CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Vol 23, No 4, May 2012
218
AFRICA
There were four cases of warfarin embryopathy (three
presented for antenatal care in the second trimester and the other
in the third trimester). The maternal and foetal characteristics
together with the dose of warfarin at admission and sonographic
findings are outlined in Table 5. The most common maternal
complications during the antenatal period and immediately post
delivery are listed in Table 6.
Discussion
In this retrospective audit on prosthetic heart valves in pregnancy,
the mean age was 24 years and 56% were primigravidae. The
low mean age and high number of primigravidae are in keeping
with studies originating from other under-resourced countries,
4,10
but not from those of affluent societies.
11,12
A Canadian study
reported that the mean age at first antenatal booking was 32
years.
13
This implies that the severity of rheumatic heart disease
may be greater in under-resourced countries, warranting valve
replacement at an early age. Furthermore, rheumatic heart
disease is uncommon in affluent countries and congenital
abnormalities form the majority of cardiac conditions seen in
pregnancy.
13
The high number of pregnancies at an early age in our study
may also be due to cultural and socio-economic factors. Such
factors may have influenced late booking for maternity care, as
37 (61%) patients attended antenatal care in the second trimester
of pregnancy. Late booking for antenatal care and large patient
numbers on warfarin throughout the first and second trimesters
of pregnancy may indicate that women with cardiac disease do
not receive adequate and/or consistent information on family
planning, contraceptive services, sexually transmitted infections
and the hazards of warfarin therapy in the first trimester.
The challenge for health professionals in under-resourced
countries, irrespective of their medical discipline, is to ensure
that such information is provided, not only to the individual
woman, but also to partners, families and the community at
large. Further, it begs the question whether a family planning
TABLE 3. CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR PATIENTSWITH MECHANICAL HEARTVALVE THROMBOSIS
