CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 6, November/December 2017
AFRICA
365
Effect of melatonin treatment
in vivo
on glucose
uptake by insulin-resistant cardiomyocytes
After 20 to 23 weeks, rats fed a high-calorie diet exhibited
significantly increased body weight (C: 433
±
25 vs D: 538
±
43
g,
p
<
0.05), visceral fat mass (C: 17.7
±
1.8 vs D: 37.5
±
7.5 g,
p
<
0.001) as well as adiposity index (Table 3). Melatonin treatment
for six weeks reduced body weight and adiposity index values in
group D rats (
p
<
0.05) (Table 3).
To evaluate the glucose uptake by cardiomyocytes fromcontrol
and obese rats, a dose response with increasing concentrations of
insulin was performed (Fig. 4). The diet had no effect on basal
glucose uptake by cardiomyocytes isolated from both group
C and D rats (Fig. 4). However it reduced insulin-stimulated
glucose uptake in group D rats (Fig. 4, Table 2). Oral melatonin
treatment
in vivo
for six weeks increased the basal glucose uptake
by cardiomyocytes from group D rats (DM: 26.4
±
2.1 vs D: 19.8
±
3.4 pmol/mg protein/30 min,
p
<
0.05) while having no effect in
group C rats (CM: 22.6
±
3.7 vs C: 21.1
±
3.5 pmol/mg protein/30
min,
p
>
0.05) (Fig. 4). Additionally, compared to their respective
untreated group, cardiomyocytes isolated from the control
treatment group (CM) had elevated insulin-stimulated glucose
uptake (
p
<
0.05) (Fig. 4). Furthermore, cardiomyocytes from
the D treatment group (DM) also showed a further elevation of
insulin-stimulated glucose uptake with insulin administration
Table 2. Body weight and visceral mass of rats fed for 20 to 23 weeks and their corresponding glucose uptake by the cardiomyocytes
Group
Body weight and visceral fat mass
Glucose uptake (pmol/mg protein/30 min)
Body weight (g)
Visceral fat (g)
Adiposity index
Basal
Insulin
Ins + Mel
Mel
C
457
±
14
18.4
±
10.9
4
±
0.2
19.9
±
2.6**
35.3
±
6.3
#
33.5
±
5.9
19.2
±
1.7
D
575
±
61
###
38.7
±
2.6
###
6.7
±
0.6
###
18.1
±
1.6**
25.9
±
1.6
27.8
±
1.1
18.4
±
2.3
n
6
6
6
6
6
5
6
C: control, D: high-calorie diet, adiposity index [(visceral fat/body weight) × 100], Ins: insulin (1 nM), Mel: melatonin (100 nM), **
p
<
0.01 (vs Ins or Ins + Mel),
#
p
<
0.05 (vs D),
###
p
<
0.001 (vs C),
n
=
five to six individual preparations per group, uptake determined in duplicate for each preparation.
Table 3 Body weight, visceral fat mass and IPGT
after 20 weeks of feeding
Parameters
C
CM
D
DM
Body weight (g)
433
±
25 411
±
17
538
±
43***
488
±
21
#
Visceral fat (g)
17.7
±
1.8 14.33
±
1.9* 37.50
±
7.5***
28
±
4
#
Adiposity index 4.1
±
0.2 3.4
±
0.16* 6.9
±
0.23*** 5.7
±
0.3
#
AUC for IPGT 761.5
±
27.7 760.2
±
38.8 870.7
±
25.2* 826.7
±
32.5
n
6
6
6
6
C: control, D: high-calorie diet, CM and DM: control and diet receiving mela-
tonin for six weeks, adiposity index [(visceral fat/body weight) × 100], AUC:
area under the curve, IPGT: intraperitoneal glucose tolerance, *
p
<
0.05 (vs C),
***
p
<
0.001(vs C),
#
p
<
0.05 (vs D),
n
=
six per group.
Basal
C
Ins C Ins +
Mel C
Mel C Basal
D
Ins D Ins +
Mel D
Mel D
3
2
1
0
2DG (fold stimulation)
*
**
**
#
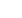
Fig. 2.
Effect of
in vitro
melatonin treatment on insulin-stimu-
lated glucose uptake of cardiomyocytes isolated from
control (C) and high-calorie diet (diet-induced obesity)
(D) groups after 16 to 19 weeks. 2DG: 2 deoxyglucose,
Ins: insulin (1 nM), Mel: melatonin (100 nM); *
p
<
0.05
(Ins C vs Ins
+
Mel C), **
p
<
0.01(basal vs Ins or Ins
+ Mel; Ins C vs Ins D),
#
p
<
0.05 (Ins
+
Mel D vs Ins
+
Mel C),
n
=
four to six individual preparations/group;
analysed in duplicate.
