
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 28, No 2, March/April 2017
AFRICA
127
(GLUT) protein content. Denervation of skeletal muscle results
in rapid decreases in both muscle GLUT-4 contents and insulin-
stimulated glucose uptake, therefore resulting in hyperglycaemia
and concomitant hyperinsulinaemia (both CHD hallmarks) in
non-diabetic patients.
10
Lack of physical exercise may also contribute to the
accumulation of visceral fat, reduced lipoprotein lipase activity
and reduced clearance of triglycerides, leading to increased
LDL levels, decreased HDL levels, and increased LDL-to-HDL
ratios, and eventually to hypercholesterolaemia.
11
This state
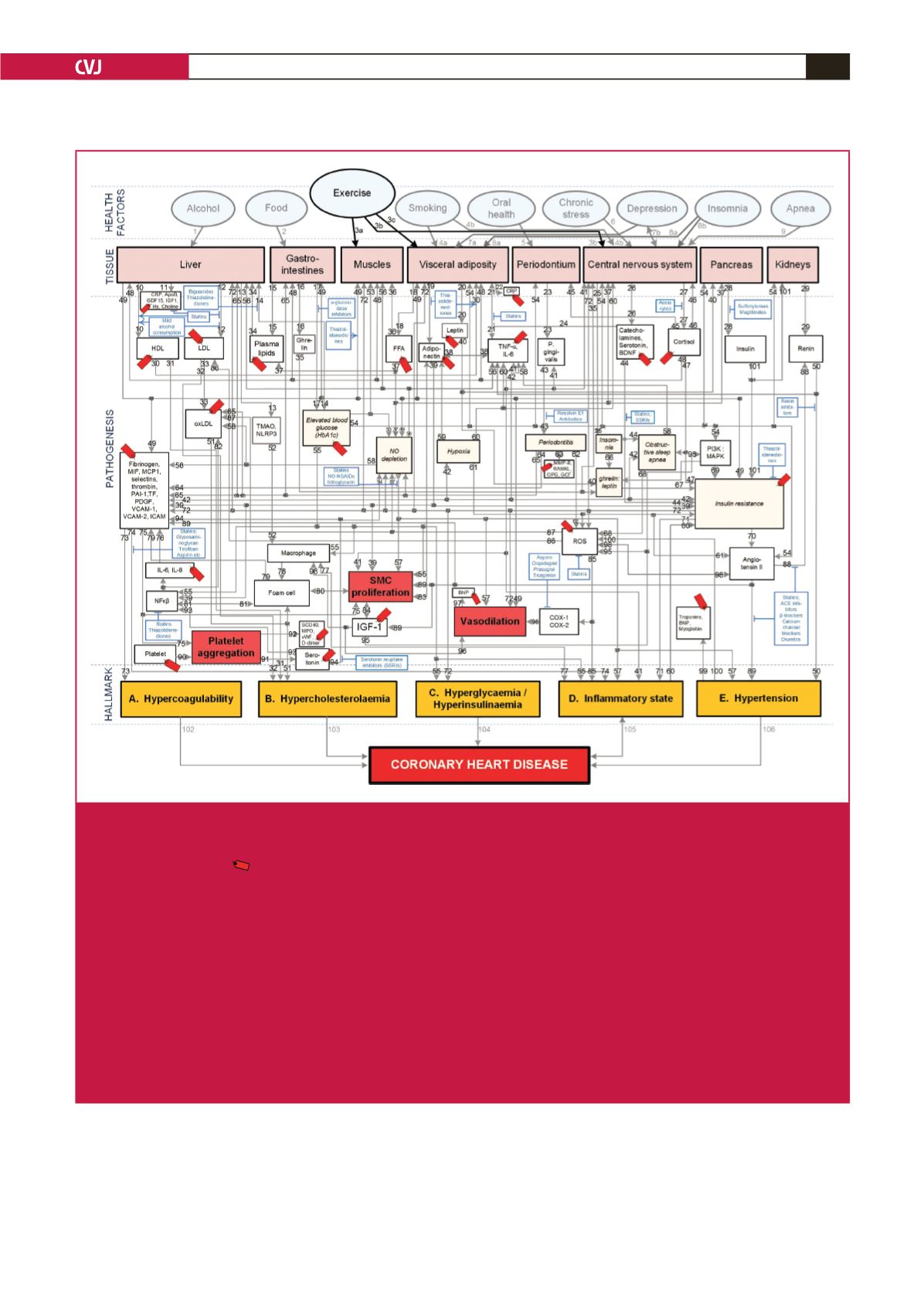
Fig. 1.
Conceptual model of general health factors, salient CHD pathogenetic pathways and CHD hallmarks. (From: M Mathews,
L Liebenberg, E Mathews. How do high glycemic load diets influence coronary heart disease?
Nutr Metab
2015; 12(1): 6
.
7
)
The affective pathway of pharmacotherapeutics (blue boxes) is shown in Fig. 1, and salient serological biomarkers are indi-
cated by the tags ( ). The blunted arrows denote antagonise or inhibit, and pointed arrows denote up-regulate or facilitate.
ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor;
β
-blocker, beta-adrenergic antagonists; BNP,
B-type natriuretic peptide; COX, cyclooxygenase; CRP, C-reactive protein; D-dimer, fibrin degradation product D; FFA, free
fatty acids; GCF, gingival crevicular fluid; HbA
1c
, glycosylated haemoglobin A
1c
; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; Hs, homocyst-
eine; ICAM, intracellular adhesion molecule; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IL, interleukin; LDL, low-density lipoprotein;
MAPK, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase; MCP, monocyte chemo-attractant protein; MIF, macrophage migration
inhibitory factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NF
κβ
, nuclear factor-
κβ
; NLRP3, Inflammasome
responsible for activation of inflammatory processes as well as epithelial cell regeneration and microflora; NO, nitric oxide;
NO-NSAIDs, combinational NO-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; OPG, osteoprotegerin; oxLDL, oxidised LDL; PAI,
plasminogen activator inhibitor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor;
P gingivalis
,
Porphyromonas gingivalis
; PI3K, phosphati-
dylinositol 3-kinase; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-beta ligand; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCD-40,
recombinant human sCD40 ligand; SMC, smooth muscle cell; SSRI, serotonin reuptake inhibitors; TF, tissue factor; TMAO,
an oxidation product of trimethylamine (TMA); TNF-
α
, tumour necrosis factor-
α
; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule;
vWF, von Willebrand factor.

