Patient
no
Age
(years)
GA at 1st
antenatal visit
Parity
Age at valve
surgery
Anticoagulant at 1st antenatal visit
Mode of
delivery
Neonatal
outcome
1
22
21
1
12
Defaulted on therapy prior to pregnancy
NVD
IUD
2
25
36
1
15
Warfarin 5 mg
C/S
Alive
3
21
12
0
11
Warfarin 5 mg
NVD
Alive
4
18
19
0
9
Defaulted on therapy prior to pregnancy
NVD
IUD
IUD
=
intrauterine death; NVD
=
normal vaginal delivery; C/S – caesarean section.
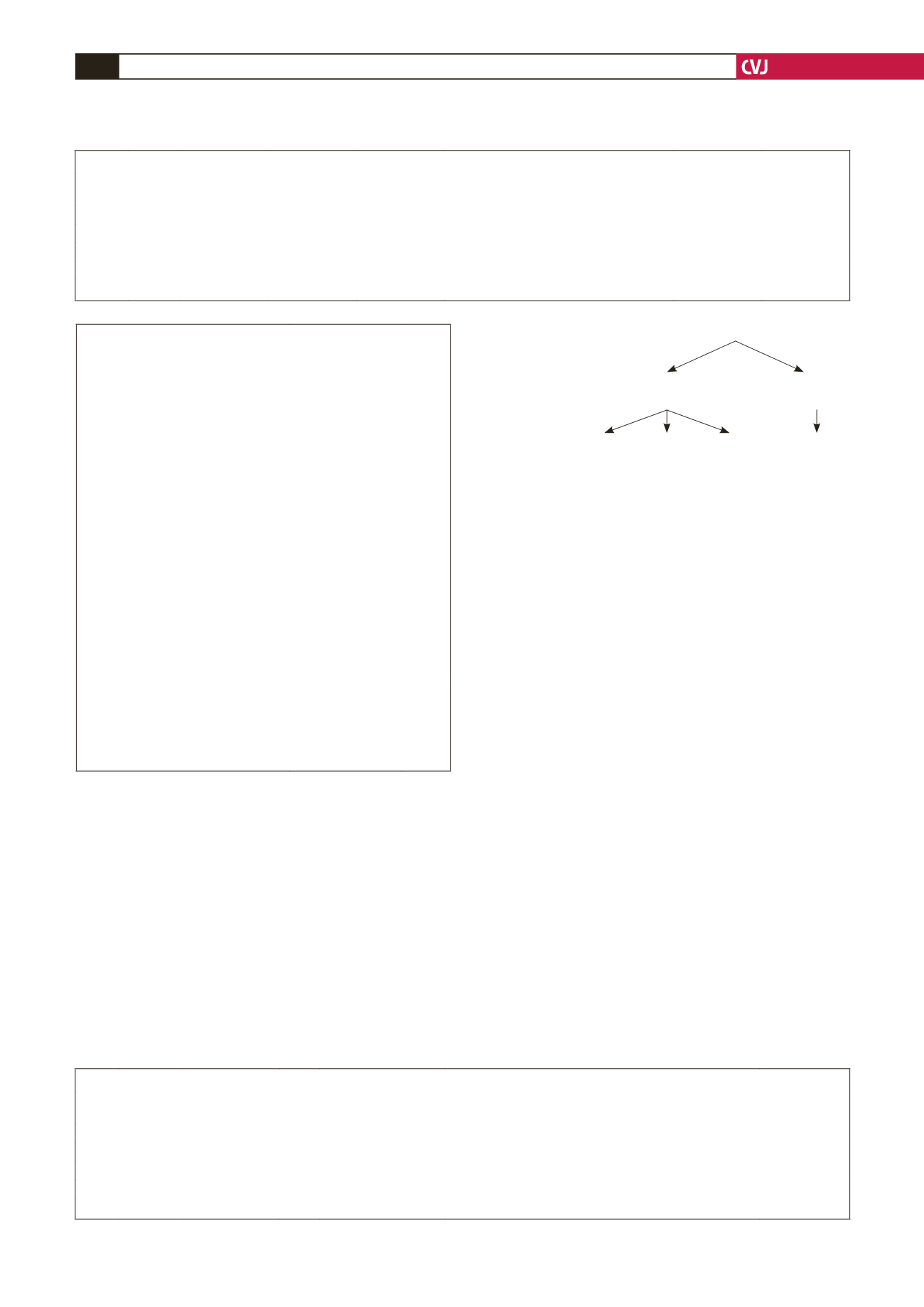
Prosthetic heart valves (
n
=
61)
Mechanical heart
valves (
n
=
59)
Tissue heart
valves (
n
=
2)
Position of valve
replacement
mitral
(
n
=
44)*
aortic
(
n
=
1)
mitral and aortic
(
n
=
11)
mitral
(
n
=
2)
Prophylactic
anticoagulation
yes
yes
yes
no
Valve thrombosis yes (
n
=
4)
no
no
no
Maternal death yes (
n
=
1)
no
no
no
*Three patients with MPHV stopped medication of their own accord prior
to pregnancy.
Fig. 1. Flow diagram showing position of prosthetic heart
valve replacement.
TABLE 4. DELIVERY DETAILS
Characteristics
Number
Percent-
age
Anaesthetic
Spinal
9
22
Epidural
28
68
General anaesthetic
4
10
Live babies (
n
=
41)
Spontaneous labour
Delivered vaginally
2 (epidural)
40
Emergency caesarean
3 (1 epidural
+
2 GA)
60
Induced labour
Delivered vaginally
3 (epidural)
50
Emergency caesarean
2 (2 epidural
+
GA)
50
Elective caesarean (
n
=
31)
Epidural
21
67
Spinal
9
30
Emergency (GA)
1 (failed spinal)
03
Stillbirths (
n
=
6)
NVD (spontaneous)
2
33
Induced
4
67
Miscarriages (
n
=
12)
Warfarin exposure in 1st trimester (NVD)
12
100
GA
=
general anaesthetic; NVD
=
normal vaginal delivery.
TABLE 5. CONGENITALABNORMALITIES DUE TOWARFARIN EMBRYOPATHY
Patient
no
Maternal
age (years)
GA (weeks) at 1st
antenatal visit
Parity Anticoagulant and dose
Sonography – congenital abnormalities
Foetal outcomes
of pregnancy
1
20
32
1
Warfarin 7.5 mg
Choanal atresia/ microcephaly nasal hypoplasia
ENND
2
22
26
1 Warfarin 5 mg/2. 5 mg Hydrocephalus, flattening of nasal bone polyhydraminos
SB
3
36
10
2
Warfarin 7.5 mg Skeletal deformity of spine, nasal hypoplasia, hydrocephalus
SB
4
30
29
0
Warfarin 5 mg
Nasal hypoplasia, mid-facial hypoplasia diaphragmatic hernia
ENND
ENND
=
early neonatal death; SB
=
stillbirth; GA
=
gestational age.


