CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 4, July/August 2017
260
AFRICA
P-P interval is therefore not necessarily a multiple of the normal
R-R interval (Fig. 7).
1
In second-degree AV block, the atrial depolarisation
intermittently fails to conduct to the ventricles. On the 12-lead
ECG, this will manifest as intermittent absent QRS complexes,
i.e. more P waves than QRS complexes.
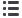
Mobitz type 1 second-degree AV block manifests with group
beating, with variable PR intervals. The PR interval typically
increases in length until the pause, with the PR interval after
the pause shorter than the PR interval before the pause (Fig. 8).
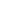
Mobitz type 2 second-degree AV block has constant PR
intervals, with unpredictable loss of conduction of P waves not
followed by QRS complexes. The QRS complexes in Mobitz
type 2 are typically wide with typical bundle branch morphology
(Fig. 9).
Management of sinus node dysfunction
Management of sinus node dysfunction depends on whether the
patient is experiencing symptoms or not. Whereas asymptomatic
patients do not require treatment, patients who are symptomatic
are treated by insertion of a permanent pacemaker. Pacemaker
therapy does not prolong life but relieves symptoms.
4
The authors thank Prof Rob Scott Millar for the ECG examples used in Figs 4–9,
from the Rob Scott Millar ECG Library at the Groote Schuur Cardiac Clinic.
References
1.
Millar RS.
The ECG Atlas of Cardiac Rhythms
. Cape Town: Clinics
Cardive Publishing, 2015.
2.
Ferrer MI. The sick sinus syndrome.
Circulation
1973;
47
(3): 635–641.
3.
Mangrum JM, DiMarco JP. The evaluation and management of brady-
cardia.
N Engl J Med
2000;
342
(10): 703–709.
4.
Brignole M, Auricchio A, Baron-Esquivias G, Bordachar P, Boriani
G, Breithardt OA,
et al
. 2013 ESC guidelines on cardiac pacing and
cardiac resynchronization therapy: the Task Force on cardiac pacing
and resynchronization therapy of the European Society of Cardiology
(ESC). Developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm
Association (EHRA).
Eur Heart J
2013;
34
(29): 2281–2329.
Group beating predictable pauses
Pause with absent QRS
Regular P waves
Variable PR intervals
PR before pause longer than PR after pause
Fig. 8.
Mobitz type 1 second-degree AV block (Wenckebach).
Pause with absent QRS
Regular P waves
Regular PR interval
Wide QRS
(typical bundle branch morphology)
Fig. 9.
Mobitz type 2 second-degree AV block.