CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 4, July/August 2017
258
AFRICA
Similarly, the P-P interval during the pause was twice that of the
P-P interval before and after the pause. These ECG features are
in keeping with sino-atrial (SA) exit block.
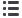
A 24-hour Holter ECG was subsequently done (Fig. 2), which
showed intermittent SA exit block and an episode of sinus arrest
lasting seven seconds, which did not trigger any escape beats. The
patient was diagnosed with symptomatic sinus node dysfunction
and an AAIR pacemaker was implanted. The patient has been
asymptomatic since.
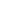
Causes of pauses
The electrocardiographic term ‘pause’ refers to the prolonged
R-R interval that represents the interruption in ventricular
depolarisation. The differential diagnosis of a pause with the
characteristic feature of each is shown in Fig. 3.
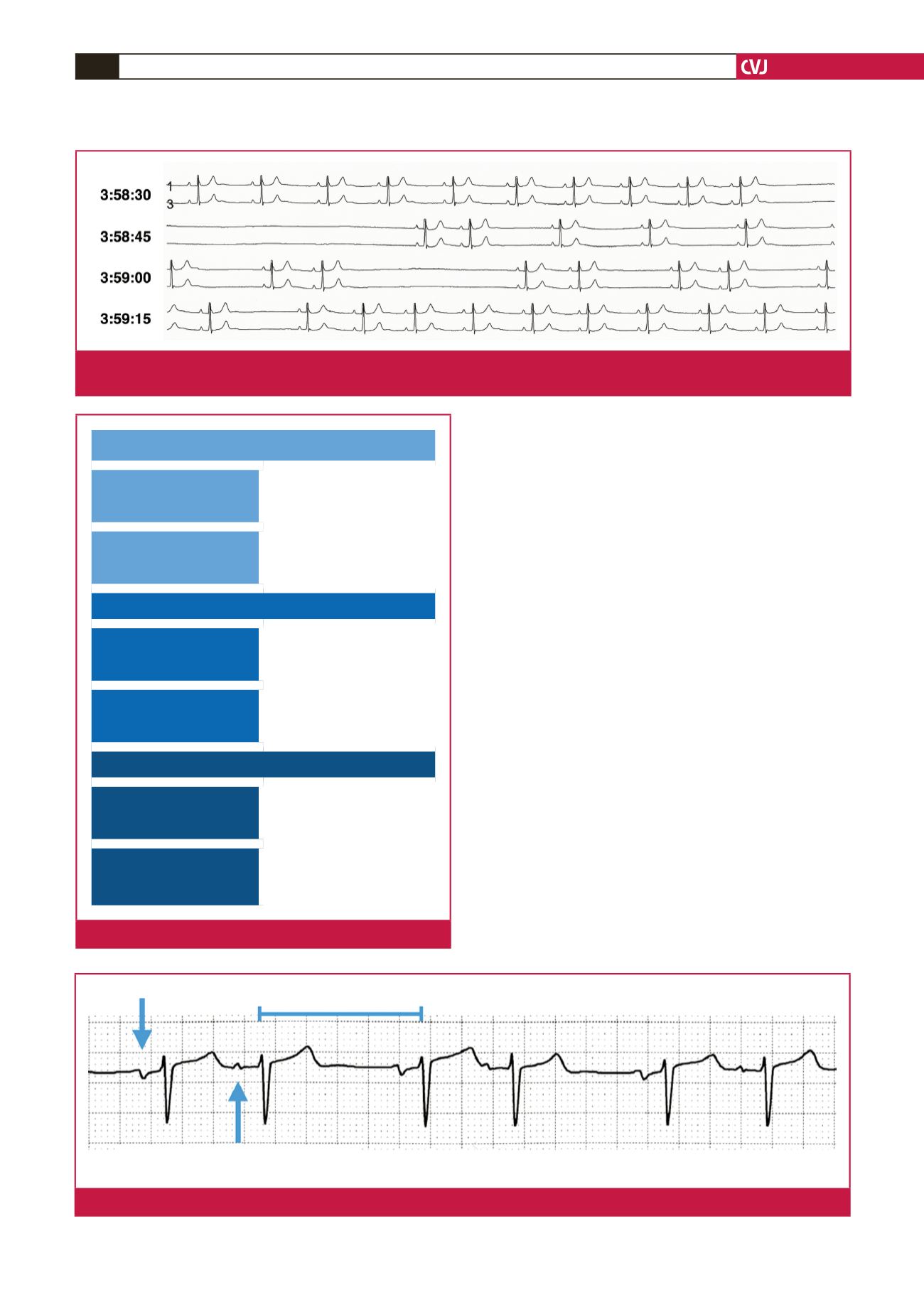
In the presence of a pause, one should exclude premature
complexes with compensatory pause. If the ectopic beat failed
to reset the sinus node, the premature complex would be
followed by a compensatory pause, i.e. the R-R interval after
the premature complex is longer than the R-R interval between
normal sinus beats. A premature atrial complex is recognised as
an early P wave with a different morphology from the sinus P
wave (Fig. 4), and a premature ventricular complex is the wide
QRS complex with abnormal morphology that is not preceded
by a P wave (Fig. 5).
In the absence of premature complexes, one should determine
whether the pause is caused by intermittent absent impulse
generation (i.e. sinus node dysfunction) or intermittent absent
impulse conduction [i.e. second-degree atrio-ventricular (AV)
Premature complexes
Intermittent ectopic generation
Premature atrial complex
P wave with different
morphology and earlier-
than-expected P wave
Premature ventricular
complex
Wide QRS with abnormal
morphology, not preceded
by P wave
Sinus node dysfunction
Intermittent absent generation
SA exit block
P-P interval around the
pause is a multiple of P-P
interval without pause
Sinus arrest
P-P interval around the
pause has variable or
random lengths
2nd degree AV block
Intermittent absent conduction
Mobitz type 1
PR interval before pause
longer than PR interval after
pause
Mobitz type 2
Regular PR interval, usually
followed by wide QRS
complex
Fig. 3.
A diagnostic approach to electrocardiographic pauses.
Fig. 2.
A 24-hour Holter ECG showing an episode of sinus arrest lasting seven seconds (starting just before 3:58:45) and intermit-
tent sino-atrial exit block (just after 3:59:15).
Compensatory pause
Premature atrial complex
different morphology from sinus P wave
Sinus P wave
Fig. 4.
Premature atrial complex with compensatory pause.