subjected to normoxia (20% O
2
), hypoxic (1% O
2
) and
hypoxic (1% O
2
) conditions in the presence of YC-1 for
24 hours. (A) Immunoblotting analysis for Bnip3, Bax and
Bad expression. (B) Quantification of the expression of
Bnip3 using western blot (#
p
<
0.01).
A
B
Bax
21 kD
Bad
23 kD
Bnip3
19 kD
b
-actin
42 kD
Normoxia Hypoxia YC
Relative density
(Bnip3/
b
-actin)
Normoxia Hypoxia YC
0.60
0.40
0.20
0.00
#
#
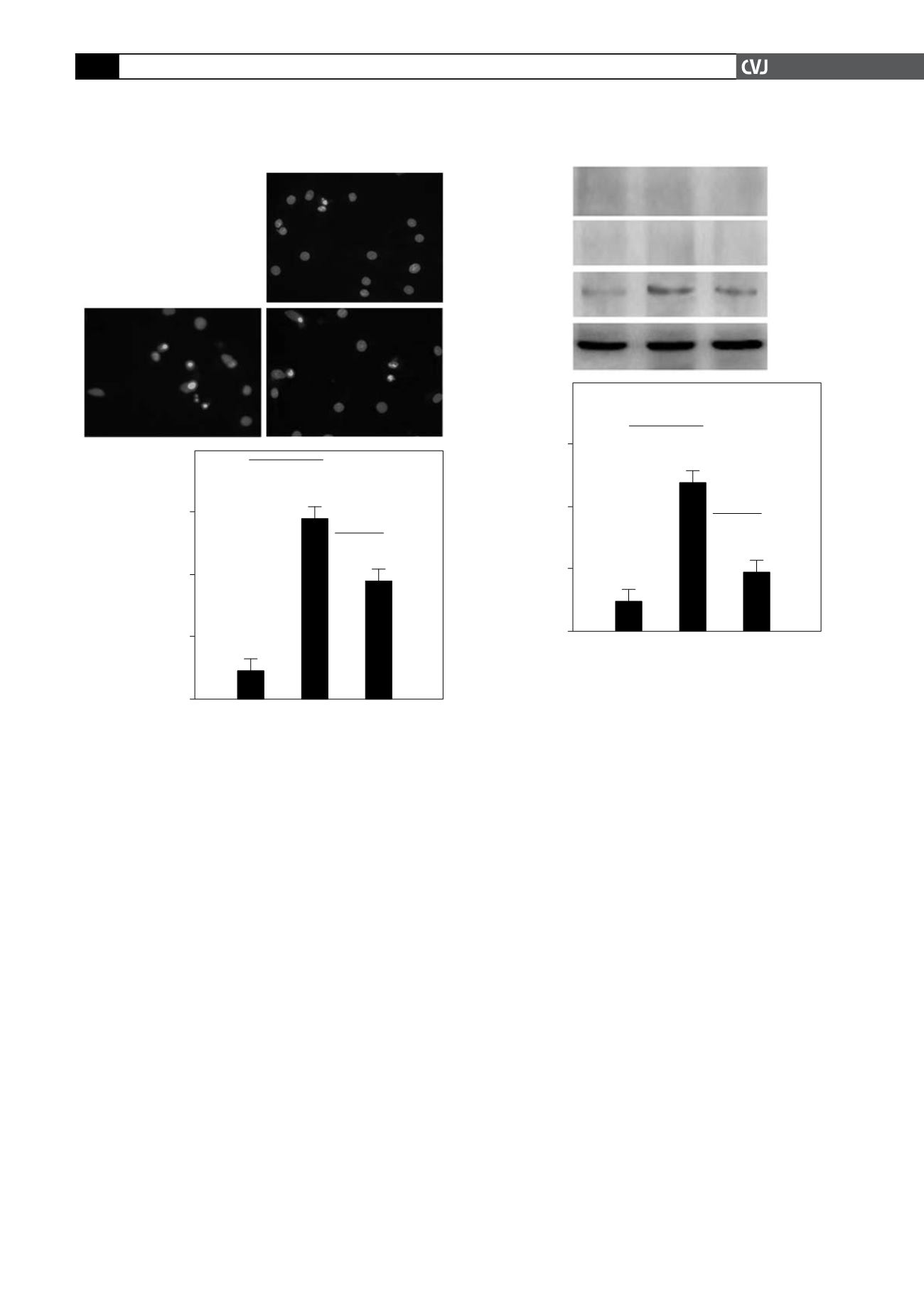
Fig. 4. Hypoxia-induced apoptosis decreased after inhi-
bition of HIF-1
α
in primary neonatal rat ventricular
myocytes. Cells were subjected to normoxia (20% O
2
),
hypoxic (1% O
2
) and hypoxic (1% O
2
) condition in the pres-
ence of YC-1 for 24 hours. (A) Hoechst 33258 staining of
cultures under (1) normoxia, (2) hypoxia, and (3) hypoxia
in the presence of YC-1. (B) Hoechst 33258-positive apop-
totic cells were quantified (per high-power field). Original
magnification was
×
400.YC-1 significantly decreased the
apoptosis induced by hypoxia (#
p
<
0.01).
A
B
% Apoptic cells
Normoxia Hypoxia YC
60.00
40.00
20.00
0.00
#
#
Hoechst 33258 staining
1 Normoxia
2 Hypoxia
3 YC
1
3
2


