
CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 29, No 2, March/April 2018
e6
AFRICA
own connections to the left atrium independently of the superior
and inferior pulmonary veins. These variants mainly include (1)
one accessory right middle pulmonary vein, (2) two accessory
right middle pulmonary veins, and (3) one accessory right middle
pulmonary vein and one accessory right upper pulmonary vein.
Other infrequent variations are also seen: a superior segment
right lower lobe vein, basilar segments of the right lower lobe,
and a right upper pulmonary vein. A right upper pulmonary
vein enters the left atrium at a point super-medial to the right
superior pulmonary vein and drains into the superior right lower
lobe segment, the posterior right upper lobe segment, or both
segments.
1,4
LVPV
LA
AV
RLPV
RVPV
IV
VV
AV
CV
SVC
V
LPA
LVPV
RVPV
RLPV
LMPV
LLPV
LA
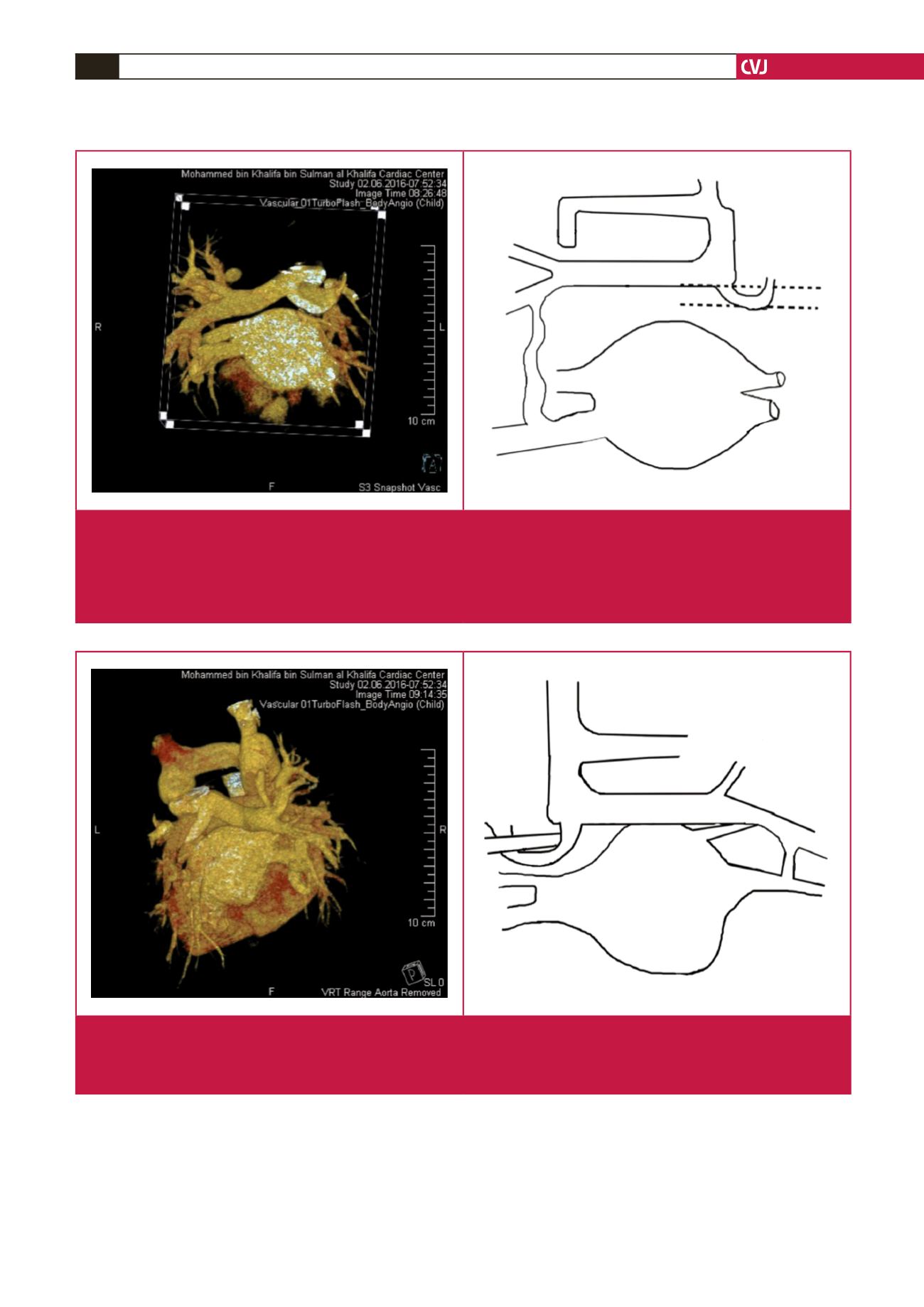
Fig. 1.
CT angiogram (anterior view). Normal drainage of the right upper (RUPV) and right lower pulmonary vein (RLPV) into the
upper pole of the left atrium (LA), and a small left middle pulmonary vein (LMPV) and left lower pulmonary veins (LLPV)
into the left atrium. Large right-sided accessory pulmonary vein (AV) drains into the right upper lobe of the lung. Left upper
pulmonary vein (LUPV) makes a U-turn around the left pulmonary artery (LPA) and joins with the anomalous right acces-
sory pulmonary vein draining into the vertical vein (VV). Right-sided anomalous accessory pulmonary vein also connects
(CV) with the RLPV.
IV
VV
AV
SVC
PA
LVPV
RLPV
LA
IV
VV
AV
CV
PA
LVPV
RLPV
LLPV
LA
Fig. 2.
CT angiogram (posterior view). The left upper pulmonary vein (LUPV), making a U-turn around the left pulmonary artery
(LPA), joins the accessory pulmonary vein (AV), which drains via a dilated vertical vein (VV) into the innominate vein (IV)
and finally into the dilated right-sided superior vena cava (SVC). RLPV, right lower pulmonary vein; LA, left atrium; LLPV, left
lower pulmonary vein; CV, connecting vein.

















