CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 4, July/August 2017
AFRICA
259
block].
1
Sinus node dysfunction refers to the pause in atrial
depolarisation, which is either caused by sinus arrest or SA exit
block.
2
The hallmark of sinus node dysfunction is missing P
waves on the 12-lead ECG.
3
In SA exit block, the atria fail to depolarise after the SA
node discharges, because the impulse cannot leave the SA node.
Because the atria do not depolarise, there is no P wave visible on
the ECG tracing each time the impulse fails to leave the SA node.
The SA node discharge is too small to be seen on a 12-lead ECG,
therefore there is no waveform visible during the SA exit block.
The P-P interval during SA exit block is a multiple of the normal
P-P interval, because when P waves appear, they occur at their
scheduled time (Fig. 6).
1,3
In sinus arrest, the SA node does not discharge. If there is no
other atrial ectopic that takes over as a pacemaker, there will be
no atrial depolarisation, and therefore no P waves will be visible
on the ECG for the duration of the sinus arrest. If sinus arrest is
long enough, an escape beat or escape rhythm may be triggered,
which will manifest as QRS complexes that are not preceded by P
waves. In sinus arrest, the pause duration can be variable, and the
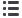
Premature ventricular complex
wide QRS with abnormal morphology
Compensatory pause
Fig. 5.
Premature ventricular complex with compensatory pause.
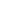
Variable RR intervals
Variable P-P intervals
All P waves followed by QRS complexes
Pause with absent P wave
Pauses have variable lengths
Fig. 7.
Sinus arrest with no escape beats.
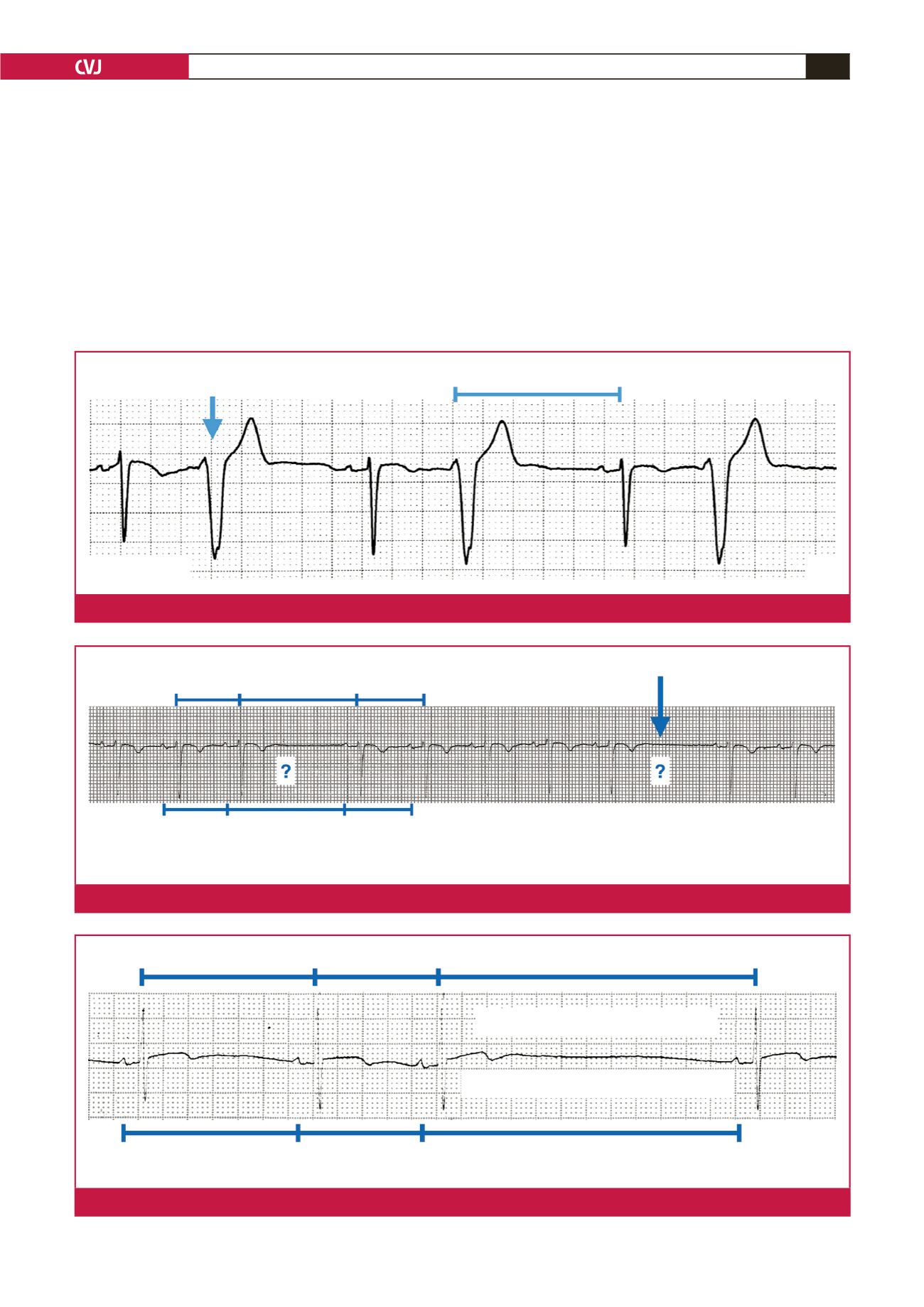
Pause with absent P wave
R-R interval
P-P interval
All P waves are followed by QRS complexes
x
x
x
x
2
x
2
x
Fig. 6.
Sino-atrial exit block.