Basal
C
Ins C Ins +
Mel C
Mel C Basal
D
Ins D Ins +
Mel D
Mel D
3
2
1
0
2DG (fold stimulation)
**
**
*
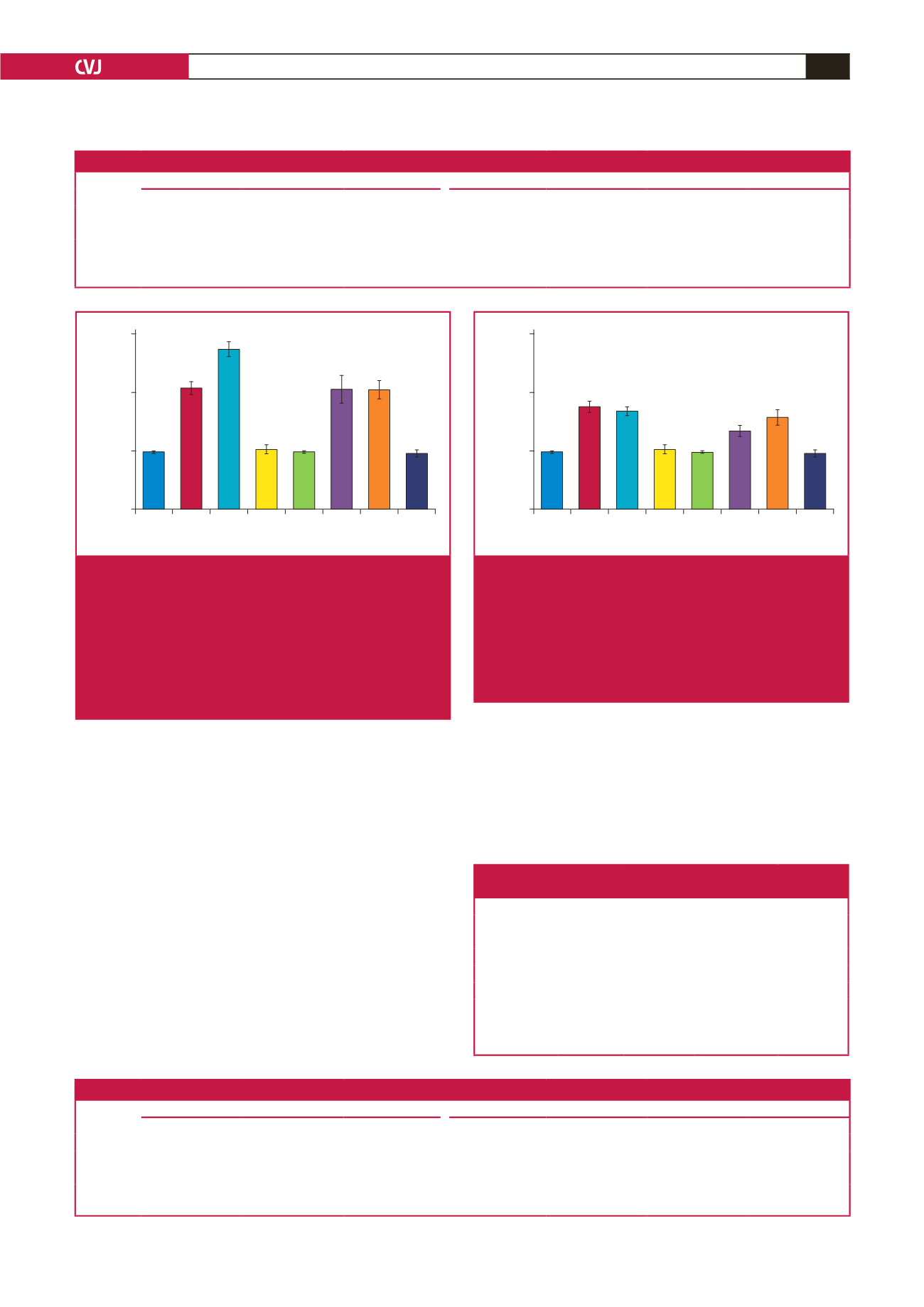
Fig. 3.
Effect of
in vitro
melatonin treatment on insulin-stimu-
lated glucose uptake of cardiomyocytes isolated from
control (C) and high-calorie diet (diet-induced obesity)
(D) groups after 20 to 23 weeks. 2DG: 2 deoxyglucose,
Ins: insulin (1 nM), Mel: melatonin (100 nM); *
p
<
0.05
(Ins C vs Ins D), **
p
<
0.01 (basal vs Ins or Ins + Mel),
n
=
four to six individual preparations/group; analysed
in duplicate.
Table 1. Body weight and visceral mass of rats fed for 16 to 19 weeks and their corresponding glucose uptake by the cardiomyocytes
Group
Body weight and visceral fat mass
Glucose uptake (pmol/mg protein/30 min)
Body weight (g)
Visceral fat (g)
Adiposity index
Basal
Insulin
Ins + Mel
Mel
C
435
±
21
17.0
±
1.4
3.8
±
0.18
25.6
±
2.8
49.3
±
5.6*
73.9
±
4.1***
#
25.5
±
4.4
D
517
±
11
###
33.3
±
1.3
###
6.39
±
0.3
###
20.8
±
3.1
40.8
±
3.8*
47.5
±
4.9*
20.0
±
3.4
n
6
6
6
6
6
4
6
C: control, D: high-calorie diet, adiposity index
=
[(visceral fat/body weight) × 100], Ins: insulin (1 nM), Mel: melatonin (100 nM), *
p
<
0.05 (vs basal), ***
p
<
0.001 (vs
basal),
#
p
<
0.05 (vs D),
###
p
<
0.001 (vs C),
n
=
four to six individual preparations per group, uptake determined in duplicate for each preparation.